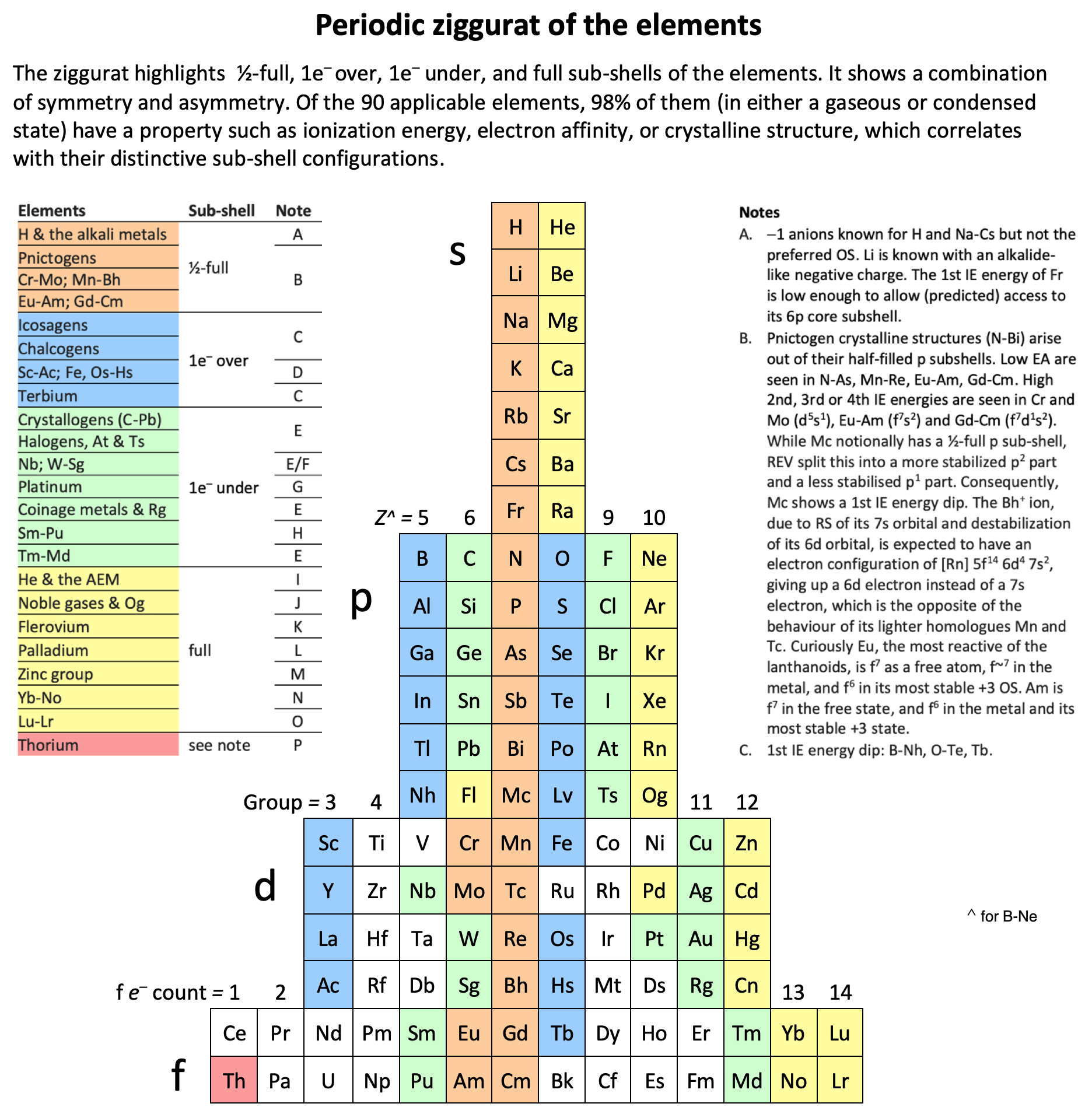
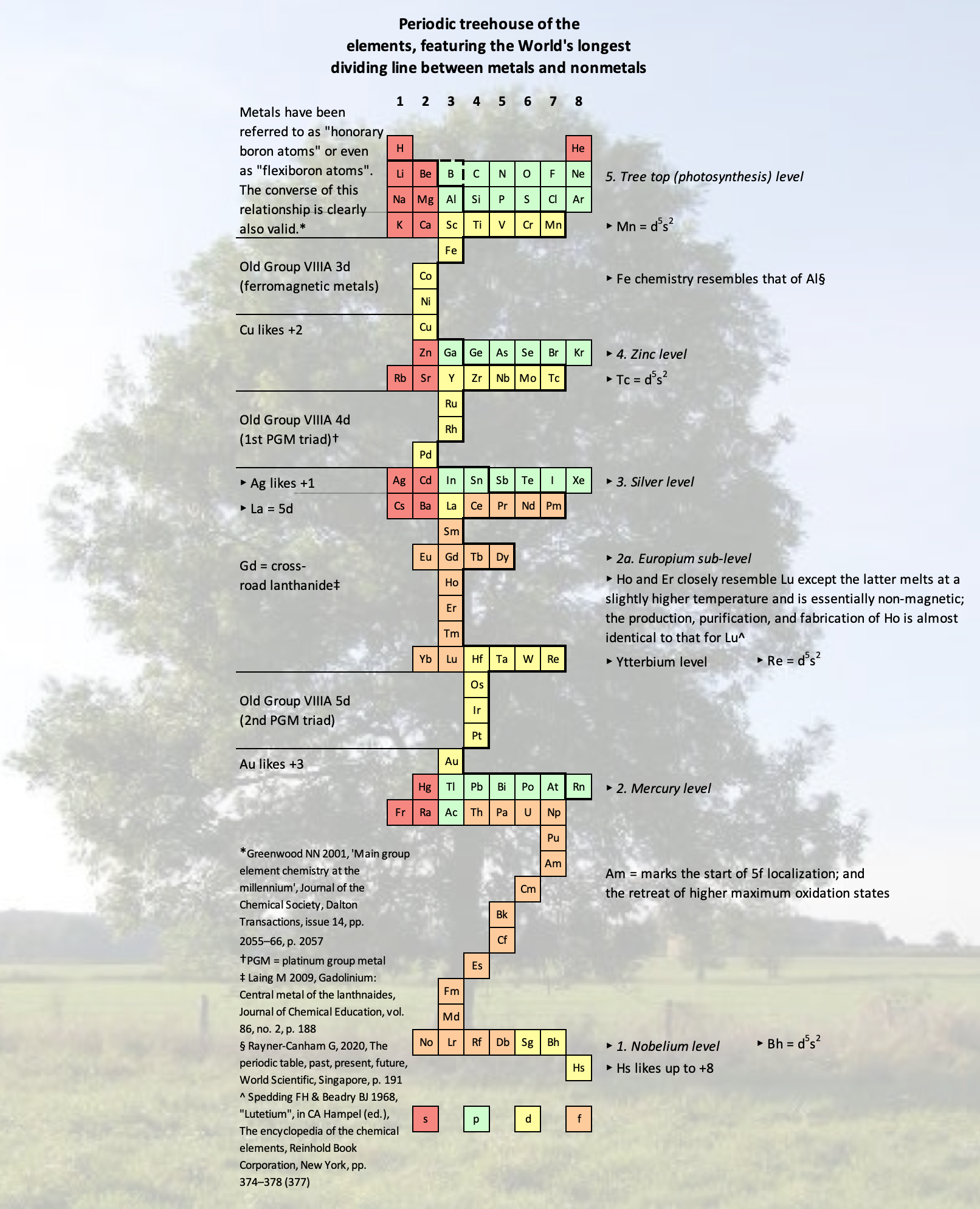
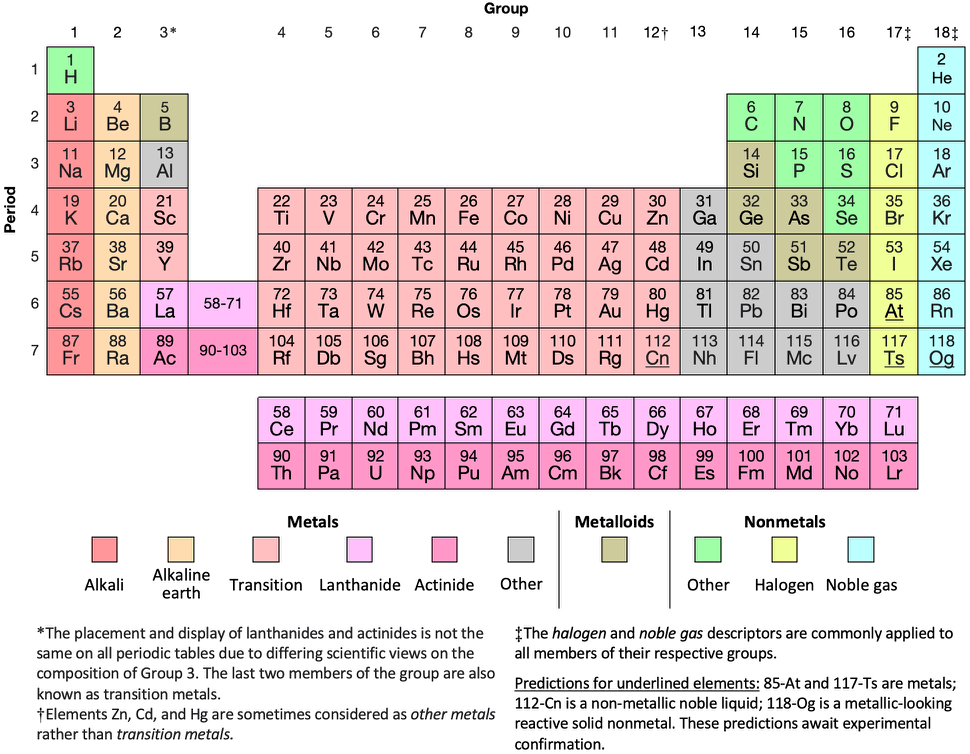
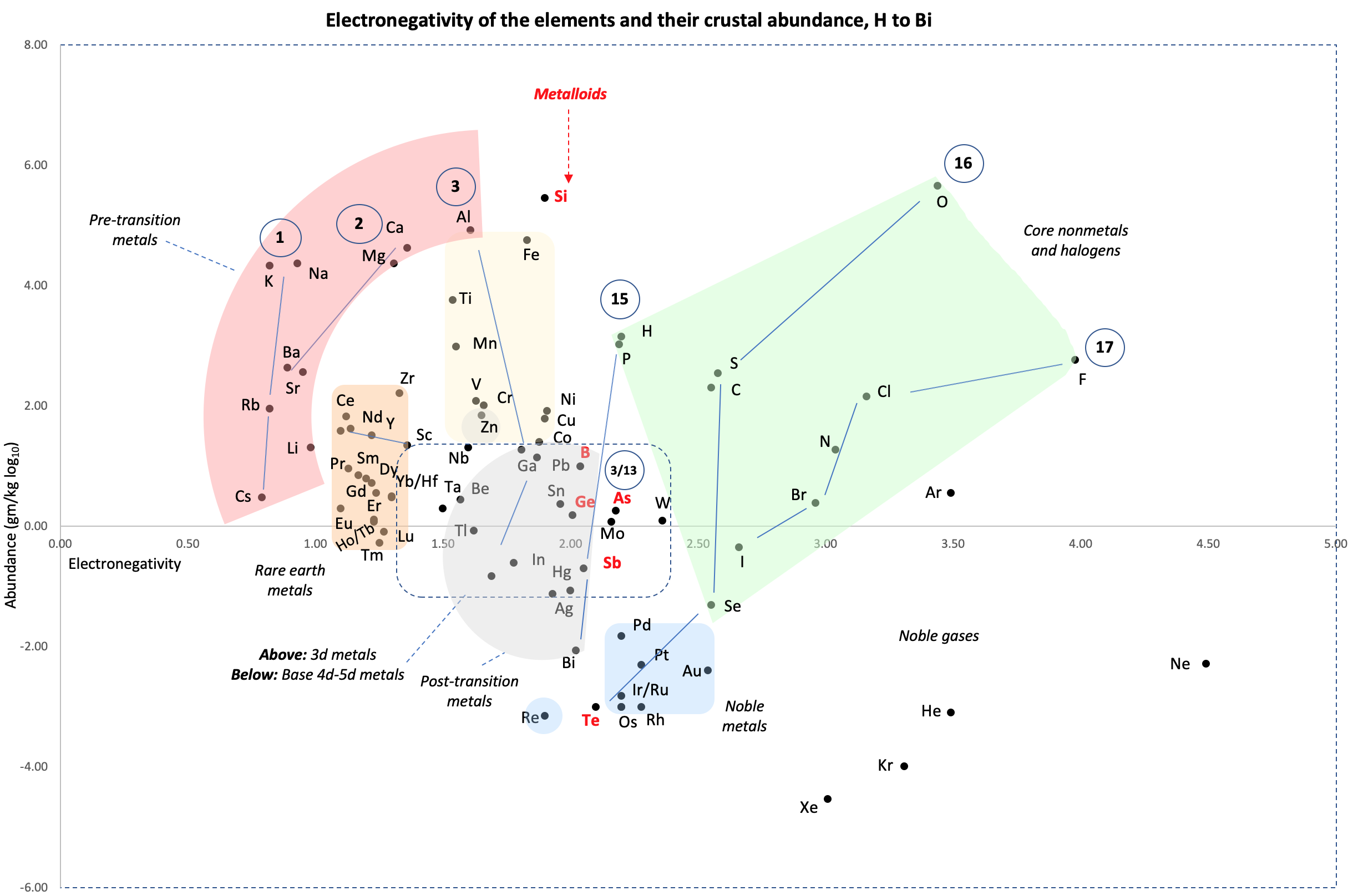
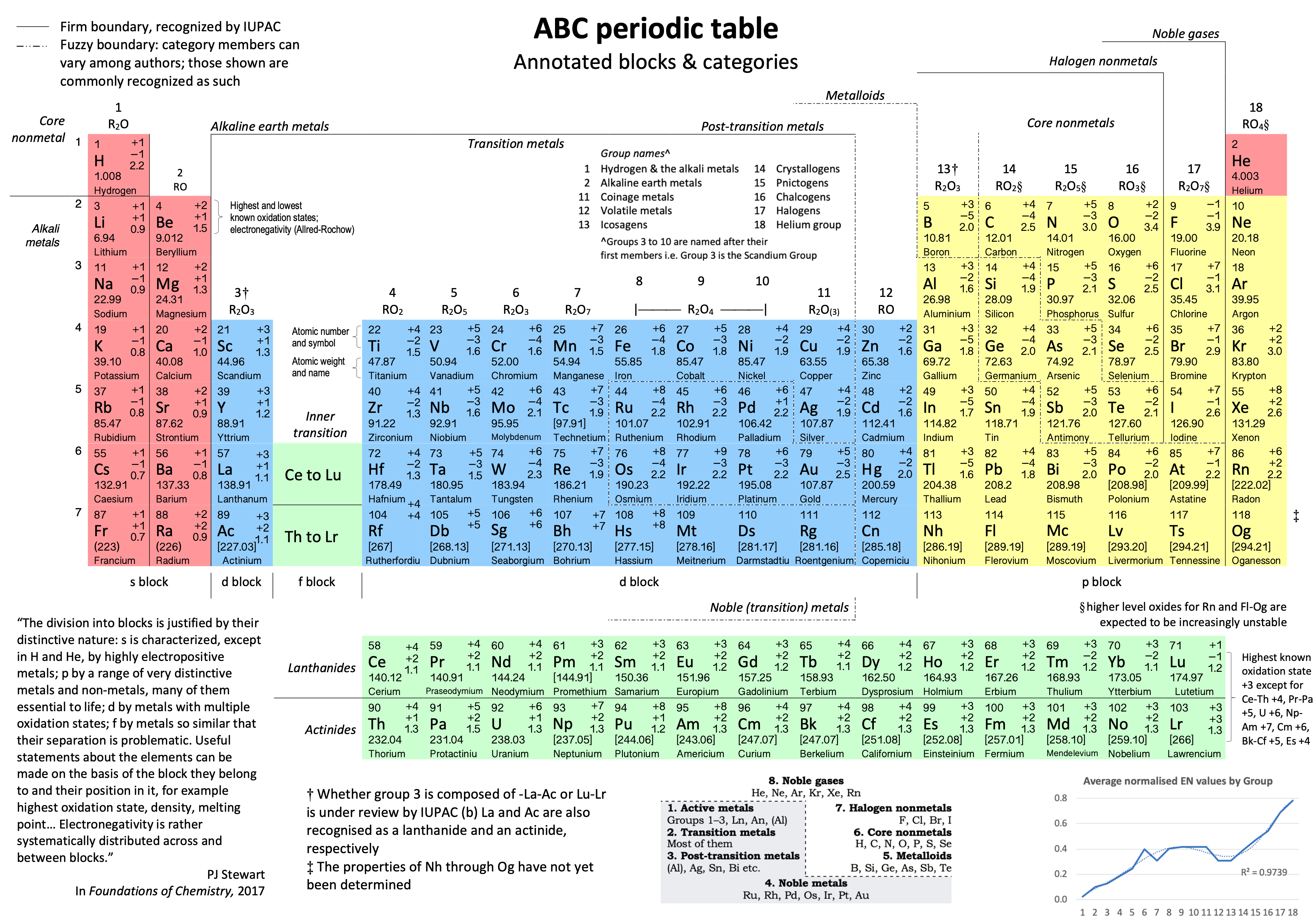
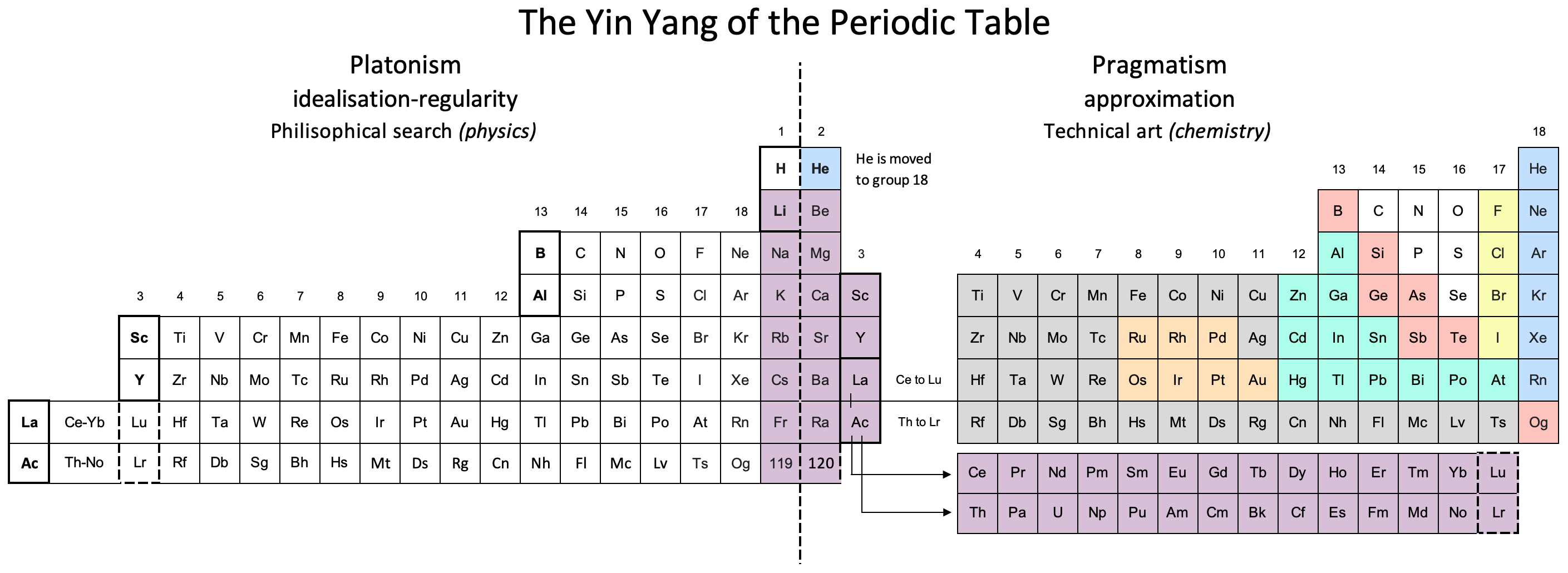
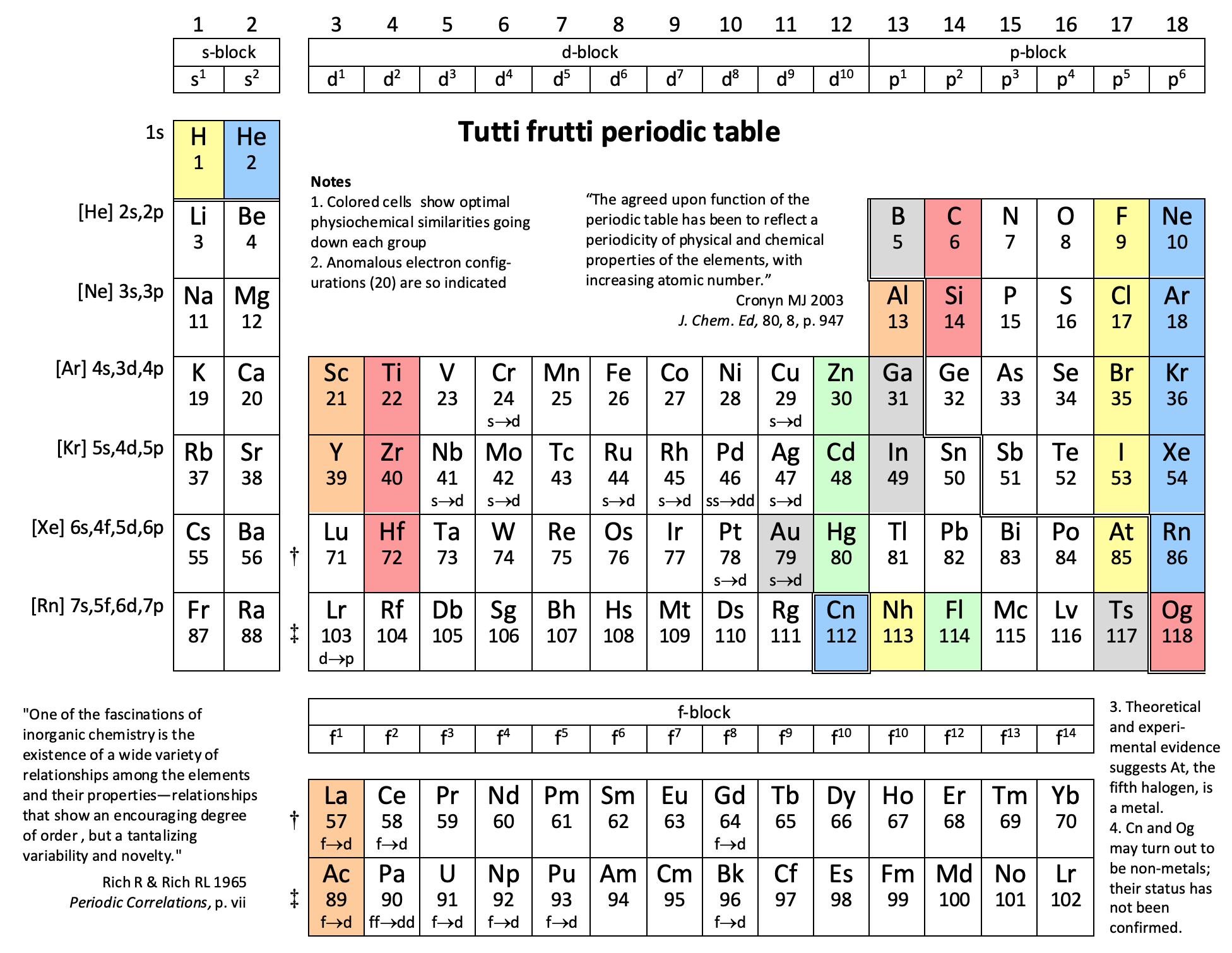
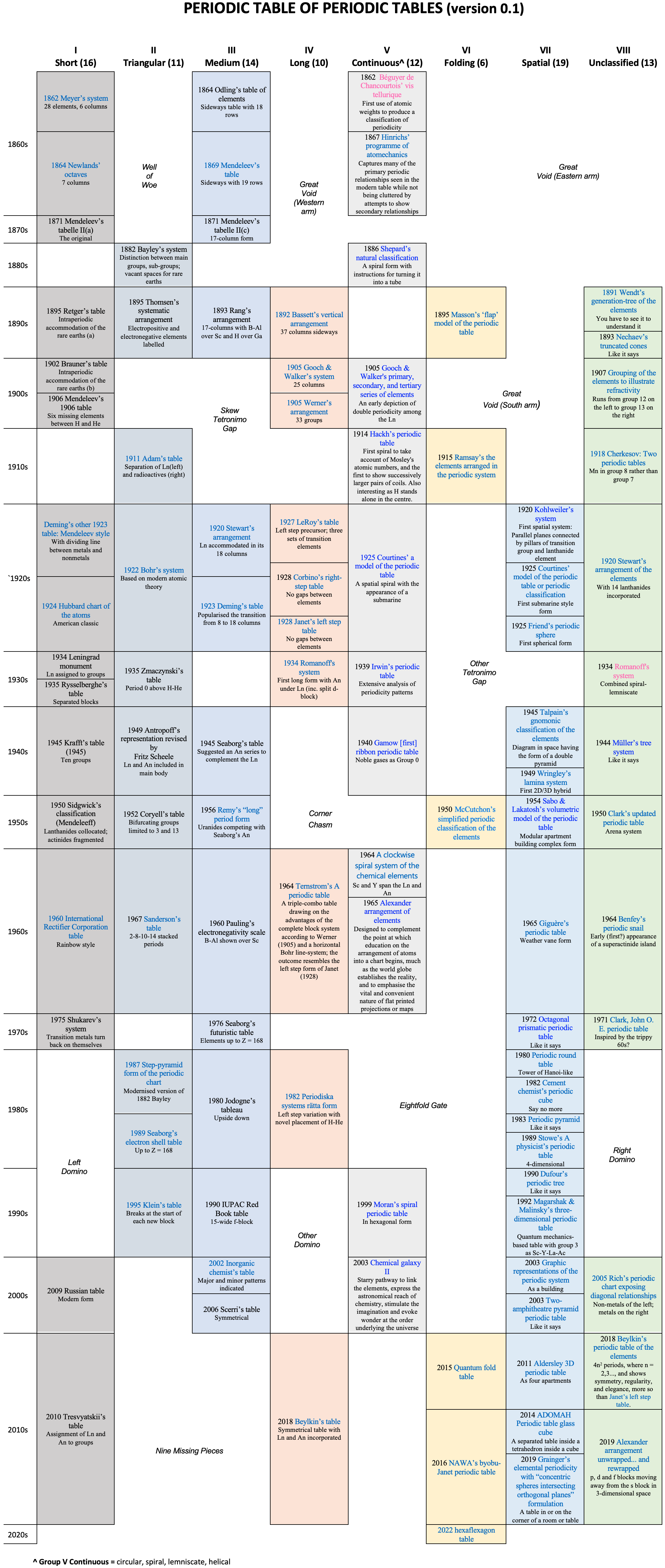
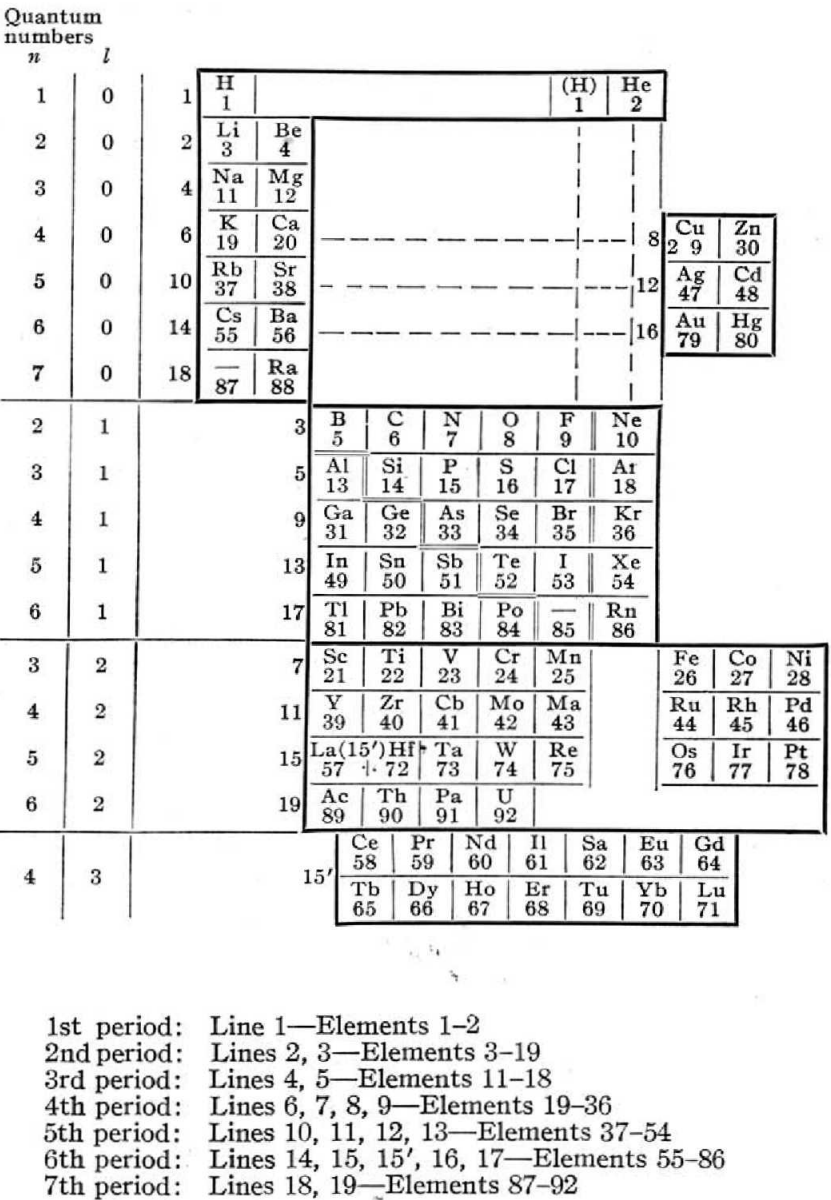
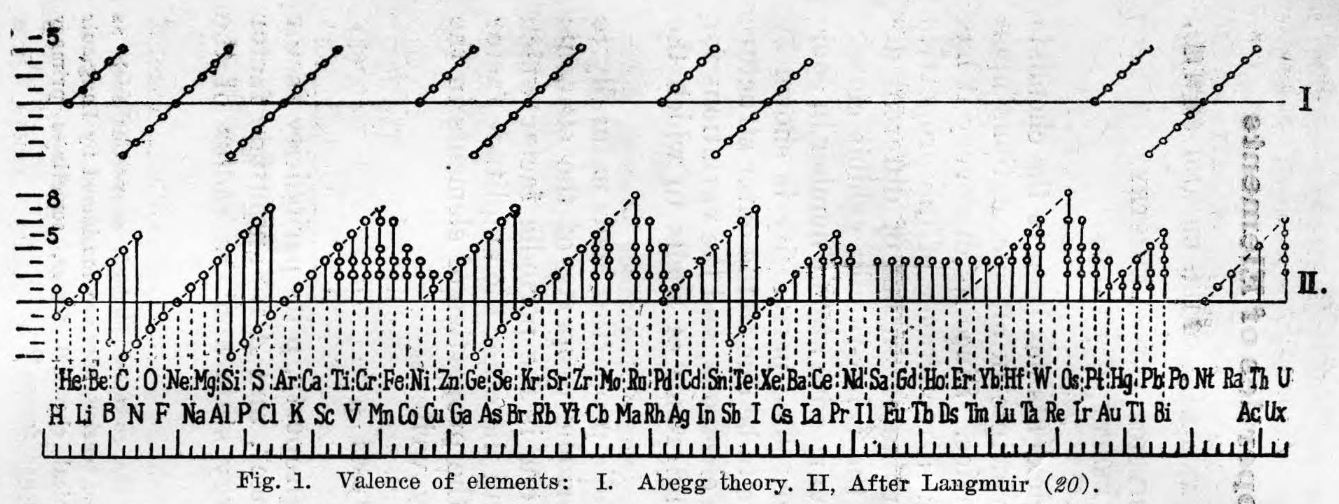
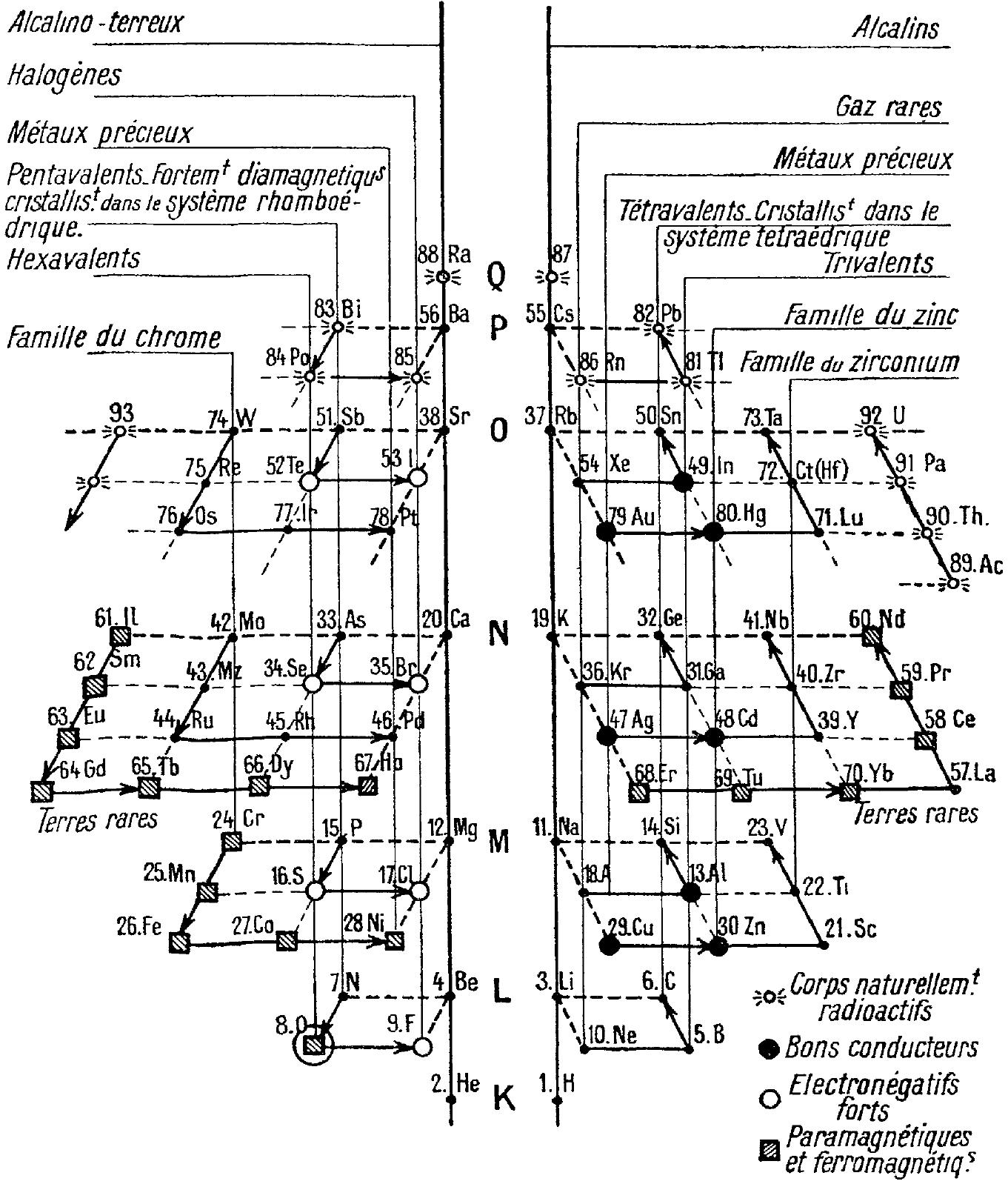
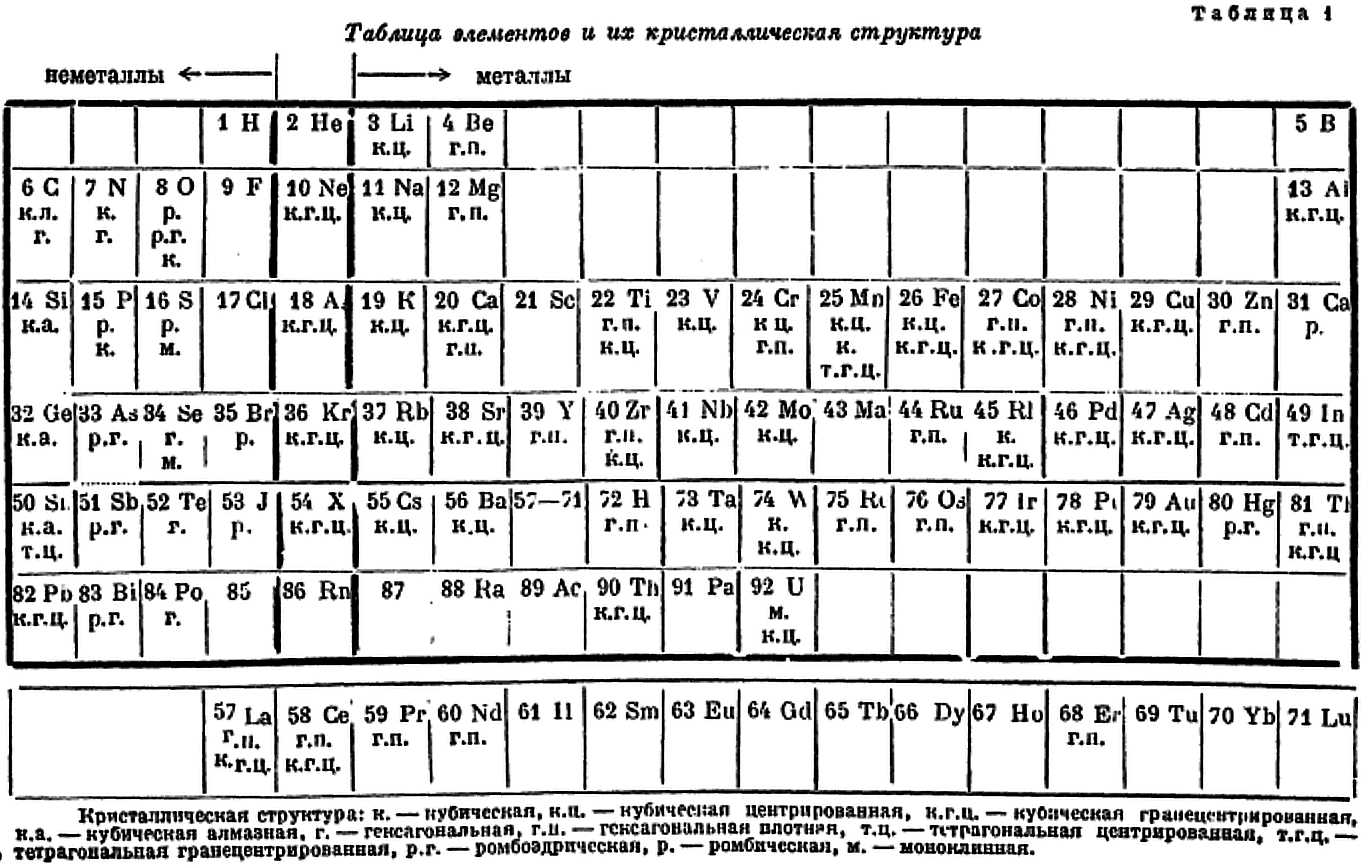
Periodic Table |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The INTERNET Database of Periodic Tables
There are thousands of periodic tables in web space, but this is the only comprehensive database of periodic tables & periodic system formulations. If you know of an interesting periodic table that is missing, please contact the database curator: Mark R. Leach Ph.D.
Use the drop menus below to search & select from the more than 1300 Period Tables in the database:
- SEARCH:
- By Decade
- By Type
-
Pre-Selected
Best Four Periodic Tables for Data All Periodic Tables by Name All Periodic Tables by Date All Periodic Tables by Reverse Date All Periodic Tables, as Added to the Database All Periodic Tables, reverse as Added Elements by Name Elements by Date Discovered Search for: Mendeleev/Mendeléeff Search for: Janet/Left-Step Search for: Eric Scerri Search for: Mark Leach Search for: René Vernon Search for: Electronegativity
-
By Year
2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 1985 1984 1983 1982 1981 1980 1979 1978 1977 1976 1975 1974 1973 1972 1971 1970 1969 1968 1967 1966 1965 1964 1963 1962 1961 1960 1959 1958 1957 1956 1955 1954 1953 1952 1951 1950 1949 1948 1947 1946 1945 1944 1943 1942 1941 1940 1939 1938 1937 1936 1935 1934 1933 1932 1931 1930 1929 1928 1927 1926 1925 1924 1923 1922 1921 1920 1919 1918 1917 1916 1915 1914 1913 1912 1911 1910 1909 1908 1907 1906 1905 1904 1903 1902 1901 1900 1899 1898 1897 1896 1895 1894 1893 1892 1891 1890 1889 1888 1887 1886 1885 1884 1883 1882 1881 1880 1879 1878 1877 1876 1875 1874 1873 1872 1871 1870 1869 1868 1867 1866 1865 1864 1863 1862 1861 1860 1859 1858 1857 1856 1855 1854 1853 1852 1851 1850 1844 1843 1842 1838 1836 1831 1830 1829 1825 1824 1817 1814 1813 1811 1808 1807 1804 1803 1802 1801 1800 1798 1794 1791 1789 1787 1783 1782 1781 1778 1775 1774 1772 1771 1766 1753 1751 1748 1735 1718 1700 1690 1687 1682 1671 1669 1624 1617 1520 1000 -300 -450 -800 -1000 -2000 -3500 -3750 -5000 -6000 -7000 -9000
Periodic Tables referencing the text string "Ren%26eacute%3B", listed by date:
| Year: 1875 | PT id = 1136 |
Concentric Ring Arrangement of Wiik
From page 133 of The Development of the Periodic Law by Venable, Francis Preston (1856-1934), Easton, Pa. Chemical Pub. Co (1896). The full text (scanned) is available from archive.org.
Venable writes:

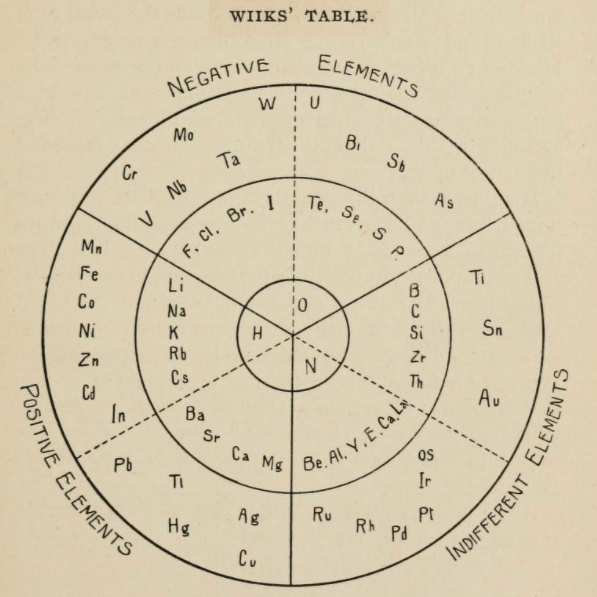
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1885 | PT id = 1145 |
von Richter's Periodic System of the Elements
From page 244 of A Text-book of Inorganic Chemistry by Victor von Richter, Published by Blakiston (US ed. in English, 1885). The full text (scanned) is available from archive.org. The first edition was published in 1874 in German. von Richter was was from the Baltic region, in the the Russian empire at the time.
von Richter's work is almost certainly the first chemistry textbook based on the periodic system. Many (indeed most) modern Inorganic Chemistry texts follow this format, but NOT the Chemogenesis web book!
von Richter, writes:

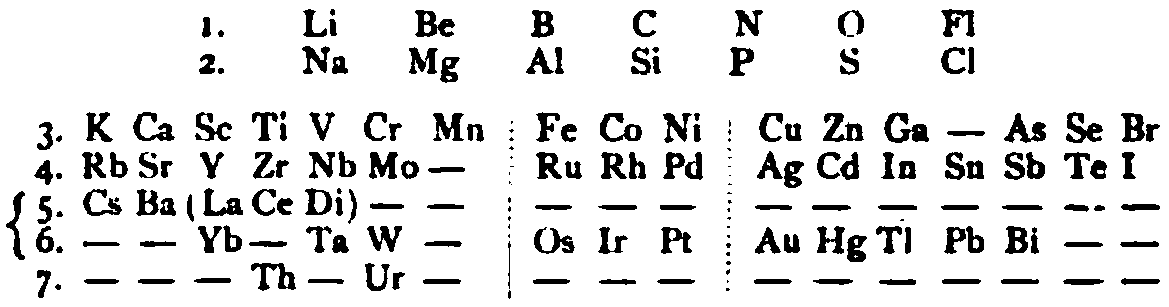

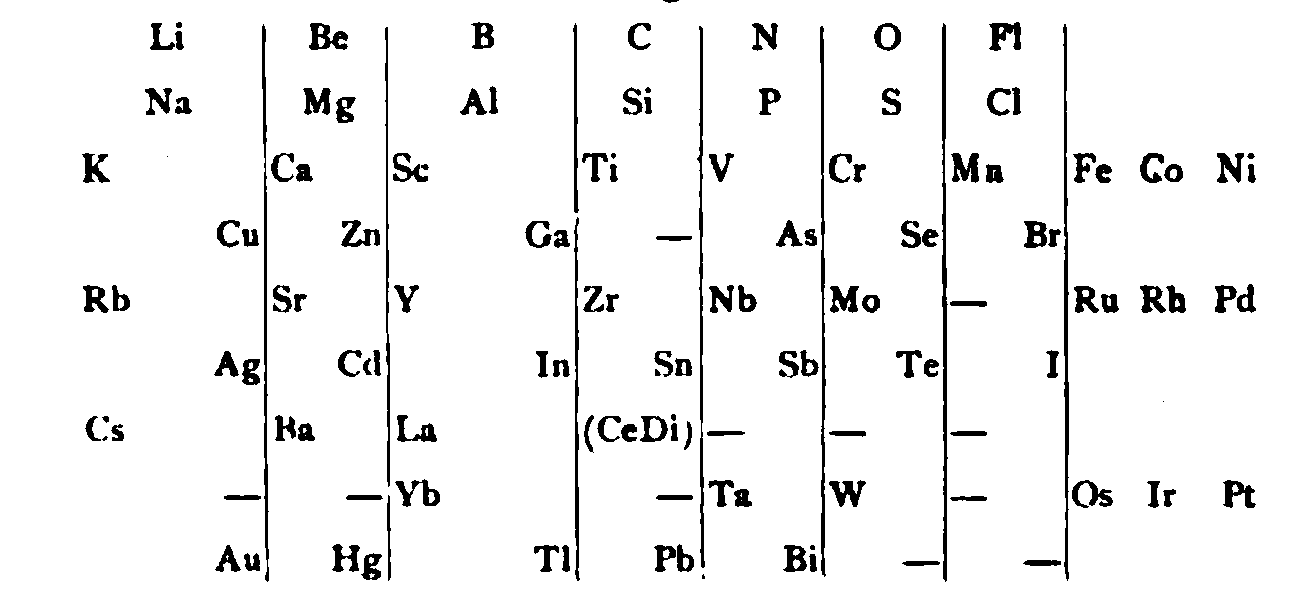
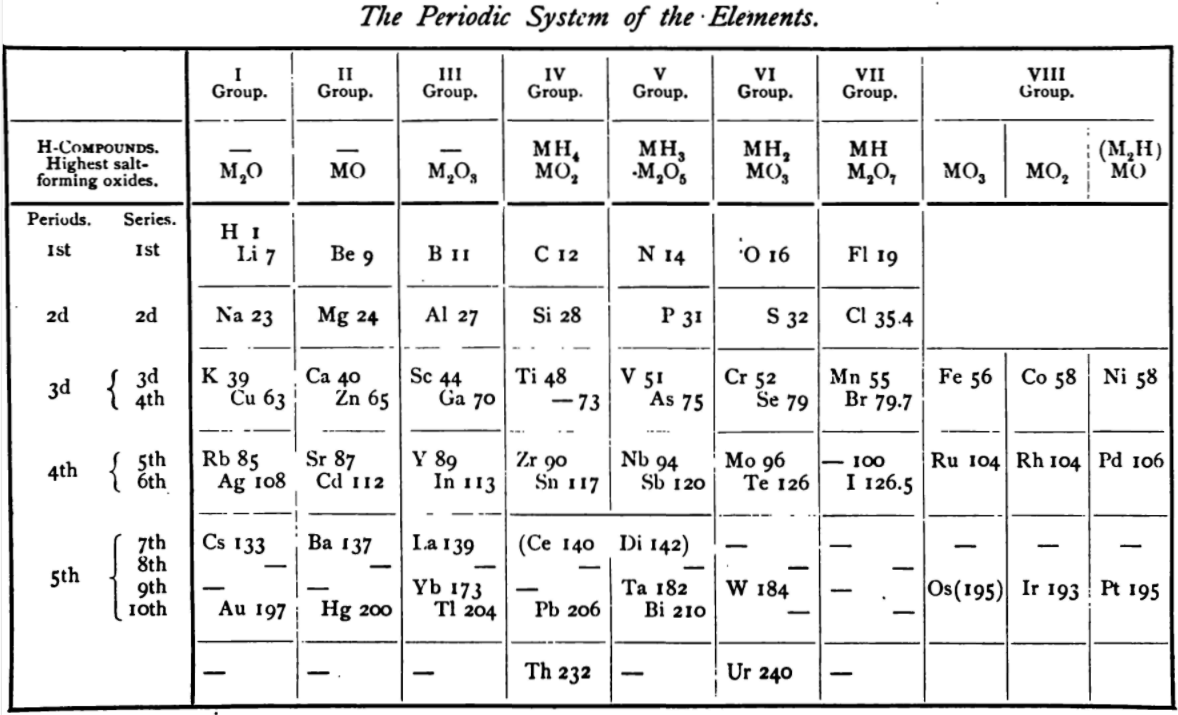
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1886 | PT id = 1107 |
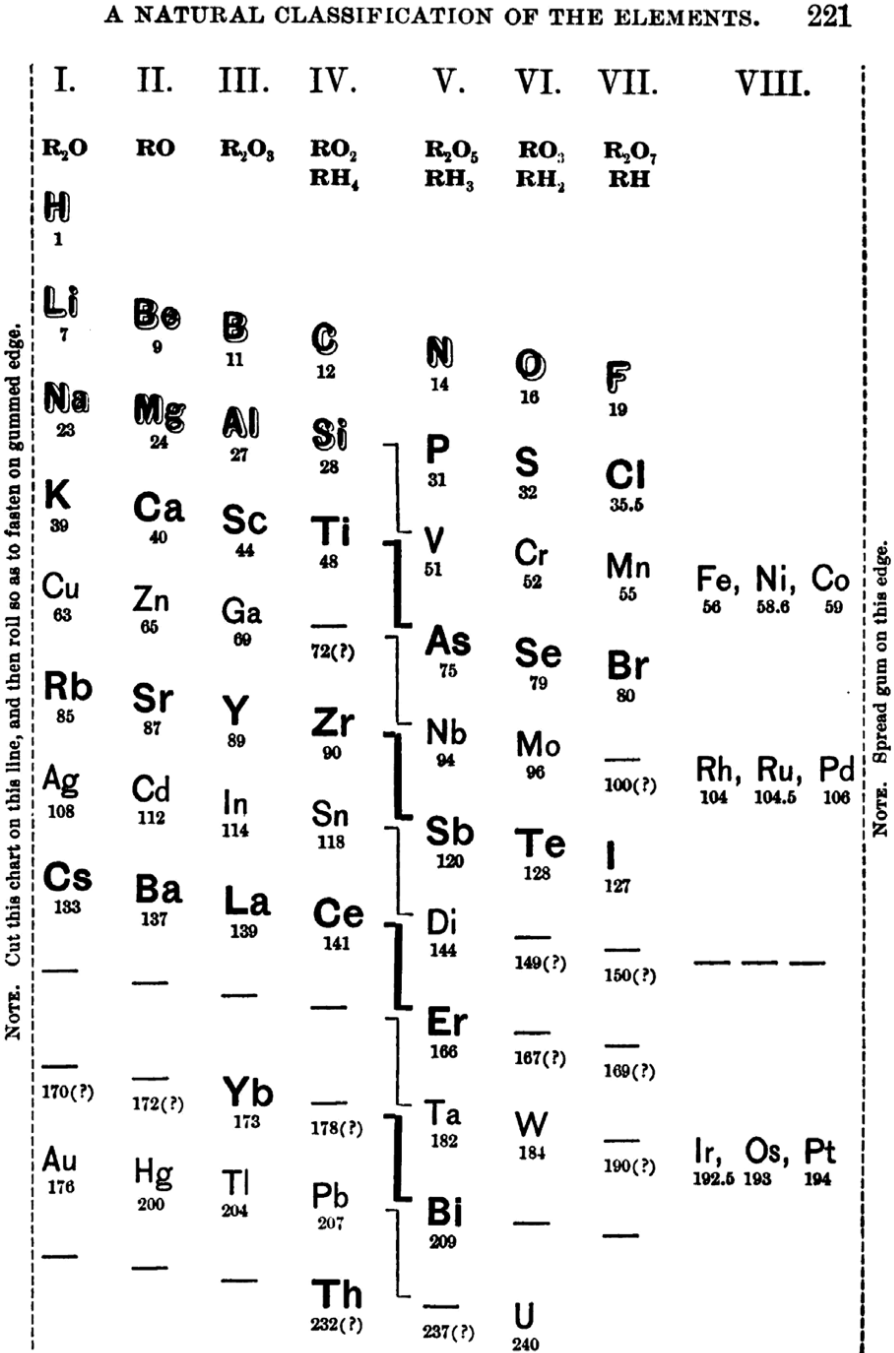
Shepard's Natural Classification
Shepard's Natural Classification of the Elements, a spiral formulation with instructions for turning it into a three-dimensional table. From: Elements of Inorganic Chemistry, Descriptive and Qualitative (pp221), by J. H. Shepard, (1886), Boston MA, pub. D. C. Heath
René Vernon writes:
Note the instructions along the side, to turn the table into a tube (spiral form) and the 19 spaces from La to eka-Ce. Here, Yb needs to be moved back one column into group II, so as to leave room for Lu under La. Then eka-Ce becomes Hf. This results in La + 15 lanthanoids.
The accompanying text says:
"Elements of most distinct basic character are found towards the left; non-metals predominate in the upper and middle parts of Groups V., VI., and VII. ; while the lower part of the table is marked by the more indifferent elements.
"A double spiral will be traced beyond Si (beginning with P and V respectively) and distinguished by heavy-face and light-face type.
"The harmony of nature here exhibited is most impressive. Is it possible that the so-called elements are really compounds? Did the various 'elements' of the earth and sun once exist as hydrogen, when our solar system was a nebula? And will modern chemists ever revive the famed problem of the alchemists, and seek to turn the base metals into gold? Far more precious than gold is the search for truth; and the more we learn of science, the broader becomes our conception of what we know in part, and the deeper should be our reverence for the infinite thought of the Creator."
| Year: 1888 | PT id = 1267 |
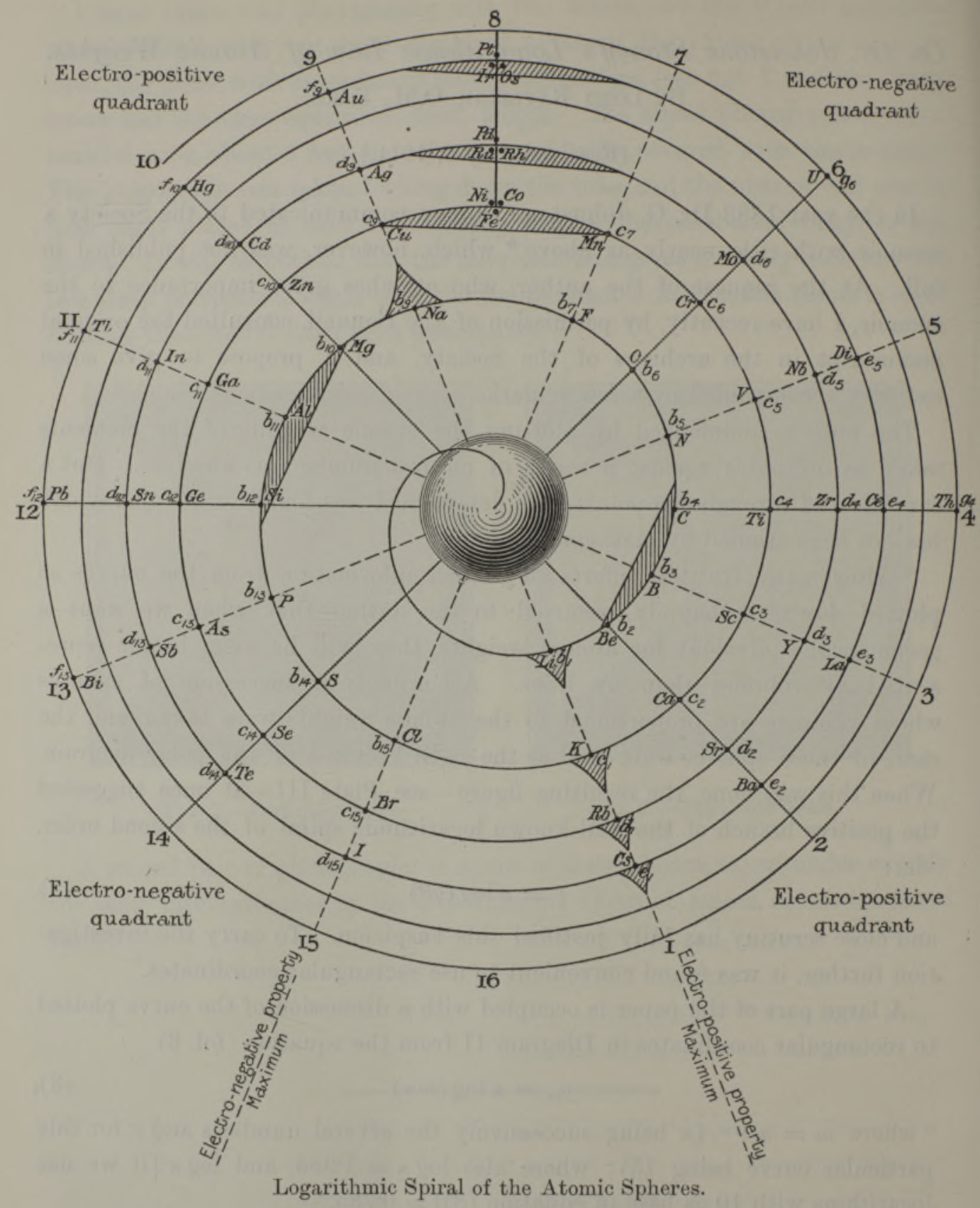
Stoney's Spiral Periodic Table
In the Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character, Volume 85, Issue 580, Aug 1911, p. 472, there is an article On Dr. Johnstone Stoney's Logarithmic Law of Atomic Weights, by Lord Rayleigh (who co-discovered argon in 1894), who writes :
"In the year 1888, Dr. G. Johnstone Stoney communicated to the Society a memoir with title nearly as above, which, however, was not published in full. At the request of the author, who attaches great importance to the memoir, I have recently, by permission of the Council, consulted the original manuscript in the archives of the Society, and I propose to give some extracts, accompanied by a few remarks. The author commenced by plotting the atomic weights of the elements taken as ordinates against a series of natural numbers as abscissæ. But a curve traced through the points thus determined was found to be 'one which has not been studied by mathematicians.
"This sudden transition may have some connection with the fact that no elements have been found on sesqui-radius 16, although the investigation in § 3 shows that the values of m corresponding to the stations on sesqui-radius 16 cannot be dispensed with.
"The vacant places here pointed out are now occupied by the since discovered inert gases. The anticipation is certainly a remarkable one, and it goes far to justify the high claims made for the diagram, as representing in a telling form many of the leading facts of chemistry."
Comment from Mark Leach:
"Notice how the electronegative elements are positioned top right & bottom right and the electropositive elements top left & bottom right."
René Vernon writes:
"Stoney has another article in the September 1902 edition of the The London, Edinburgh and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, called Law of Atomic Weights, pp. 411–415. At the back of the journal is an updated fold-out version of Stoney’s table, image attached.
- Ar, Kr and Xe fit on the spiral, and on spoke 16.
- Neon fits on the spiral but is instead on spoke 8.
- Helium is on spoke 18 but is not on the spiral.
- The circle in the middle represents H (p. 414).
"On the page after the updated spiral, there looks to be some printed content, but it is hidden by what looks to be a folded over page."
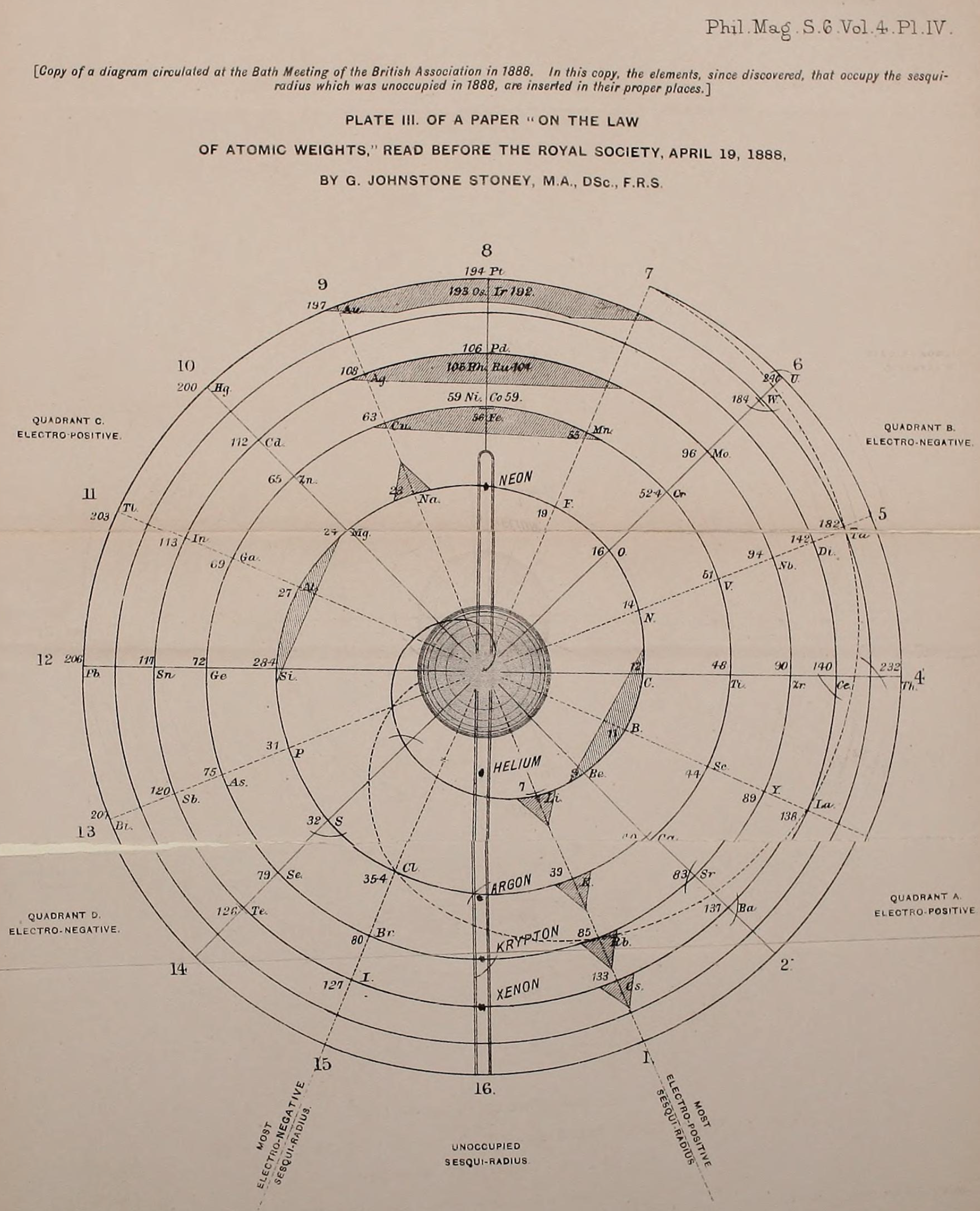
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1891 | PT id = 1140 |
Wendt's Generation-Tree of the Elements
From page 244 of The Development of the Periodic Law by Venable, Francis Preston (1856-1934), Easton, Pa. Chemical Pub. Co (1896). The full text (scanned) is available from archive.org.
Venable writes:
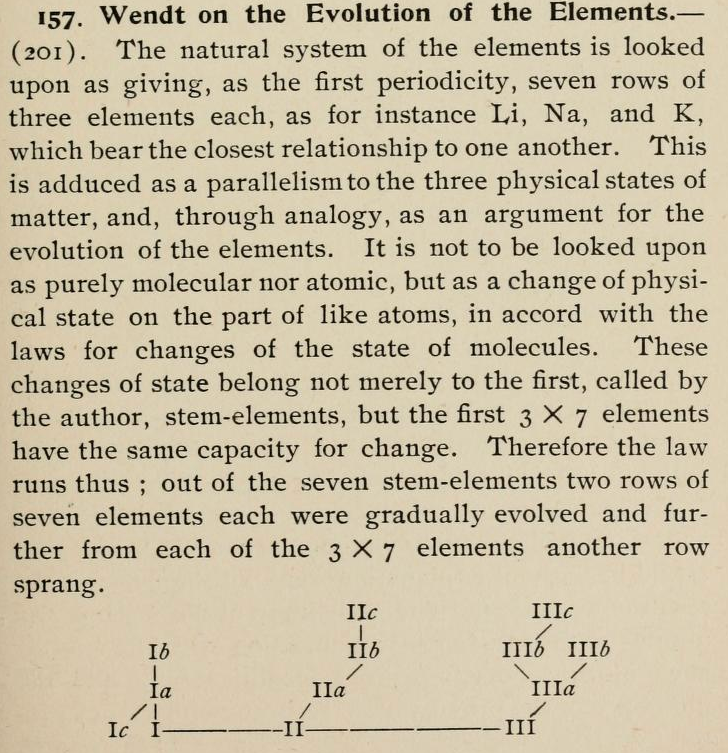
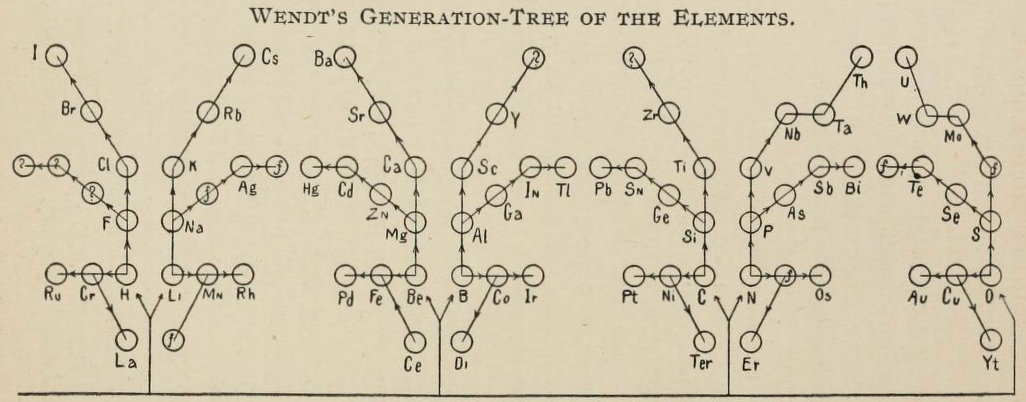
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1893 | PT id = 1151 |
Nechaev's Truncated Cones
René Vernon (who found this formulation) writes:
This weird and wonderful table appears in Teleshov & Teleshova (2019, p. 230). It is attributed by them to Nechaev (1893) and is apparently discussed by Ipatiev (1904):
- The caption accompanying the table is: "Scanning of the projection of rotational bodies in the form of truncated cones as used in Nechaev's spatial construction of the periodic system, 1893."
- Looking at the table it seems to anticipate, after a fashion, the double periodicity noticed by later authors.
- Alternatively, if turned on its side, it would be just five columns wide.
- Between Ce (ignoring Di) and Yb, there are spaces for 12 missing elements, which is one too many.
- Pulling Yb back by one position would have done the trick.
"... We would also like to mention one more version of the periodic table, namely the one offered by V. Ipatiev. Ipatiev's version was one of the first to have been applied in a school textbook, and is also concise and accompanied by a detailed methodological commentary. More specifically, Ipatiev is important in directing our attention to the fact that an essential feature common to all elements should be chosen if the elements are to be systematized. Furthermore, Ipatiev also offered another crucial insight in arguing that this selected feature must satisfy certain conditions, namely: 1) it must be measurable, 2) it must be common to all elements and 3) it must be paramount, i.e. that all the remaining properties of the elements must depend on it [Ipatiev]."
References:
Ipat'ev, V. & Sapozhnikov, A. (1904). Kratkij kurs himii po programme voennyh uchilishh [A concise course in chemistry for military academies]. Sankt-Peterburg: tip. V. Demakova.
Nechaev N. P. (1893). Graficheskoe postroenie periodicheskoj sistemy jelementov Mendeleeva. Sposob Nechaeva [Graphic construction of Mendeleev's periodic system of elements. Nechaev's way]. Moskva: tip. Je. Lissnera i Ju. Romana
Teleshov S, Teleshova E.: The international year of the periodic table: An overview of events before and after the creation of the periodic table. In V Lamanauskas (ed.).: Science and technology Education: Challenges and possible solutions. Proceedings of the 3rd International Baltic Symposium on Science and Technology Education, BalticSTE2019, Šiauliai, 17-20 June, 2019. pp. 227-232, (2019)

| Year: 1911 | PT id = 1296 |
Emerson's Periodic Table of Atomic Weights
Emerson BK, Helix chemica: A study of the periodic relations of the elements and their graphic representation, American Chemical Journal, vol. 45, pp. 160–210 (1911). The formulation below appears on page 173; a scanned pdf version of the paper can be viewed here.
René Vernon writes:
Emerson includes two elements before hydrogen: "E" (either the luminiferous ether or the electron) and "Coronium". There are also two elements between hydrogen and helium: "Nebulium" and "Protofluorine".
This is the first time I have seen a PT showing four extra elements and where they are supposed to fit.
After La, Emerson incorporates 13 lanthanides (Ce to Lu) as transition elements into his 7th period.
Emerson missed dysprosium, between Tb and Ho.
"A, B and C" at the bottom right are supposed to be 'halogen emanations'.
Mark Leach adds that Emerson's very odd Periodic Table of Atomic Weights does not actually show any atomic weights.
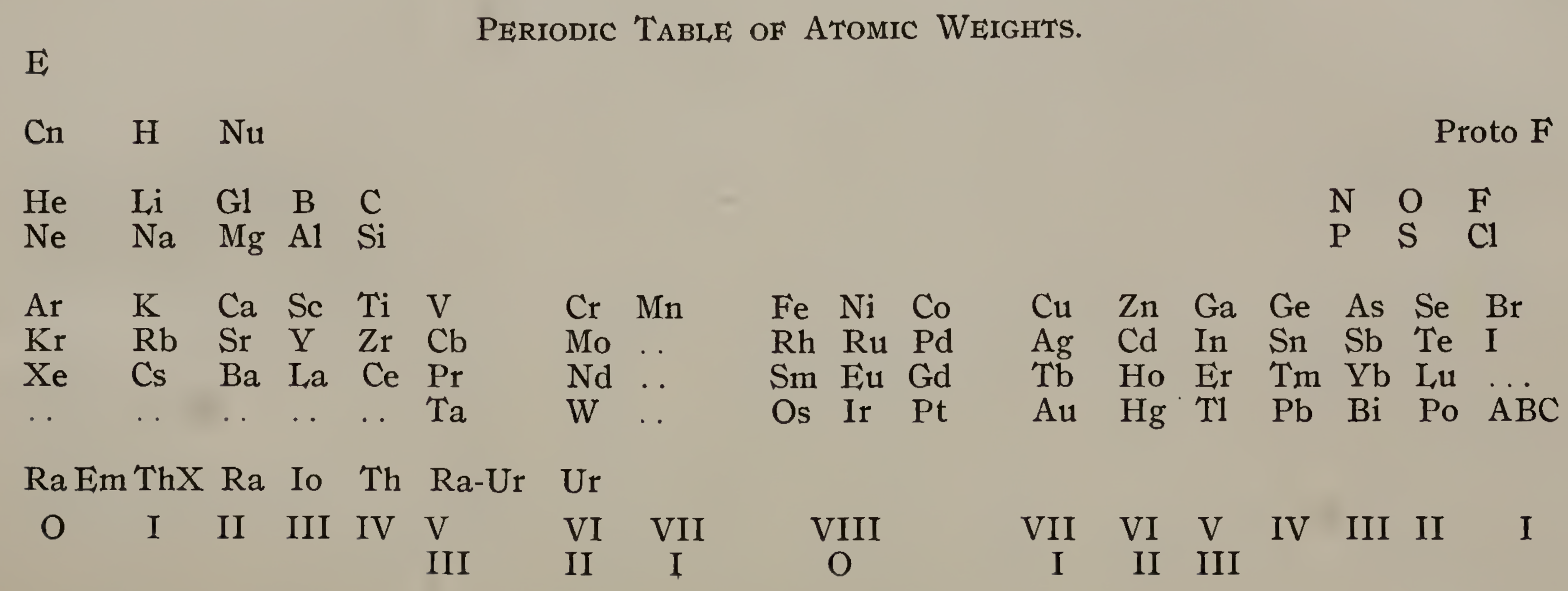
| Year: 1917 | PT id = 1155 |
Friend's Periodic Table (1917)
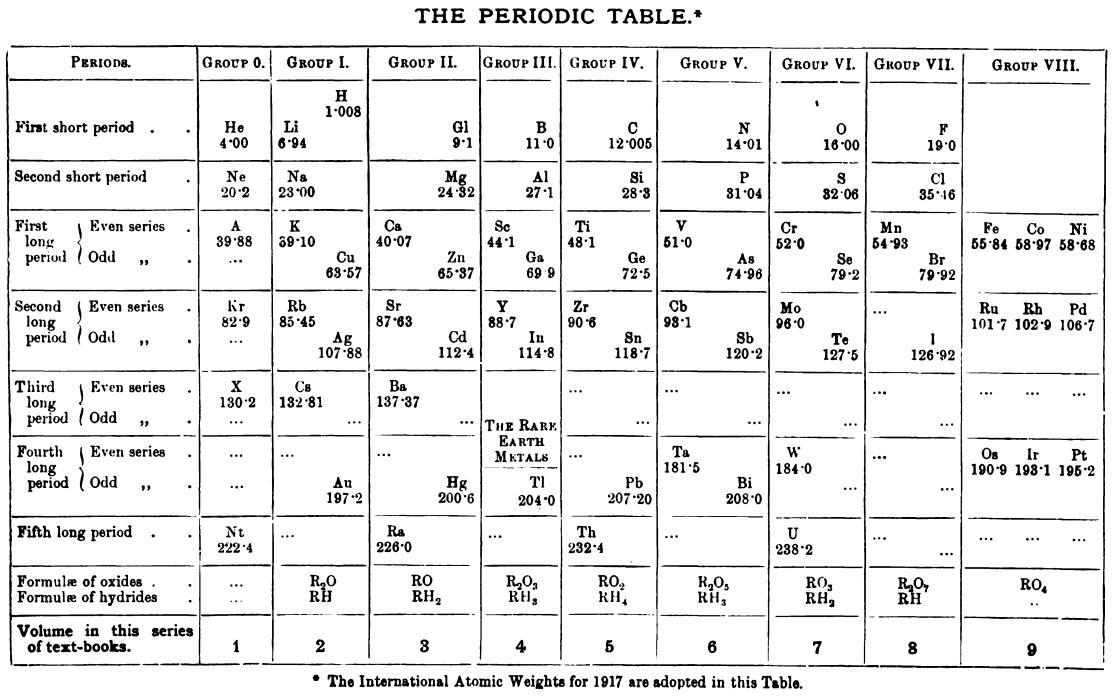
Thanks to René Vernon for the tip.
| Year: 1918 | PT id = 1260 |
Cherkesov: Two Periodic Tables
von Bichowsky FR, The place of manganese in the periodic system, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 7, 1040–1046 Publication Date: July 1, 1918 https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02240a008
René Vernon writes:
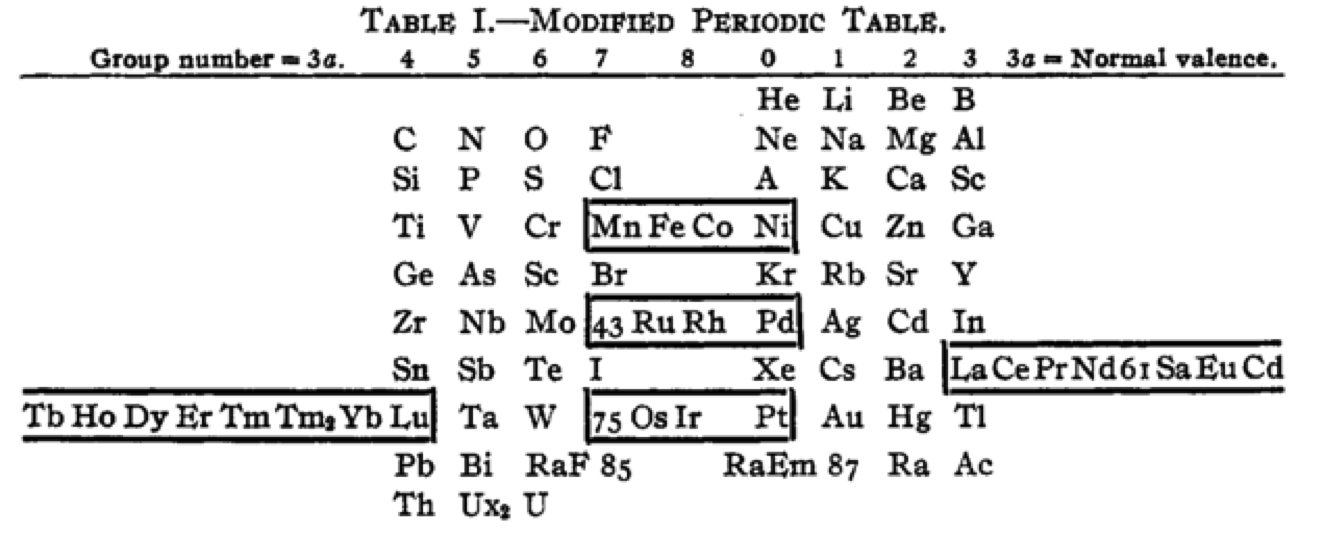
"In this curious article, von Bichowsky, a physical chemist (1889-1951), mounted an argument for regarding Mn as belonging to group 8 (see table 1 below) rather than group 7 (table 2). His article has effectively been assigned to the dustbin of history, having apparently gathered zero citations over the past 103 years.
"Items of note in his 24-column table:
- While Mn, 43 and 75 are assigned to group 8 they remain in alignment with group 7. Se is shown as Sc
- 14 lanthanides, from Ce to Yb, make up group 3a; If La and Lu are included, there are 16 Ln
- Gd is shown as Cd
- Positions of Dy and Ho have been reversed
- Tm and Tm2
- Po shown as "RaF"
- Ra shown as "RaEm"
- Pa shown as Ux2
von Bichowsky made his argument for Mn in group 8, on the following grounds:
- by removing the Ln from the main body of the table all of the gaps denoted by the dashes (in table 2) were removed
- the eighth group links Cr with Cu; Mo with Ag; and W with Au
- the symmetry of the table is greatly increased
- the triads are replaced by tetrads and a group of 16 Ln which accords better with "the preference of the periodic system for powers of two"
- about eight chemistry-based differences between Ti-V-Cr and Mn, including where Mn shows more similarities to Fe-Co-Ni, for example:
- divalent Ti, V, Cr cations are all powerful reducing agents, Cr being one of the most powerful known; divalent Mn, Fe, Co, Ni are either very mild reducing agents as divalent Mn or Fe, or have almost no reducing power in the case of divalent Co or Ni;
- metal titanates, vanadates and chromates are stable in alkaline solution and are unstable in the presence of acid whereas permanganates are more stable in acid than alkali; their oxidizing power is also widely different.
I can further add:
- Mn, Fe, and Co, and to some extent Ni, occupy the "hydrogen gap" among the 3d metals, having no or little proclivity for binary hydride formation
- the +2 and +3 oxidation states predominate among the Mn-Fe-Co-Ni tetrad (+3 not so much for Mn)
- in old chemistry, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni represented the "iron group" whereas Cr, Mo, W, and U belonged to the "chromium group": Struthers J 1893, Chemistry and physics: A manual for students and practitioners, Lea Brothers & Co., Philadelphia, pp. 79, 123
- Tc forms a continuous series of solid solutions with Re, Ru, and Os
Moving forward precisely 100 years, Rayner-Canham (2018) made the following observations:
- Conventional classification systems for the transition metals each have one flaw: "They organise the TM largely according to one strategy and they define the trends according to that organisation. Thus, linkages, relationships, patterns, or similarities outside of that framework are ignored."
- There are two oxide series of the form MnO and Mn3O4 which encompass Mn through Ni. Here the division is not clear cut since there are also the series Mn2O3 for Ti-Cr and Fe; and MnO2 for Ti to Cr.
- Under normal condition of aqueous chemistry, Mn favours the +2 state and its species match well with those of the following 3d member, Fe.
Rayner-Canham G 2018, "Organizing the transition metals" [a chapter in] in E Scerri & G Restrepo, Mendeleev to Oganesson: A multidisciplinary perspective on the periodic table, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 195–205
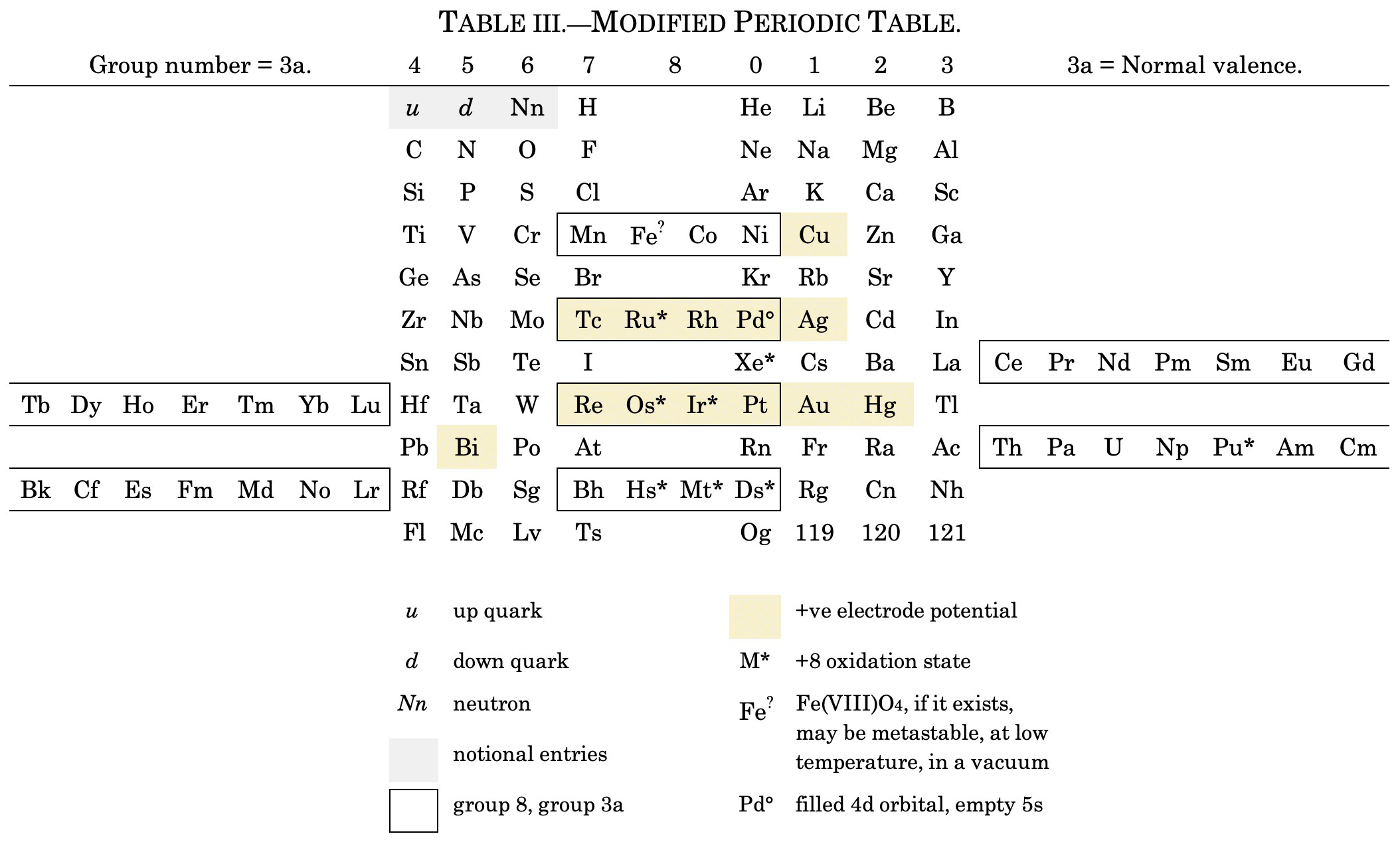
I've also attached a modern interpretation of von Bichowsky’s table. It's curious how there are eight metals (Fe aside) capable of, or thought to be capable of, achieving +8. I am not sure that a table of this kind with Lu in group 3 is possible, without upsetting its symmetry."

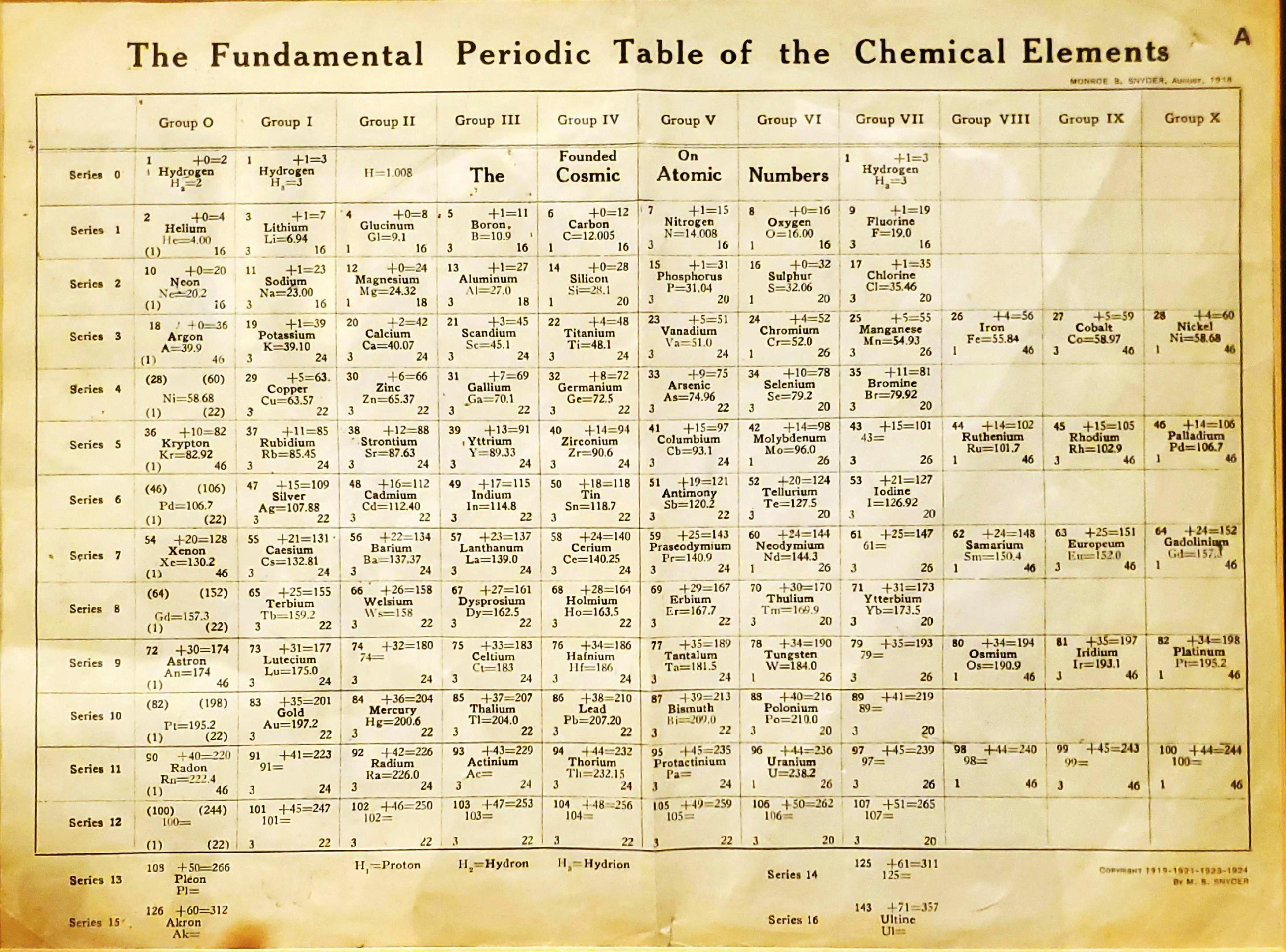
| Year: 1919 | PT id = 1293 |
Snyder's Fundamental Periodic Table of The Elements
Snyder MB 1919, The Fundamental Periodic Table of the Chemical Elements, filed in Congressional Library, Washington.
René Vernon writes:
"Notable for:
- Its attempted integration of the Ln and An into the short form of the periodic table
- Placement of H over He, Li and F
- Elements 108 = Pleon; 126 = Akron; 143 = Ultine"
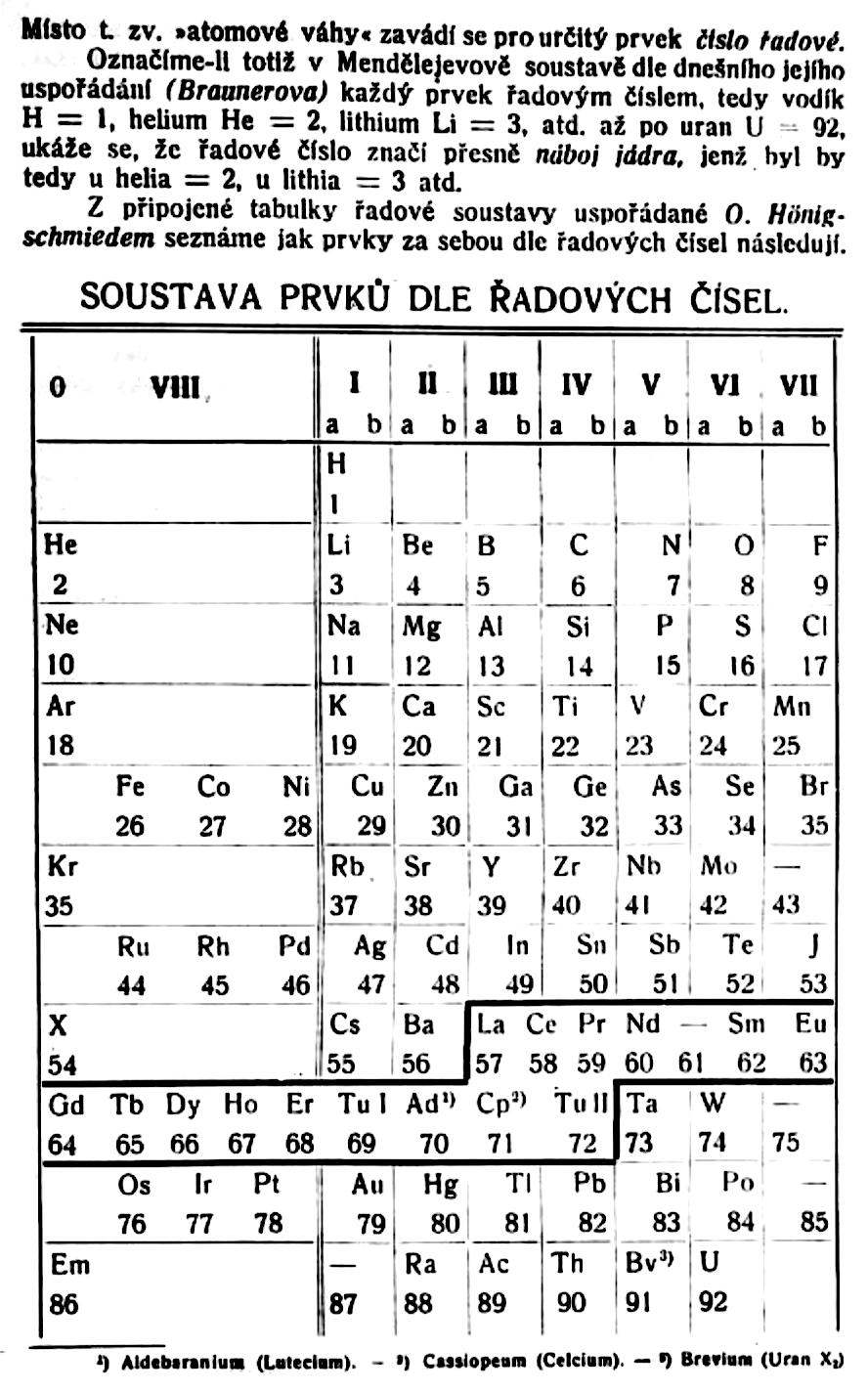
| Year: 1921 | PT id = 1192 |
Formánek's Periodic Table
Formánek J. 1921, Short Outline of Inorganic Chemistry (in Czech), 2nd ed., Ministerstvo zemedelstvi CSR, Praha. p. 281
René Vernon writes:
Here is an eight column table with some interesting features.
Main groups 0, Ia, IIa, Vb, VIb, and VIIb, correspond to what we have today:
- 0 Noble gases
- Ia Alkali metals
- IIa Alkaline earths
- Vb Pnictogens
- VIb Chalcogens
- VIIb Halogens
Main group IIIa is B-Al-Sc-Y... Ac whereas these days B-Al have been moved over Ga on electronic grounds. This happened despite the fact that the average trend line for chemical and physical properties v Z going down B-Al-Sc-Y... Ac is more regular.
In main group IV, notice how C and SI are positioned in the middle of the cell, unlike their neighbours to either side. The group thus bifurcates after Si into a Ti branch and a Ge branch. This is quite reasonable since there is not much difference in the average trendlines going down either option. In any case, C-Si came to be moved over Ge again on electronic grounds.
He survived the electronic revolution, staying over Ne.
| Year: 1923 | PT id = 1198 |
Fajans' Periodic Table
Fajans K., Radioactivity and the latest developments in the study of the chemical elements, trans. TS Wheeler, WG King, 4th German edition, Methuen & Co., London, pp. 116-117, 1923.
René Vernon writes: "An addition to the long list of tables with B-Al over Sc."
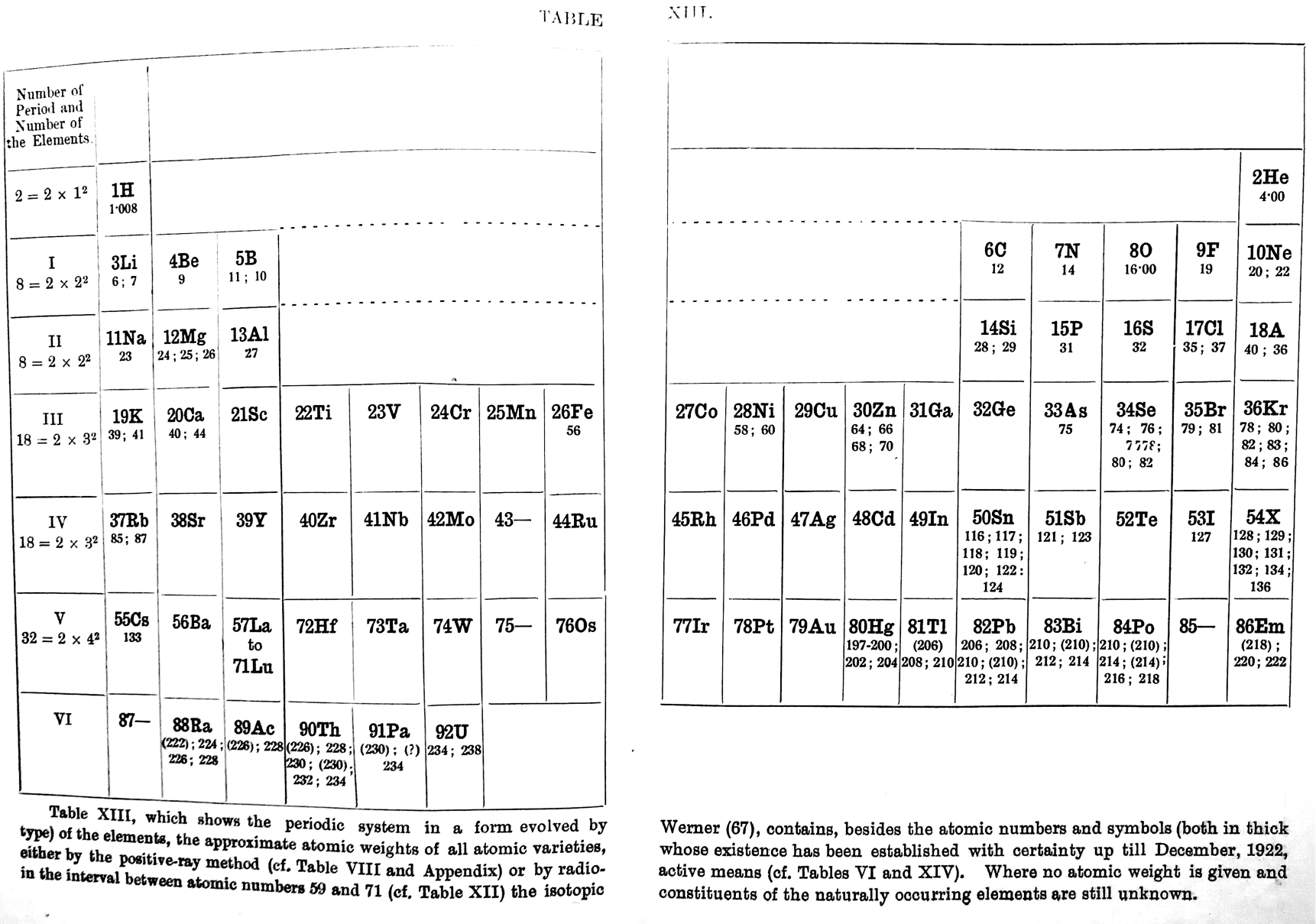
| Year: 1923 | PT id = 1256 |
Deming's Periodic Table With Commentry by Vernon
René Vernon writes:
Deming's 1923 periodic table is credited with popularizing the 18-column form.
I now see Deming used different thickness sloping lines to represent the different degrees of similarity between the main groups and their corresponding transition metal groups.
- The line between Li-Na and group 11 is dashed, denoting the weakest relationship.
- Be-Mg are in group 2 The line between Be-Mg and group 12 is not dashed, denoting a stronger relationship.
- B-Al are in group 3
- The line between B-Al and Ga-In-Tl is thicker yet.
When I plot up to 20 chemical properties v Z going down these options I get the following values for the average smoothness of the trendlines:
- 73.5% for Li-Na-Cu(+2)-Ag(+1)-Au(+3) versus 84% for Li-Na-K-Rb-Cs
- 70% Be-Mg over Zn versus 85% for Be-Mg-Ca-Sr-Ba
- 81% for B-Al-Ga-In-Tl versus 88% B-Al-Sc-Y-La
I would have thought the smoothness for the line between Li-Na and Cu would be < 70%, consistent with Deming’s dashed line. But the thickness of the line would depend on what Deming took into account when he drew it. The common wisdom about groups 1 and 11 is that their similarities are: "confined almost entirely to the stoichiometries (as distinct from the chemical properties) of the compounds in the +1 oxidation state." (Greenwood & Earnshaw 2002, p. 1177). Kneen et al. (1972, p. 521) say that, "the differences between the properties of the group IA and IB elements are those between a strongly and weakly electropositive metal." On this basis I follow Deming’s dashed line. I’ve appended some notes about Group 1 and Group 11.
- Main group 4 is C-Si-Ge-Sn-Pb
- The line between Si and Ti-Zr-Hf is thick
- The line between N-P and V is less thick
- The line between O-S and Cr is less thick again
- The line between F-Cl and Mn is dashed
I have [calculated] a smoothness for C-Si-Ti-Zr-Hf of 86% versus 70% for C-Si-Ge-Sn-Pb. Since Ti shows some transition metal chemistry but not C-Si, it is perhaps plausible to keep C-Si-Ge-Sn-Pb together (as Deming did ).
Deming was a smart author. Nigh on a century later and the metrics check out.
More about group 1 and group 11
There may be a little more to the relationship between Li-Na & Cu-Ag-Au, than is ordinarily appreciated. For example:
- The resulting composite "group" has two electropositive metals and three more electronegative metals so its overall nature is more nuanced then purely group 1 or purely group 11
- The ionic radii of Li+ and Cu+ are 0.76 and 0.77 Å, and there is at least some discussion in the literature about substitution phenomena (Vasilev et al. 2019, p. 2-15; Udaya et al. 2020, p. 98; Kubenova 2021 et al.)
- Group 1 and 11 metal atoms form clusters relatively easily including Au_42+, Ag_64+, Rb_75+, Na_43+ (Mile et al. 1991, p. 134; Wulfsberg 2000, p. 631).
- In an organometallic context, Schade & Scheyler (1988, p. 196) wrote that, "There is much evidence that differences between group 1 and group 11 metals are not of principal but rather gradual manner."
- Although most nonmagnetic metals exhibit superconductivity it is significant that the Group 1 and 11 metals do not become superconducting at very low temperatures (Rao & Gopalakrishnan 1997, p. 398).
- Gold forms intermetallic compounds with all alkali metals (Schwerdtfeger et al. 1989. p. 1769)
References
- Greenwood NN & Earnshaw A 2002, Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd ed., Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford
- Kubenova et al. 2021, "Some thermoelectric phenomena in copper chalcogenides replaced by lithium and sodium alkaline metals", Nanomaterials 2021, vol. 11, no. 9. article 2238, https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092238
- Mile et al. 1991, "Matrix-isolation studies of the structures and reactions of small metal particles", Farady Discussions, vol. 92, pp. 129–145 (134), https://doi.org/10.1039/FD9919200129
- Rao CNR & Gopalakrishnan J 1997, New Directions on Solid State Chemistry, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
- Schade C & Schleyer PVR 1988, "Sodium, potassium, rubidium, and cesium: X-Ray structural analysis of their organic compounds", Advances in Organometallic Chemistry, vol. 27, Stone FGA & West R (eds), Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 169–278
- Schwerdtfeger et al. 1989, "Relativistic effects in gold chemistry. I. Diatomic gold compounds.", The Journal of Chemical Physics, vol. 91, no. 3, pp. 1762–1774. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.457082
- Udaya et al. 2020, Metal sulphides for lithium-ion batteries, in Inamuddin, Ahmer & Asiri (eds), Lithium-ion batteries: Materials and applications, Materials Research Forum, Millersville PA, pp. 91–122
- Vasiliev AN et al. 2019, Low-dimensional Magnetism, CRC Press, Boca Raton
- Wulfsberg 2000, Inorganic chemistry, University Science Books, Sausalito, CA
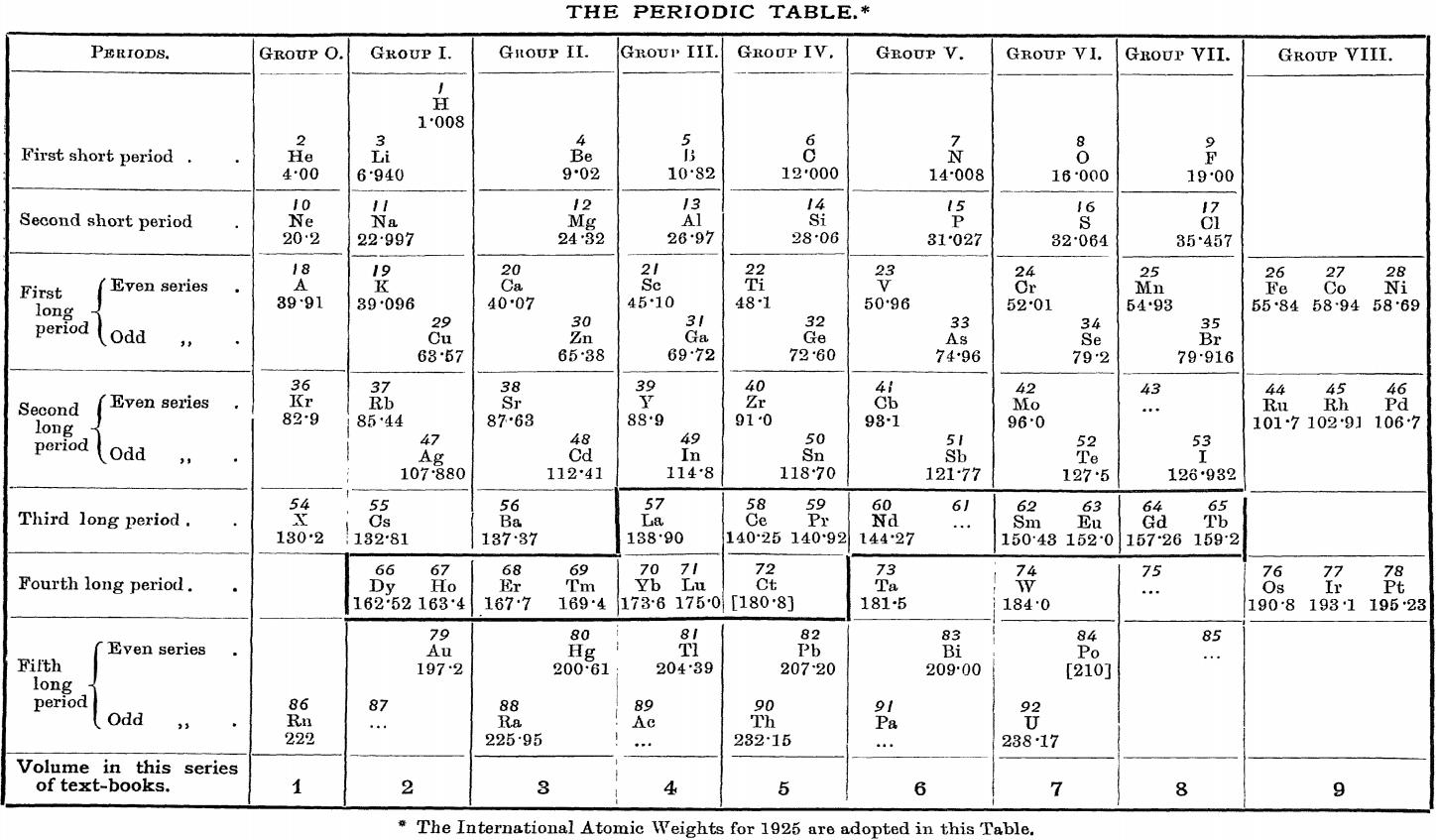
| Year: 1926 | PT id = 1156 |
Friend's Periodic Table (1926)
Vallance RH & Eldridge AA, A Text-Book of Inorganic Chemistry, Vol. VII, Part III, Chromium and its Congeners, JN Friend (ed.) Charles Griffin & Company, London (1926), front paper.
René Vernon (who found this formulation) writes:
"I can't recall seeing a table in which the lanthanoids were allocated in quite such a manner: across seven groups. And, 16 such lanthanoids shown. Even curiouser, Argon = A; xenon = X; are shown in group 0. Wonderful nomenclature from nearly a century ago."
| Year: 1930 | PT id = 1264 |
Gardner's Table of Electronic Configurations of the Elements
A table of electronic configurations of the elements. Nature 125, 146 (1930). https://doi.org/10.1038/125146a0
Abstract:
"MR. ROY GARDNER gave an interesting paper on A Method of Setting out the Classification of the Elements at a recent meeting of the New Zealand Institute. The paper included the accompanying Table, which shows the distribution of electrons into groups corresponding to the principal quantum numbers for all the elements and at the same time preserves the most essential features of the two-dimensional arrangement of Mendeleef. Elements having the same complete groups (that is, all stable groups of 8 or 18) are placed in the same horizontal row, and the vertical columns include elements with the same number of electrons in the incomplete outer groups. The electronic configurations are those given by Sidgwick ("Electronic Theory of Valency", 1927). An asterisk marks elements for which the 'normal' atom is thought to have only one electron in the outermost group, but as practically all these give divalent ions, the point is of minor interest chemically. Distribution of electrons into k-subgroups is unnecessary; these have at present little significance for chemical purposes, and in any case the subgroups are considered to be filled in order to the maxima 2, 6, and 10."
René Vernon writes:
In this table Gardner emphasises the existence of four types of elements:
- those with all "groups" complete
- those with one incomplete group
- those with two incomplete groups (transition elements)
- those with three incomplete groups (rare earth elements)
The upper limits of existence of covalencies of 8, 6, and 4 are marked by heavy horizontal lines.
Note:
- there are nine groups of d-block elements [as we would now call them], and but 13 f-block elements
- La and Lu are treated as d-block elements
- while Yb is counted as an f-block element it was later realised (1937) that the 4f shell is full at Yb, hence it is not clear where Gardner would have placed it (Yb)—seemingly in the 0 column

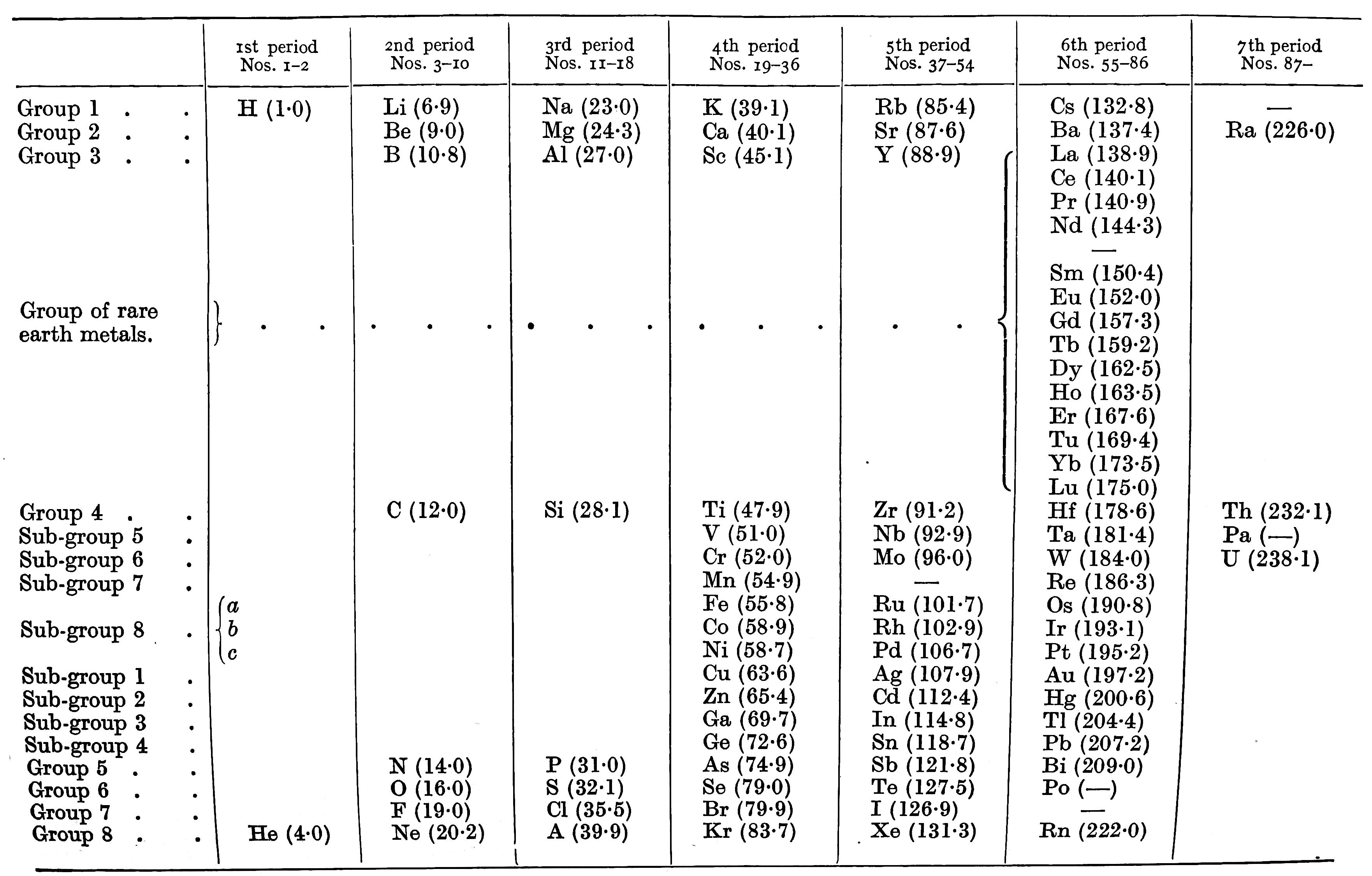
| Year: 1932 | PT id = 1211 |
Bejerrum's Periodic Table
Bjerrum N, Inorganic chemistry, trans. (1936) from the 3rd Danish edition (1932) by N Bjerrum and RP Bell, William Heinemann, London
René Vernon observes:
- There are split blocks everywhere in Bjerrum's periodic system: s once; f once; d twice; p twice.
- As per old chemistry: B and Al are over Sc
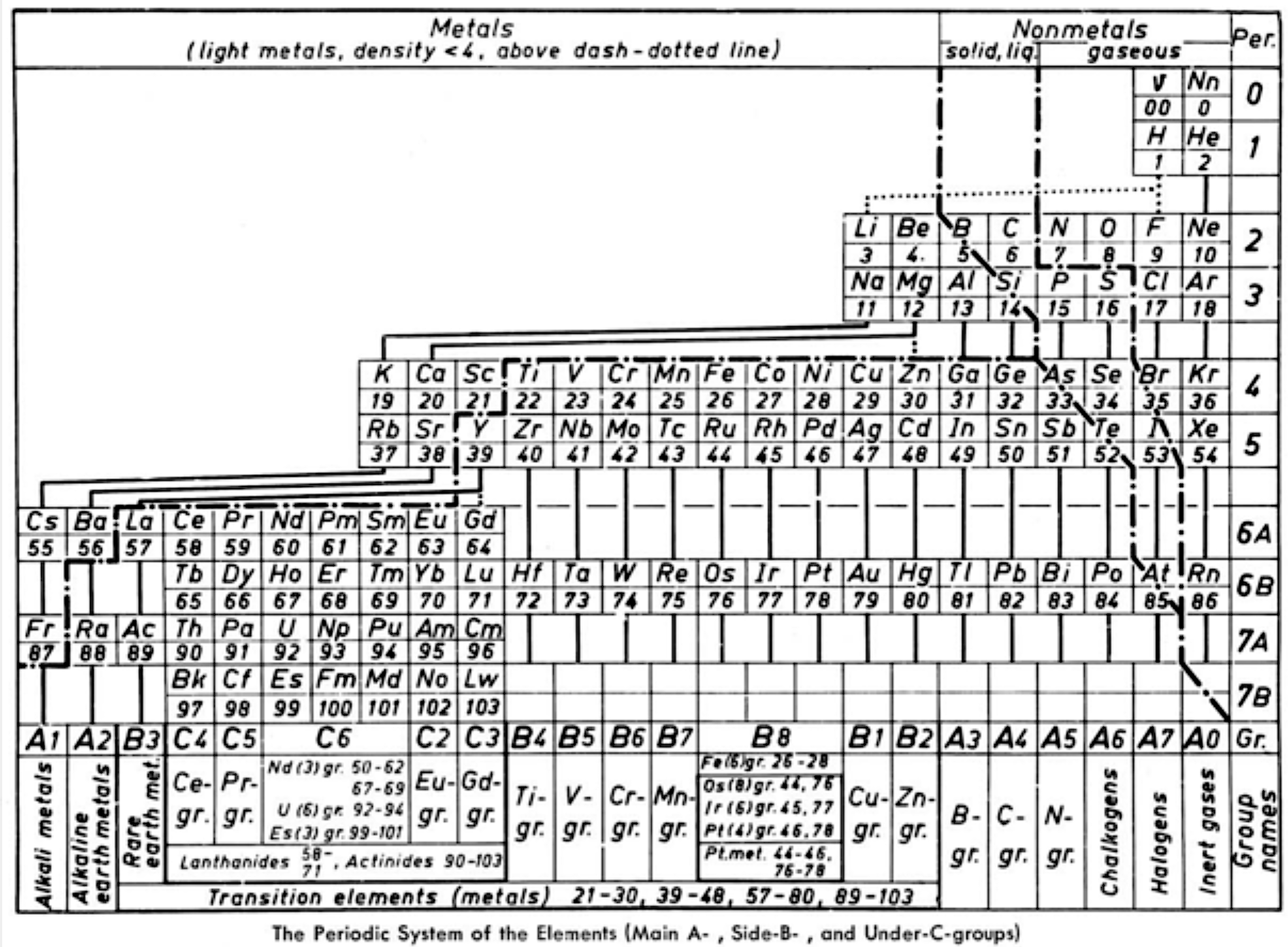
- The group numbering is interesting: eight groups and eight sub-groups
- Bjerrum says the metals fall naturally into two groups: the light metals with a density below 4 gm/cm^3; the heavy metals with a density above 7 gm/cm^3, many of which form coloured salts
- Bjerrum refers to the transition metals as being those in subgroups 8a, 8b and 8c
| Year: 1935 | PT id = 1011 |
Rysselberghe's Periodic Table
Pierre Van Rysselberghe J. Chem. Educ. vol. 12, no. 10, pp. 474—475 1935.
The author writes:
"The usual relationships between analogous elements are preserved and are in fact emphasized by this new arrangement. The only missing regularity is the natural succession of atomic, numbers, but all periodic classifications have to sacrifice it on account of the rare earths. Moreover, it can easily be restored by reading the horizontal lines n the order indicated by the numbers written on the left of the heavy frame line. Each horizontal line is limited by the frame of the table. For instance, K and Ca on the one hand, Cu and Zn on the other hand, form two distinct horizontal lines, as shown by the different numbers given to these groups. They are at the same level because the valence electrons have the same quantum numbers."
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1940 | PT id = 1262 |
Hsueh & Chiang's Periodic Properties of the Elements
Hsueh & Chiang, Periodic Properties of the Elements, J. Chinese Chem. Soc., 5, 5, 253-275. See the PDF.
René Vernon writes:
"A mathematical expression of the periodic law was put forward in 1937 in an article by Chin-Fang Hsueh and Ming-Chien Chiang: J Chinese Chem Soc, 5, 263 (In English.) They derived a property equation from which the numerical magnitude of a property P is related to the atomic number Z of the element in question in terms of valence V, a function of the periodic factor y, the principal quantum number n, and two parameters a and p, which are constants for a given family of elements but different for different families."
| Year: 1945 | PT id = 1118 |
Talpain's Gnomonic Classification of the Elements
Talpain PL 1945, Gnomonic classification of elements, J.Phys. Radium 6, 176-181 (in French), https://doi.org/10.1051/jphysrad:0194500606017600
Talpain writes:
"To overcome the drawbacks presented by the various tables in rows and columns into which the classification of chemical elements is usually inserted, the author proposes a diagram in space, having the form of a double pyramid constructed according to a simple arithmetic law, inspired by Greek surveyors. Under these conditions, all the bodies belonging to the same chemical family are placed on the same column, and all those which have similar physical properties (magnetic, electrical, radioactive, crystallographic, rare earths, etc.) are grouped together. This same diagram also makes it possible to represent the electronic structure of the atoms, the quantified states of the electrons, the energy levels and the spectral lines of hydrogen. Perhaps spectroscopists will be able to use it to also represent the lines of other bodies."
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1946 | PT id = 1088 |
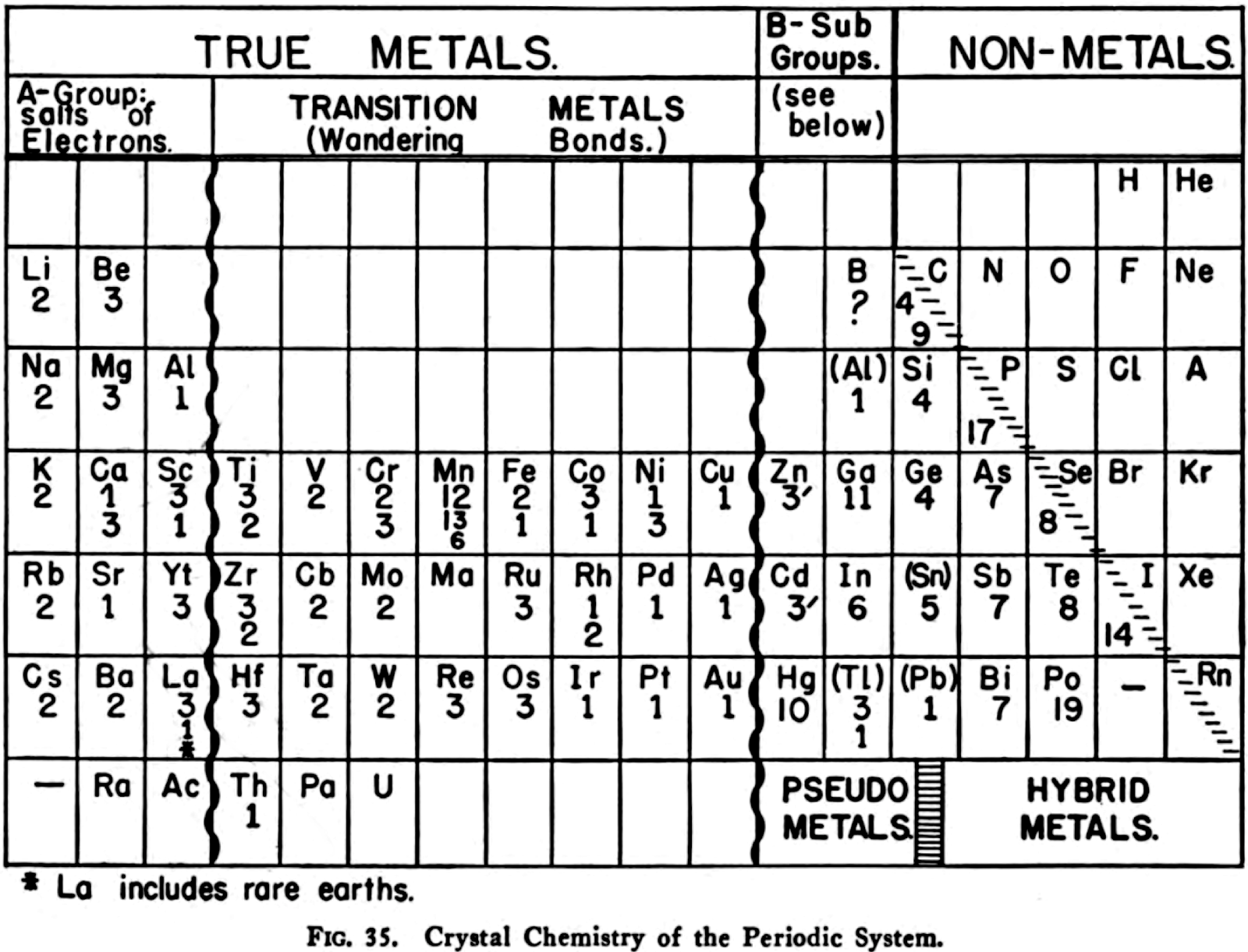
Harrington's Crystal Chemistry of the Periodic System
R.H. Harrington, The Modern Metallurgy of Alloys, John Wiley & Sons, New York, p. 143 (1946)
René Vernon writes:
- The neutron is included in group 0.
- Argon is still A; niobium Cb
- There's a blank space for Pm (discovered 1945).
- The main groups are recognisable, with the exception of group 3 as B-Al-Sc-Y-La. The other side of the table lists B-Al as being analogous to Sc-Y-La, rather than Ga-In-Tl.
The former option works better than the latter in terms of the quantitative smoothness of chemico-physical trend lines going down the group." - The position of H "Which [according to Ephraim] is difficult to place in this table in a satisfactory manner", outside of the main body of the periodic table, "remote from both Li and F, well removed from C, and above He and the inert gases"
- The old school location of B-Al in Group IIIa
- C-Si belong to both Ti-Zr-Hf-Th and Ge-Sn-Pb
- Rokhlin LL 2002, Magnesium Alloys Containing Rare Earth Metals: Structure and Properties, Taylor & Francis, London
- Shchukarev SA 1974, Neorganicheskaya khimiya, vol. 2. Vysshaya Shkola, Moscow (in Russian)
- Weaver EC & Foster LS 1960, Chemistry For Our Times. 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, p. 382
- Wiberg N 2001, Inorganic Chemistry, Academic Press, San Diego
- Wrigley AN, Mast WC & McCutcheon TP 1949, A laminar form of the periodic table, Part I, Journal of Chemical Education, 26(4), 216
- —— A laminar form of the periodic table, Part II, Journal of Chemical Education, 26(5), 248
- H over F
- the lanthanides under Y
- fifteen uranides under W (Hutton says they have, "properties increasingly similar to one another".)
- the complete block system according to Werner (1905)
- a horizontal Bohr line-system according to Spedding (1951)
- a period 0 containing the neutrino and neutron
- element number "00" for "v" suggests the neutrino has neither nuclear charge nor mass while "0" for Nn implies no nuclear charge
- regular period lengths of 2-2-8-8-18-18-32-32
- hydrogen has no direct relationship with a group, only secondary relationships with groups A1 and A7
- germanium, a semiconductor, is counted as a metal
- all groups numbered, where A = representative; B = transition
- C = Ln/An; analogous "transition" groups in the d-block (B8) and the f-block (C6)
- double periodicity among the Ln and An; and
- 25 columns wide i.e 18 + 32 = 50/2 = 25"
- Klechkovskii VM, Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR, 135. 855 (1980). [In Russian]
- Klechkovskii VM, Zh. Eksperim. i. Teoret. Fiz., 41. 465 (1961). [In Russian]
- Which type of compounds certain elements will prefer to form under given conditions of mineral genesis (elementary substance, chalcogenide, oxide, oxysalt, etc.,)
- Whether the element will play a role of a cation or anion of a certain valency
- Which type of chemical bond the resulting mineral compound will have
- Hydrogen is a category of its own.
- The semimetals include selenium and astatine.
- There is no separate category for the halogen nonmetals.
- On page 100 the author refers to the inner occupation of the TM and Ln/An being particularly clear."
- H is over F, which is a smoother fit in terms of physicochemical trends down the group
- He is over Ne, which is a smoother fit etc
- group 3 has lanthanum in it
- the modern relationships Ti-Zr-Hf, V-Nb-Ta, Cr-Mo-W, and Mn-Tc-Re can still be traced
- the lanthanides and actinides are integrated into the main body of the table
- 15 lanthanides and 15 actinides(!)
- the old school arrangement of B-Al-Sc-Y-La can still be traced, as can the less smooth alternative B-Al-Sc-Y-Lu
- the 1s "block" starts at H; the s block proper at Li; p at B; d at Sc; f at Ce
- Beylkin G 2018, The periodic table of the elements with 4n2 n = 2,3... periods, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.02337.pdf
- Eric 2006, https://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?PT_id=20
- Johansson, B., Luo, W., Li, S. et al. 2014, Cerium; crystal structure and position in the periodic table. Sci Rep 4, 6398. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06398
- Gregory Beylkin: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gregory_Beylkin
- Sc, Y, La, Ac
- Sc, Y than a gap for the lanthanides & a gap for the actinides
- Sc, Y, Lu, Lr
- Very good correspondence with natural categories
- Largely linear trends seen along main groups; two switchbacks seen in group 13; also falloffs (6p sub-shell) seen in groups 14-17
- First row anomalies seen for Li (in amphoteric territory), Be (ditto), C (misaligned), N (in noble gas territory), O (misaligned), F (ditto) and He (ditto)
- For group 13, the whole group is anomalous, no doubt due to the scandide contraction impacting Ga and the double whammy of the lanthanide and 5d contraction impacting Tl
- Nitrogen was called a noble gas before the discovery of the real noble gases and appropriately enough falls into that territory
- Rn is metallic enough to show cationic behaviour and falls just outside of noble gas territory
- F and O are the most corrosive of the corrosive nonmetals
- The rest of the corrosive nonmetals (Cl, Br and I) are nicely distributed, across the border from F
- The rest of the simple and complex anions, funnily enough, comprise the intermediate nonmetals
- The metalloids are nicely aligned; Ge falls a little outside of the metalloid line, being still occasionally referred to as a metal; Sb, being the most metallic of the metalloids falls outside the border; At is inside; Po is just outside
- Pd is located among the nonmetals due to its absence of 5s electrons; see here
- The proximity of H to Pd is astonishing given the latter's capacity to adsorb the former
- The post-transition metals (PTM) form an "archipelago of amphoterism" bounded by transition metals: Ni and C to the west; Fe and Re to the south; V, Tc and W to the east; noble metals to the north
- Curiously, Zn, Cd, and Hg are collocated with Be, and distant from the PTM and the TM proper (aside from Mn)
- Zn is shown as amphoteric, which it is. Cd is shown as cationic but is not too far away from amphoteric territory; it does show amphoterism, reluctantly; Hg is shown as amphoteric which is the case, weakly, for HgO, as is the congener sulfide HgS, which forms anionic thiomercurates (such as Na2HgS2 and BaHgS3) in strongly basic solutions
- The ostensibly noble metals are nicely delineated; Ag is anomalous given its greater reactivity; Cu, as a coinage metal, is a little further away
- The proximity of Au and Pt to the halogen line is remarkable given the former's capacity to form monovalent anions
- The ferromagnetic metals (Fe-Co-Ni) form a nice line
- The TM from groups 4-12 form switchback patterns e.g. Ti-Zr and the switchback to Hf
- The refractory metals, Nb, Ta, Mo, W and Re are in a wedge formation
- Tc is the central element of the periodic table in terms of mean radius and EA values; V is close, Cr is a little further away
- Ti is just inside the basic cation line; while Ti(IV) is amphoteric, Ti3+ is ionic
- Sc-Y-La shows a main group pattern up to La, when there is a switchback to Ac
- Sc-Y-Lu-Lr shows a TM switch back pattern
- La, and to lesser extent Ce are rather separated from the rest of the Ln, consistent with Restrepo and here.
- Sc and Lu are close to the amphoteric territory and are both in fact, weakly amphoteric
- The post-cerium Ln and An (but for Th) all fall within basic cation territory
- EA values for the An are estimates and need to be treated with due caution
- The light actinides (Th to Cm) occupy a tight locus, with the exception of Th, where the 5f collapse is thought to occur, and Pu, which sits on the border of 5f delocalisation and localisation
- While the light actinides U to Cm are shown as being cationic they are all known in amphoteric forms
- The heavy actinides, Bk to Lr, are widely dispersed
- All the Ln, bar Tm, are located within close proximity of the light An locus; Tm is the least abundant stable Ln
- The gap between La and Ce, and rest of the Ln is consistent with Restrepo's findings and here
- Nobelium in this edition of the chart falls off the bottom, having a radius 1.58 (cf Es) and an EA of -2.33
- There is an extraordinary alignment between He and the Group 2 metals
- Magnesium is on the cationic-amphoteric boundary; some of its compounds show appreciable covalent character
- Li, being the least basic of the alkali metals, is located just outside the alkalic zone; Li compounds are known for their covalent properties
- The reversal of the positions of Fr and Cs is consistent with Cs being the most electronegative metal
- A similar, weaker pattern is seen with Ba and Ra.
- s 20
- p –35
- d 125
- 4f 46,000
- 5f 522
- Ce is known at +4, Pr is known as +5, and I recall seeing some speculation about the possibility of Nd +6. (Pm +7 may be overreach.)
- Tl is lined up under Au even though Tl prefers +1. That said Au is not adverse to +1.
- I stopped at Hs since the limits of SHE chemistry just about runs out there.
- The dividing line between metals and nonmetals is 73 element box sides long.
- Dias JR 2004, "The periodic table set as a unifying concept in going from benzenoid hydrocarbons to fullerene carbons", in DH Rouvray & RB King (eds.), The periodic table: into the 21st century, Institute of Physics Publishing, Philadelphia, pp. 371–396 (375)
- Fernelius WC 1982, "Hafnium," J. Chem. Educ. vol. 59, no. 3, p. 242
- Greenwood NN & Earnshaw A 2002, Chemistry of the elements, 2nd ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, p. 1148
- Habashi F 2010, "Metals: typical and less typical, transition and inner transition", Foundations of Chemistry, vol. 12, pp. 31–39
- Lee JD 1996, Concise inorganic chemistry, 5th ed., Blackwell Science, Oxford, p. 753
- Kornilov II 1965, "Recent developments in metal chemistry", Russian Chemical Reviews, vol. 34, no. 1, p. 33
- Küpfer YJ 1954, "Rhodium uses in plating", Microtecnic, Agifa S.A., p. 294 Niedenzu K & Dawson JW 1965, Boron-nitrogen compounds, Springer, Berlin, preface
- Oshe RW (ed.) 1985, "Handbook of thermodynamic and transport properties of alkali metals", Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, p. 987
- Paine et al. 2005, "Recent developments in boron-phosphorus ring and cage chemistry", in Modern aspects of main group chemistry, M Lattman et al. (eds.), ACS Symposium Series, American Chemical Society, Washington DC, p. 163
- Rayner-Canham G 2020, The periodic table: Past, present, and future, World Scientific, Singapore
- The traditional form of periodic table is a hybrid of an electronic and a chemistry based table.
- An electronic or physics-based table would show (a) He over Be; and (b) group 3 as Sc-Y-Lu-Lr; and (c) group 13 as B-Al-Ga-In-Tl
- A chemistry-based table would show (d) He over Ne; and (e) B-Al over Sc-Y-La-Ac.
- What we have instead is a hybrid table with 1(c) and 2(d). It is not as symmetric or tidy as the pure Lu form; neither is it as irregular as the form with three split blocks.
- Rang (1893)
- Gooch & Walker (1905)
- Cuthbertson & Metcalfe (1907)
- Baur (1911)
- Rydberg (1913)
- Black & Conant (1920)
- Lewis (1923)
- Hubbard (1924)
- Deming's table (1925), which popularised the medium-long form
- Antropoff (1926)
- LeRoy's table (1927)
- Irwin (1939)
- Seaborg (1945), with B left in group 13
- Yost & Russell (1946)
- Coryell (1952)
- Pauling's table (1960)
- Habishi's Metallurgist's Periodic Table (1992), Habishi leaves B in group 13
- H and P are almost on top of one another
- The proximity of Be to the post-transition metals, and its relative scarcity in the crust
- The metalloids, with their intermediate values of electronegativity, go down the middle. At the same time they span nearly the full range of abundance.
- B-Ga-Sc-Y-La are in a row
- N falls along the halogen line
- The abundance of O and Si, which we see in the form of silica
- F is more abundant in the crust than 85 percent of metals
- Al is the most abundant metal. Al and Fe are in the same vicinity: "Curiously, the chemistry of aluminium also resembles that of the iron(III) ion... These similarities may be ascribed to the same 3+ charge and near-identical ion radii (and hence charge density)." (Rayner-Canham 2020, p. 191)
- The abundance of Ar compared to the rest of the noble gases. Apparently this is influenced by the radioactive decay of potassium-40 in Earth's core, which is considered one of the main sources of heat powering the geodynamo that generates Earth's magnetic field. It has been suggested that a large amount of Ar may be present in the core, as the compound ArNi with an L11 Laves structure (similar to an intermetallic phase, and related to a cubic close packed lattice). ArNi is stabilised by notable electron transfer from Ni to Ar, changing their electron configurations toward 3d7 and 4s1. (Adeleke et al. 2019)
- Ti, a light yet strong metal, is about 2,500 times as abundant as Sn, a weak heavy metal
- Zn is an outlaw post-transition metal
- The most active 4d-5d transition metals (Zr, Hf) occupy a boundary overlap with the rare earth metals
- Ag, which has a largely main-group chemistry, is located in the PTM region. It is about 20 times as abundant as the noble meals
- Re is an outlaw noble metal
- Adeleke AA, Kunz M, Greenberg E, Prakapenka VB, Yao Y, Stavrou R 2019, A high-pressure compound of argon and nickel: Noble gas in the Earth's core?, ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, vol. 3 no. 11, pp. 2517-2544, https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00212
- Rayner-Canham G, 2020, The periodic table: Past, present, future, World Scientific, Singapore
- Metals with lower EN, i.e. < 1.7, or active nonmetals with higher EN, tend to be concentrated in silicate or oxide phases that are more easily found in the crust due to their lower density, and hence have higher abundances.
- Metals with moderate EN 1.7 to 2.1, say the later transition metals and post-transition metals, tend to form sulfide liquid phases; are less easily found in the crust due to their relatively higher densities; and are less abundant by about two orders of magnitude compared to the metals found in silicate or oxide phases.
- Metals with EN > 2.2, i.e. the noble metals, have an affinity for a metallic liquid phase, and are depleted in the crust since they generally sank to the core and hence have very low abundances. They are about two orders of magnitude less abundant than the sulfide metals.
- Cox PA 1997, The elements: Their origin, abundance and distribution;
- Gill R 2014, Chemical fundamentals of geology and environmental geoscience;
- White WA 2020, Geochemistry
- For the nonmetals, the relative average abundance proportions are about 5: 700: 250: 1 for, respectively, the metalloids; the core nonmetals H, C, N, P, S, and Se; the halogen nonmetals; and the noble gases. Si and O were left out as outliers, in terms of their massive abundances.
- Thus, metalloids aside, the abundance of the nonmetals tends to fall with increasing EN. I don't know what's going on with the metalloids.
- The chart may prompt some further appreciative enquiry:
- In the case of exceptions to the initial three generalisations why do these occur?
- Why is Li so rare, compared to the other alkali metals?
- Why is Si good at forming a planetary crust?
- Why do the metalloids span such a wide range of abundances?
- If H is supposed to make up ca. 74% of the universe why does it have the same abundance in the Earth's crust as P?
- In what form is H found in Earth's crust—water, hydroxides?
- If H is supposed to make up ~ 74% of the universe why does it have the same abundance in the Earth's crust as P?
- Are there any chemical similarities between H and P, given both have some metalloidal character? The have virtually identically electron affinities. H is sometimes positioned above B due to chemical similarities. It then forms a diagonal relationship with C, which in turn has a diagonal relationship with P, which has a diagonal relationship with Se e.g. P reacts with Se to form a large number of compounds characterised by structural analogies derived from the white phosphorus P4 tetrahedron.
- The rare earth metals are relatively rare, having an average abundance of 1% that of the 3d metals. That being so, why is their rareness sometimes questioned? Why does the crustal abundance of the REM plummet by two orders of magnitude towards the end of the lanthanides?
- There is symmetry in this version.
- The physiochemical relationship of He to Ne is retained.
- There is a loss of physiochemical regularity in placing He over Be. Even if helium can be enticed to become chemically active, it will still be very much better located in group 18.
- While the d, p, and s blocks start with the appearance of the relevant electron, there is a loss of consistency with La at the start of the f-block. This is confusing to students since there is no such inconsistency in the La form.
- In terms of predominant differentiating electrons in each block, this form is less consistent than an La table.
- There is one less form of "element block-type" symmetry, than in the La form.
- Bjerrum, N (1936). Bjerrum’s Inorganic Chemistry. London: Heinemann
- Hein, M; Arena, S (2013). Foundations of College Chemistry. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 226, G-6. ISBN 978-1-118-29823-7.
- Oderberg DS 2007, Real Essentialism, Routledge, New York, ISBN 978-1-134-34885-5
- Vernon R 2013, "Which elements are metalloids?", Journal of Chemical Education, vol. 90, no. 12, 1703?1707, doi:10.1021/ed3008457
- Deming
- The literature since his time, as shown
- The expected behaviour of the super-heavy elements
- The smoothness of Z vs physiochemical property trendlines going down groups, for up to 40 physiochemical properties
"The numbers below each element symbol refer to the crystal: 1 = FCC, 9 = graphite structure, 11 = orthorhombic, etc. Extra numbers are for structures at higher temperatures.
"The wriggly lines between groups 3 and 4, and 11 and 12 refer to a gradation between the classes involved. Wikipedia calls these linking or bridging groups
"Harrington's class names are novel. [Who would have thought of the elements of groups 1 to 3 as being called the "salts of electrons"?] Then again, "in view of the extensive role that electrons play as anions" Dye (2015) asked: "where should electrons be placed in the periodic table?" (Note: In 1946 Achimof tried answering this, with an electron as element -1 above H and a neutron as element 0 above He.)
"Aluminium appears in group 3 and group 13 since, according to Harrington, it has the crystalline structure of a true metal. This is not quite true since its crystalline structure shows some evidence of directional bonding.
"For the transition metals as "wandering bonds", Harrington writes that the metallic bond is spatially undirected and that it may operate between any given atom and an indefinite number of neighbours" (p. 145). Since A-metals are better called, in his mind, "salts of electrons" [and B-metals show signs of significant directional bonding] the transition metals are therefore called by him as wandering bonds. This becomes confusing, however, given d electrons in partially filed d-orbitals of transition metals form covalent bonds with one another.
"Counting boron as a pseudo metals looks strange.
"Germanium is counted as a metal: "...the electrical conductivit[y]... [is] sufficiently high to show that the outer electrons are very loosely held and the linkage must be partly metallic in character." (p. 148). In fact the electrical conductivity of high purity germanium, which is a semiconductor, is around 10–2S.cm–1. Compare this with antimony, at 3.1 x 104S.cm–1
"Tin has brackets around it to show its "renegade" status, "with its white form behaving largely as would a True Metal, whereas its grey form is more non-metallic than metallic." White tin actually has an irregularly coordinated structure associated with incompletely ionised atoms.
"Thallium and lead have brackets around them since their crystalline structures are supposedly like those of true metals. This is not quite right. While both metals have close-packed structures they each have abnormally large inter-atomic distances that have been attributed to partial ionisation of their atoms.
"The B-subgroup metals are divided into pseudo metals and hybrid metals. The pseudo metals (groups 11 and 12) behave more like true metals than non-metals. The hybrid metals As, Sb, Bi, Te, Po, At – which other authors would call metalloids – partake about equally the properties of both. According to Harrington, the pseudo metals can be considered related to the hybrid metals through the carbon column.
"The location of the dividing line between metals and nonmetals, running as it does through carbon to radon is peculiar. The line is usually shown running through boron to astatine."
| Year: 1947 | PT id = 1166 |
Ageev's Crystalline Structures of The Elements
Ageev NV 1947, The nature of the chemical bond in metal alloys (Izdvo Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow/Leningrad, p. 10
René Vernon writes:
"In this curious 18-column table, showing the crystalline structures of the elements, Ageev locates the predominately non-metallic groups on the left and the remaining groups on the right.
"It's odd that he located boron and aluminium on the far left over gallium, rather than over scandium. I suppose he did this so that gallium, indium, and thallium would not be mistaken for d-block metals.
"Reading from left to right then, Ageev's table could be said to be made up of five blocs:"
[1] the nonmetallic bloc
[2] the alkaline bloc
[3] the inner transition bloc
[4] the transition metal block
[5] a post-transition metallic bloc
| Year: 1947 | PT id = 1243 |
Science Service: Two Periodic Tables
A two-sided Science Service periodic table from 1947. The one is listed as "After Bohr", the other as "After Mendeleeff".
René Vernon writes:
"Here’s a slightly odd table (with two sides):
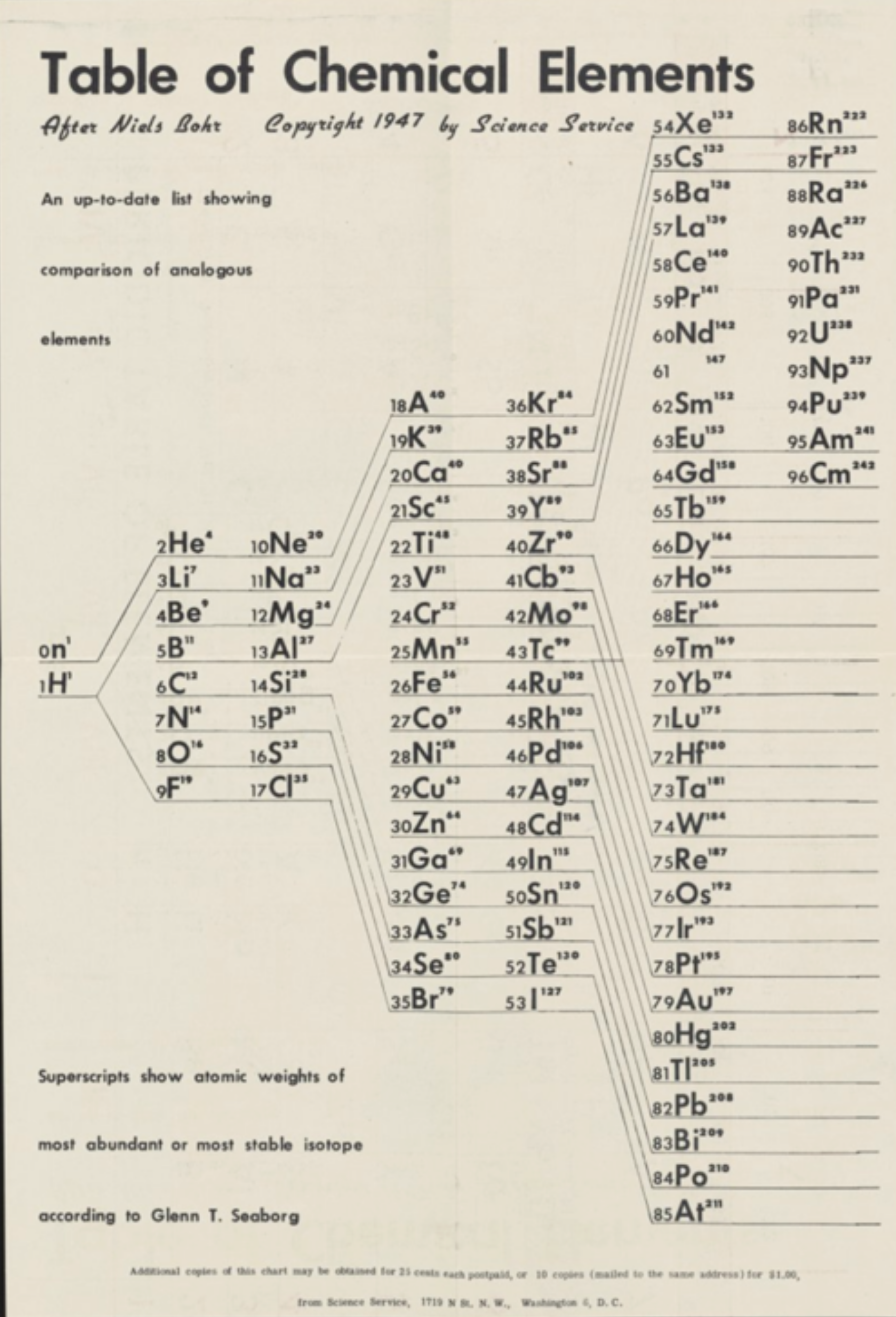
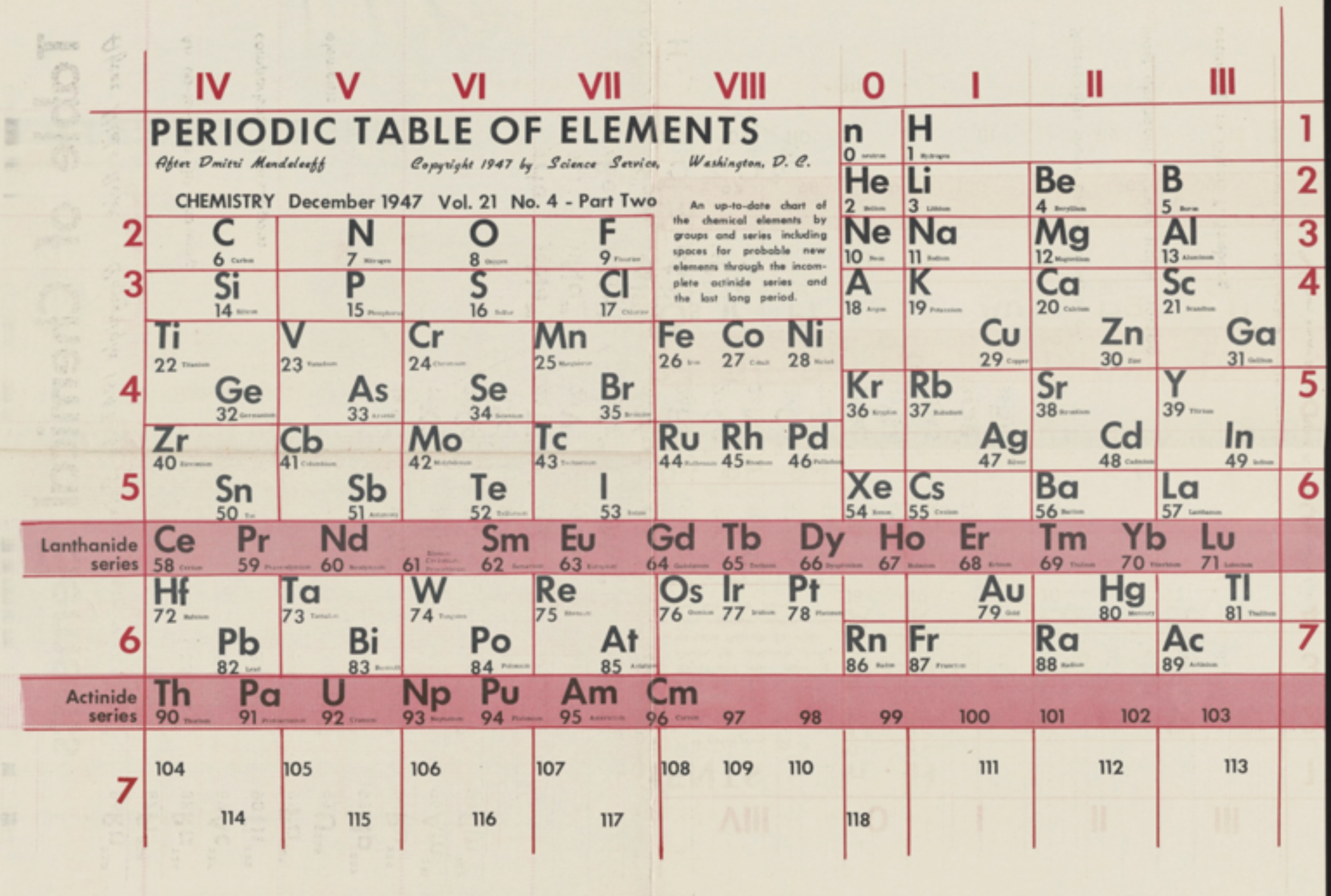
| Year: 1949 | PT id = 1052 |
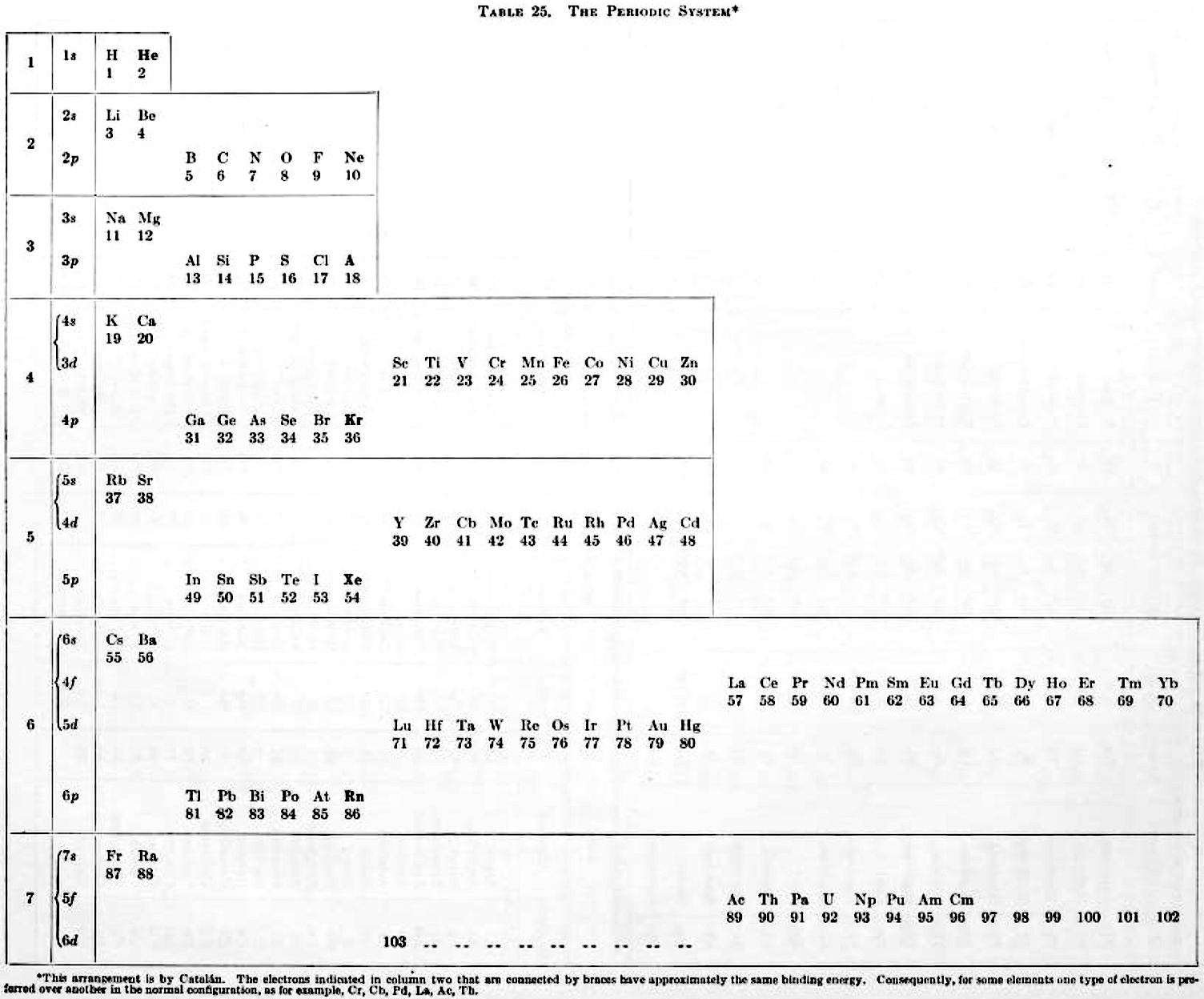
Catalán's Periodic System/Sistema Periodico Ampliado
Two versions of Catalán's Periodic System/Sistema Periodico Ampliado. The first from C.E. Moore 1949, Atomic Energy Levels, National Bureau of Standards, Circular no. 467, Washington DC, vol. 1, table 25 (1949) and the second as referenced here: http://www.miguelcatalan.net/pdfs/bibliografia/biblio09.pdf.
René Vernon, who provided the graphics, writes:
"I feel the footnote along the base of the first table could merit better attention being drawn to it. It says:
This arrangement is by Catalán. The electrons indicated in column two that are connected by braces have approximately the same binding energy. Consequently, for some elements one type of electron is preferred over another in the normal configuration, as for example, Cr, Cb, Pd, La, Ac, Th.
"The connecting braces hone in on the source of much of the controversy concerning notions of an ideal, optimal, better, this or that, or fundamental periodic table. I can't recall seeing a table with such a feature. For the second table, turning it on its side (attached) reminds of the ADOMAH [formulation].
Click on the images to enlarge:
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1949 | PT id = 1018 |
Scherer's Student Model of Spiral Periodic Chart
George A. Scherer, New Aids for Teaching the Periodic Law, School Science and Mathematics, vol. 49, no. 2 (1949).
René Vernon writes:
"This is a Left-Step periodic table with a split d-block, that can be rearranged into a cylinder. Students were expected to keep a copy of the two halves of the table in their note books, for reassembly as required. It was a clever way of introducing the 32-column form, and the transition from 2D to 3D (that faded into obscurity)":
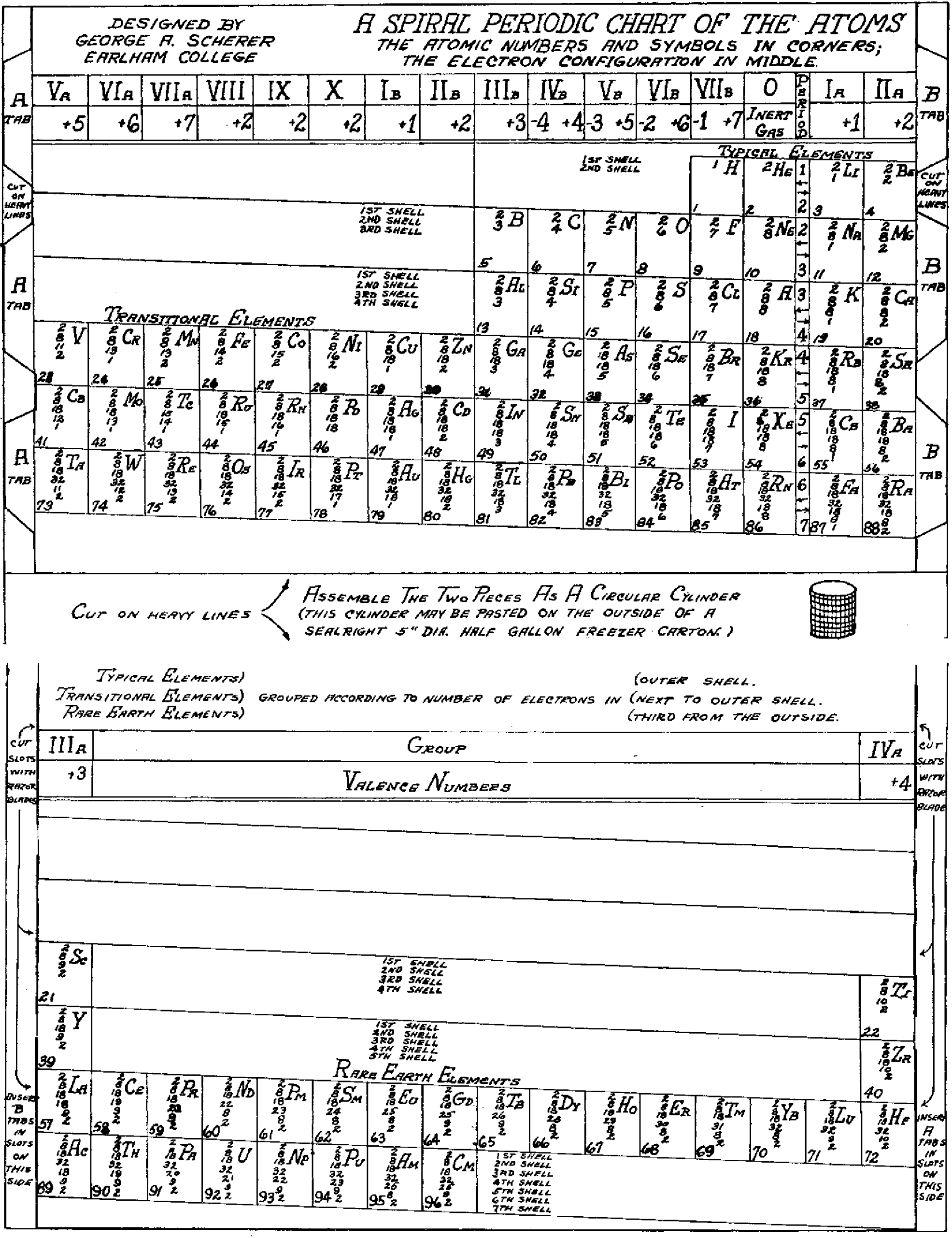
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1950 | PT id = 1119 |
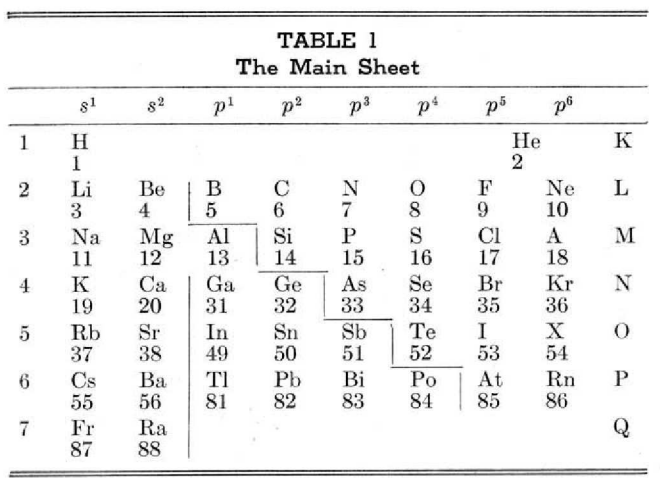
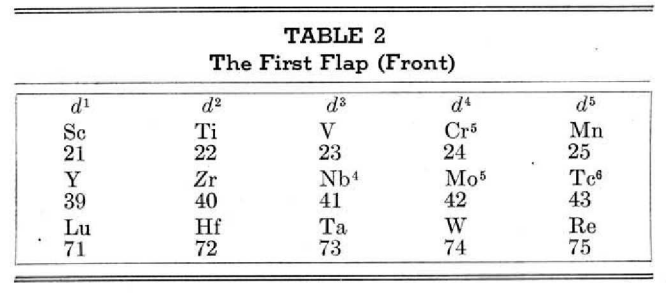
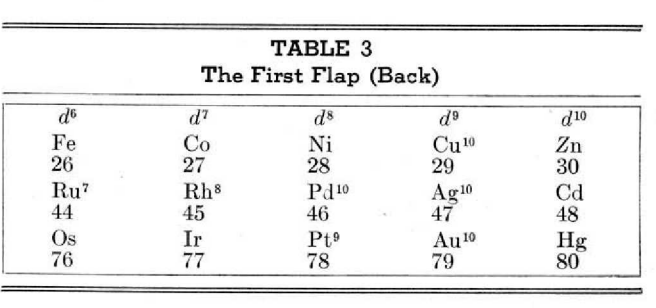
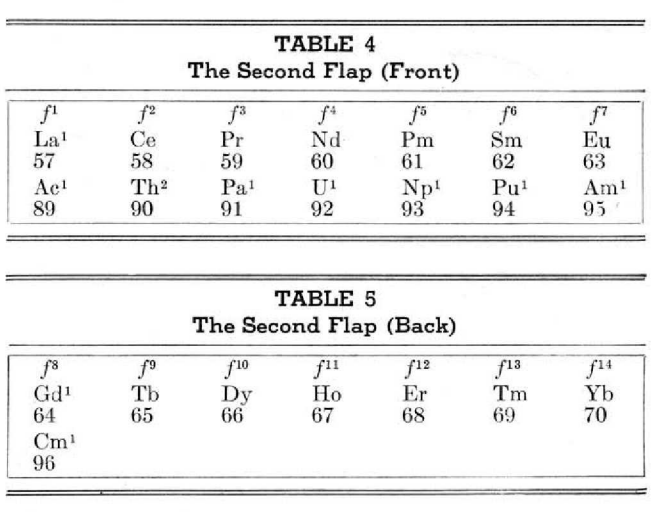
McCutchon's Simplified Periodic Classification of the Elements
McCutchon KB, A simplified periodic classification of the elements, Journal of Chemical Education, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 17–19 (1950)
This 3-dimensional table has two double-sided flaps attached. The top flap is the f bock. Under that is the d block.
The superscripts denote the number of d electrons an element has. Thus, La1 is shown as being an f1 element. But it has a 1 superscript, meaning that the f electron count is reduced by 1 and the d electron count is 1.
René Vernon writes:
"On group 3, McCutchon cryptically says: The proposed arrangement brings out certain known facts about the tertiary elements which are rarely shown by other arrangements. For example, it suggests, correctly, that the resemblance between yttrium and lutecium is greater than that between yttrium and lanthanum. It classifies lanthanum but not lutecium as a rare earth, in accordance with their chemical properties (which also contradict spectrographic evidence at this point). It also demonstrates the tetravalence of both cerium and thorium, and that thorium and protactinium show a resemblance in chemical properties to zirconium and niobium, as well as to hafnium and tantalum."
I say "cryptically" because McCutchon presents no further evidence in support of his assertion that the resemblance between Y and Lu is greater than between Y and La. He may have had in mind the fact that Lu is more often found in ores of Y than is the case for La... and I don't understand his reference to spectrographic evidence.
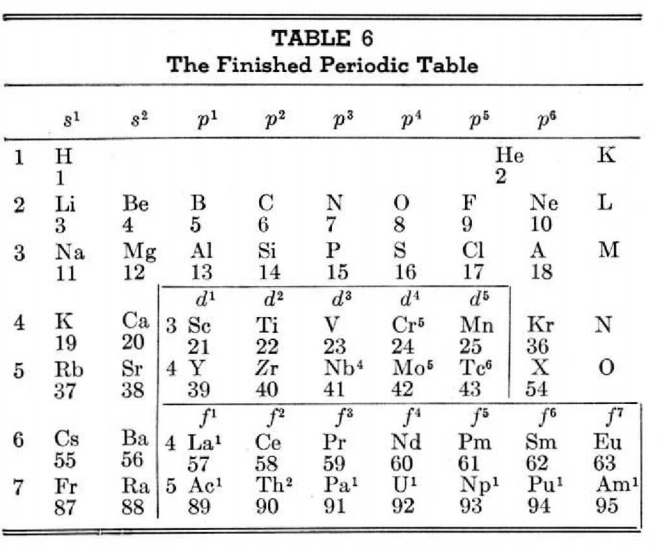
| Year: 1951 | PT id = 1245 |
Friend's Updated Periodic Table
René Vernon writes:
"This 1951 table succeeds Friend’s table of 1926. Notice how Pu, Am, and Cm have been assigned to group VIII. The splitting of the Ln across two periods is bizarre."
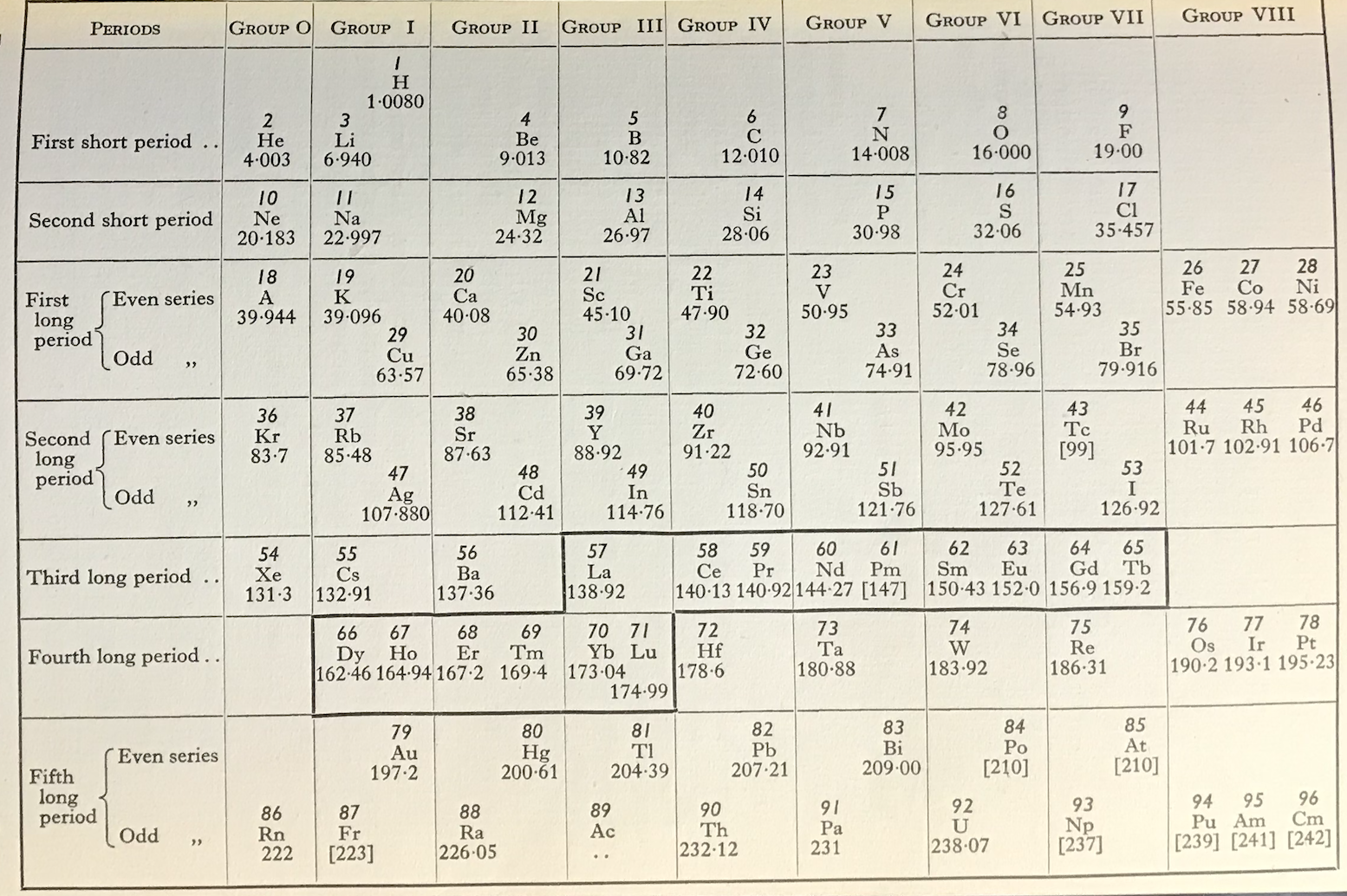
| Year: 1951 | PT id = 1272 |
Spedding's Rare Earths Periodic Table
Ref: Spedding FH 1951 The Rare Earths, Scientific American, vol. 185, no. 5, pp. 26–31
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1954 | PT id = 1255 |
Ephraim's Periodic Classification
Ephraim F 1954, Inorganic Chemistry, 6th ed., Oliver and Boyd, London (revised by PCL Thorne and ER Roberts)
René Vernon writes that items of interest include:
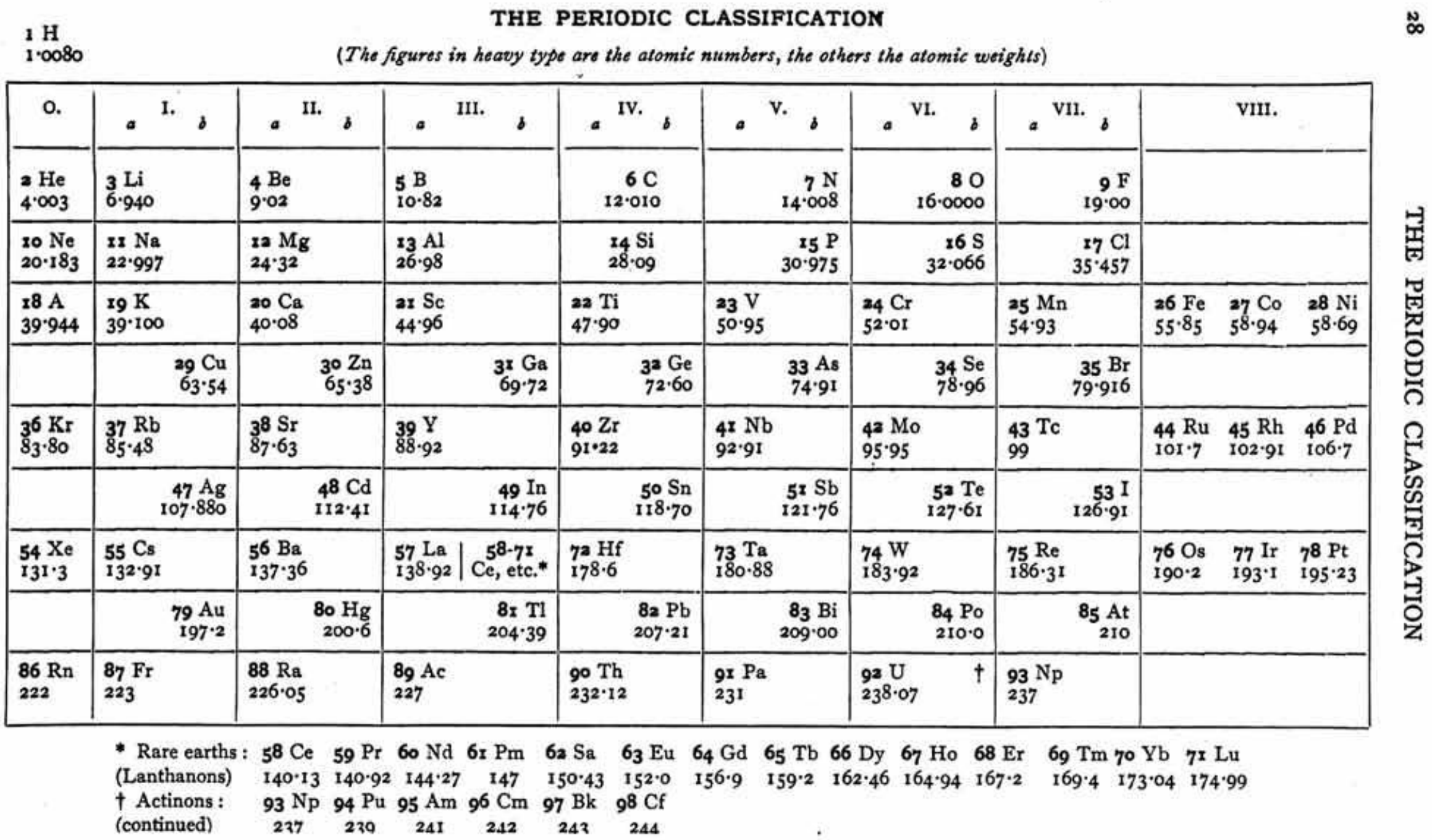
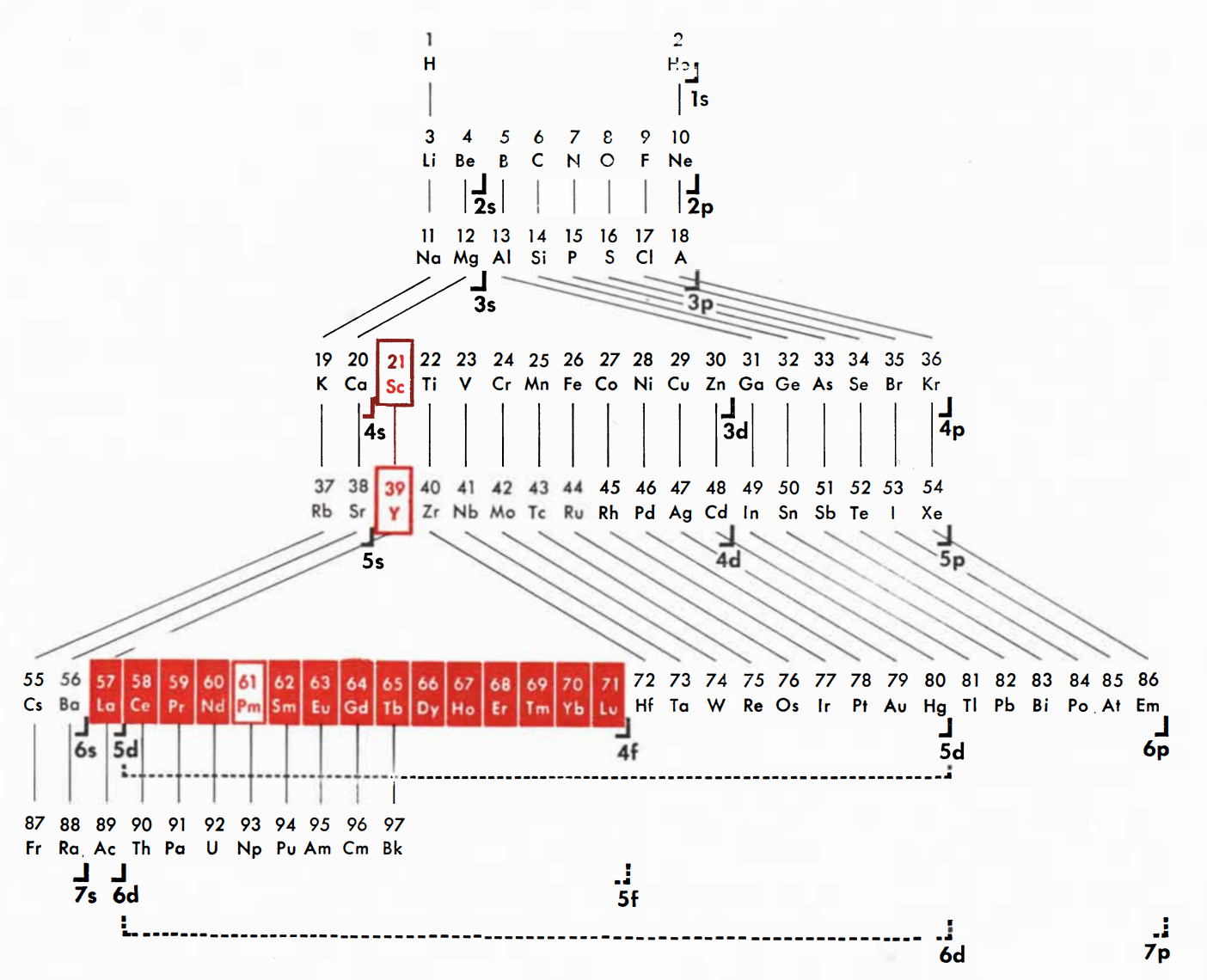
| Year: 1956 | PT id = 1009 |
Walker & Curthoys' New periodic Table Based of Stability of Atomic Orbitals
By W. R. Walker and G. C. Curthoys, A new periodic table based on the energy sequence of atomic orbitals, J. Chem. Educ., 1956, 33 (2), p 69.
The abstract states:
"Since the theory of atomic and molecular orbitals has proven to be of such value in interpreting the data of inorganic chemistry, it is hoped that a new periodic table based on the energy sequence of atomic orbitals will be an aid to the further systematizing of chemical knowledge."
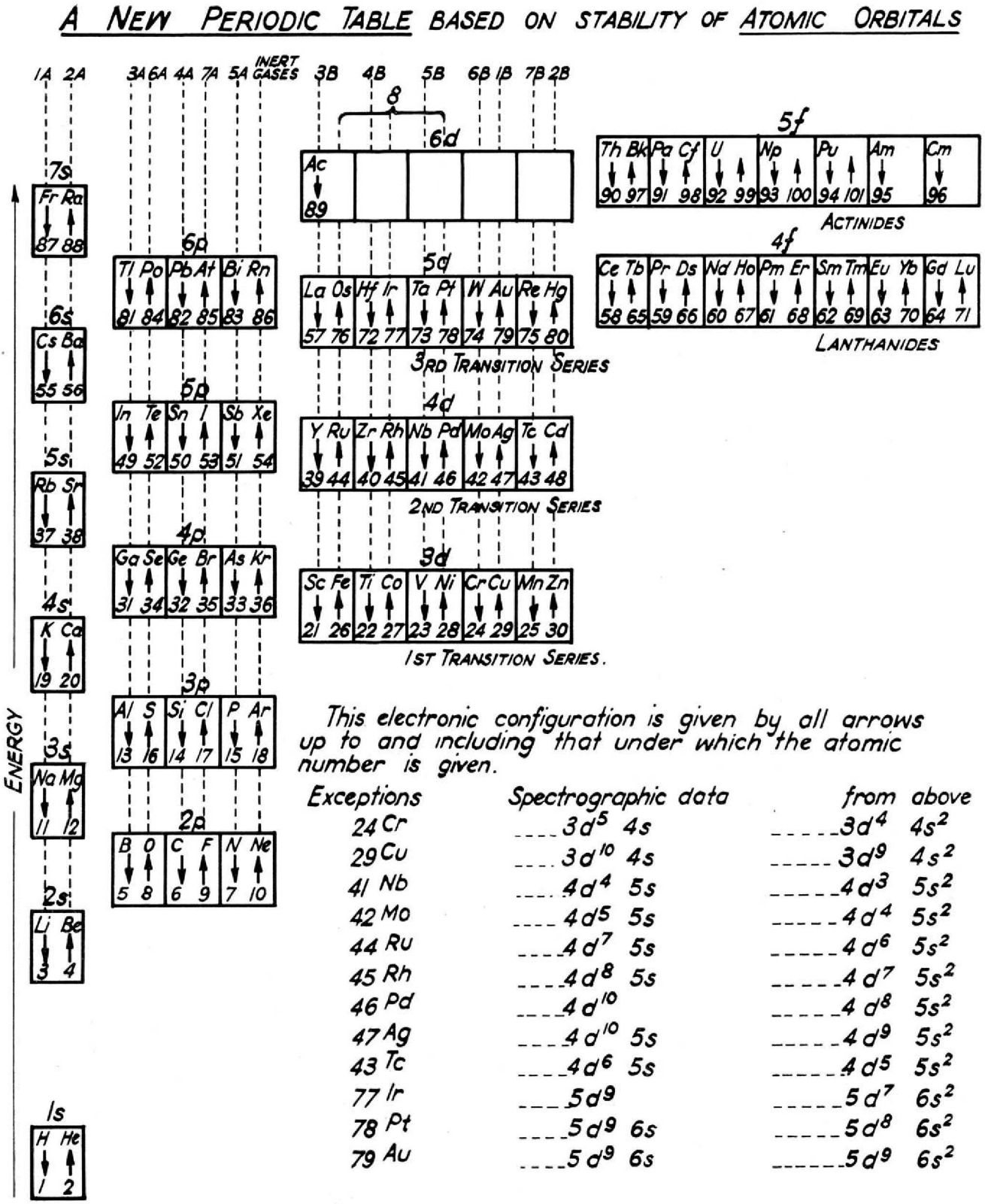
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1958 | PT id = 1148 |
Landau & Lifshitz's Periodic System of Mendeleev
L.D. Landau & E.M. Lifshitz, Quantum Mechanics (Volume 3 of A Course of Theoretical Physics), pages 255-258. (Note: First published in English in 1958, the link is to the 1963 3rd ed. of the English version translated from Russian.)
René Vernon writes:
The authors discuss aspects of the periodic system of D I Mendeleev. The electron configurations of hydrogen & helium are briefly noted. This is followed by three tables setting out the electron configurations of the s, p, d & f elements.
Some extracts from the text follow:
"The elucidation of the nature of the periodic variation of properties, observed in the series of elements when they are placed in order of increasing atomic number, requires an examination of the peculiarities in the successive completion of the electron shells of atoms." (p. 252)
"Many properties of atoms (including the chemical properties of elements...) depend principally on the outer regions of the electron envelopes." (p. 254)
"The elements containing complete d and f shells (or not containing these shells at all) are called elements of the principal groups; those in which the filling up of these states is actually in progress are called elements of the intermediate groups. These groups of elements are conveniently considered separately." (p. 254)
"We see that the occupation of different states occurs very regularly in the series of elements of the principal groups: first the s states and then the p states are occupied for each principal quantum number n. The electron configurations of the ions of these elements are also regular (until electrons from the d and f shells are removed in the ionisation): each ion has the configuration corresponding to the preceding atom. Thus, the Mg+ ion has the configuration of the sodium atom, and the Mg++ ion that of neon." (p. 255)
"Let us now turn to the elements of the intermediate groups. The filling up of the 3d, 4d, and 5d shells takes place in groups of elements called respectively the iron group, the palladium group and the platinum group. Table 4 gives those electron configurations and terms of the atoms in these groups that are known from experimental spectroscopic data. As is seen from this table, the d shells are filled up with considerably less regularity than the s and p shells in the atoms of elements of the principal groups. Here a characteristic feature is the 'competition' between the s and d states."
"This lack of regularity is observed in the terms of ions also: the electron configurations of the ions do not usually agree with those of the preceding atoms. For instance, the V+ ion has the configuration 3d4 (and not 3d24s2 like titanium) ; the Fe+ ion has 3d64s1 (instead of 3d54s2 as in manganese)."
"A similar situation occurs in the filling up of the 4f shell; this takes place in the series of elements known as the rare earths. † The filling up of the 4f shell also occurs in a slightly irregular manner characterised by the 'competition' between 4f, 5d and 6s states."
"† In books on chemistry, lutetium is also usually placed with the rare-earth elements. This, however, is incorrect, since the 4f shell is complete in lutetium; it must therefore be placed in the platinum group."
"The last group of intermediate elements begins with actinium. In this group the 6d and 5f shells are filled, similarly to what happens in the group of rare-earth elements." (p. 256–257)
The authors exclude lanthanum from the rare earths since the 4f shell has not started filling. Yet actinium and thorium are included by them with what we now call the actinoids even though these two metals have no f electrons. No explanation is provided for this puzzling lack of consistency with their categories.

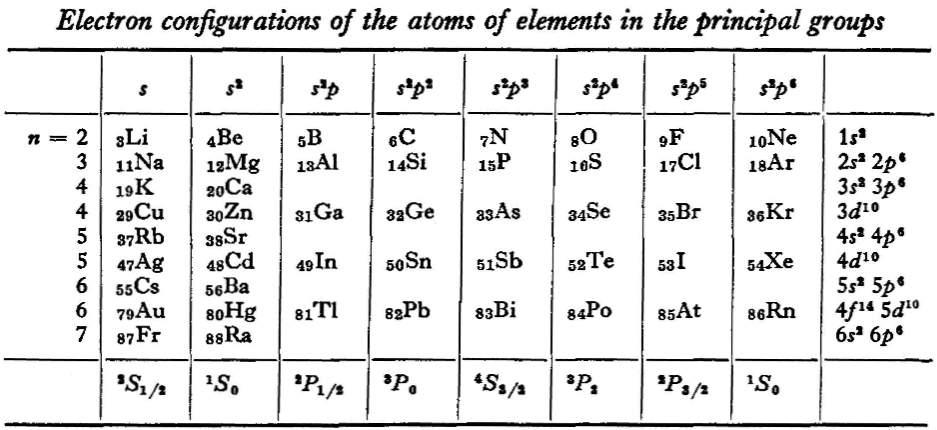
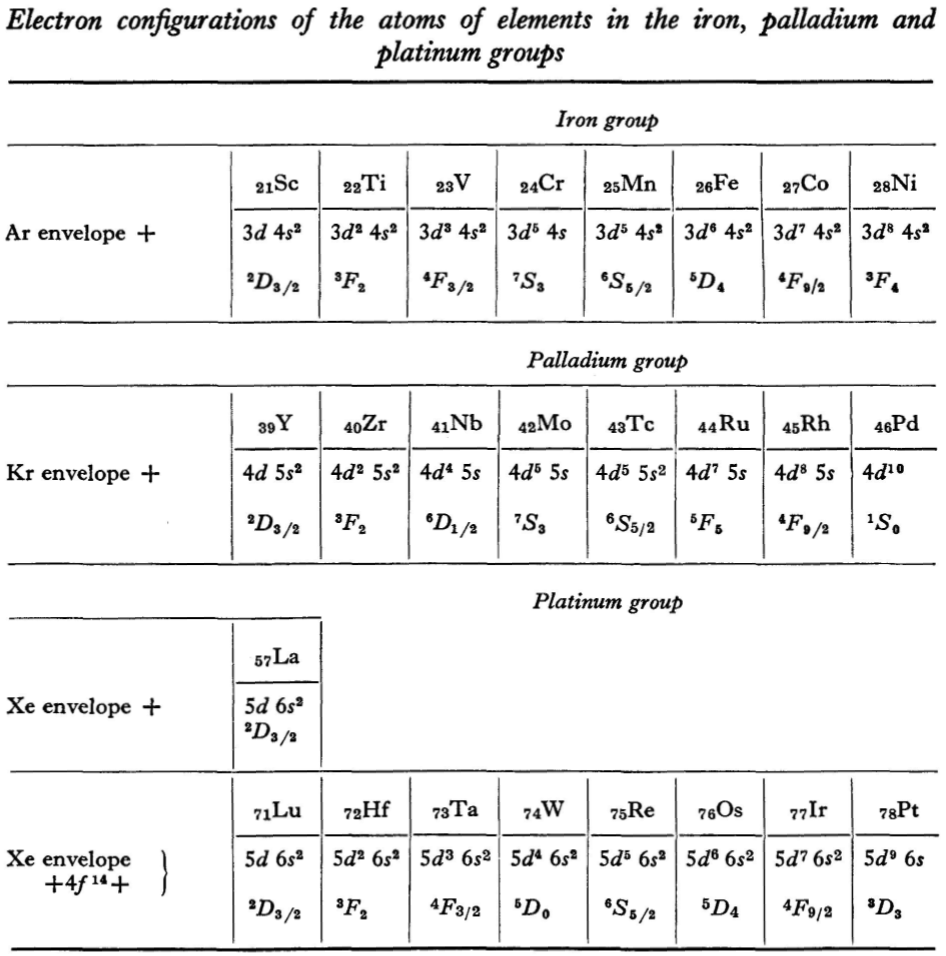
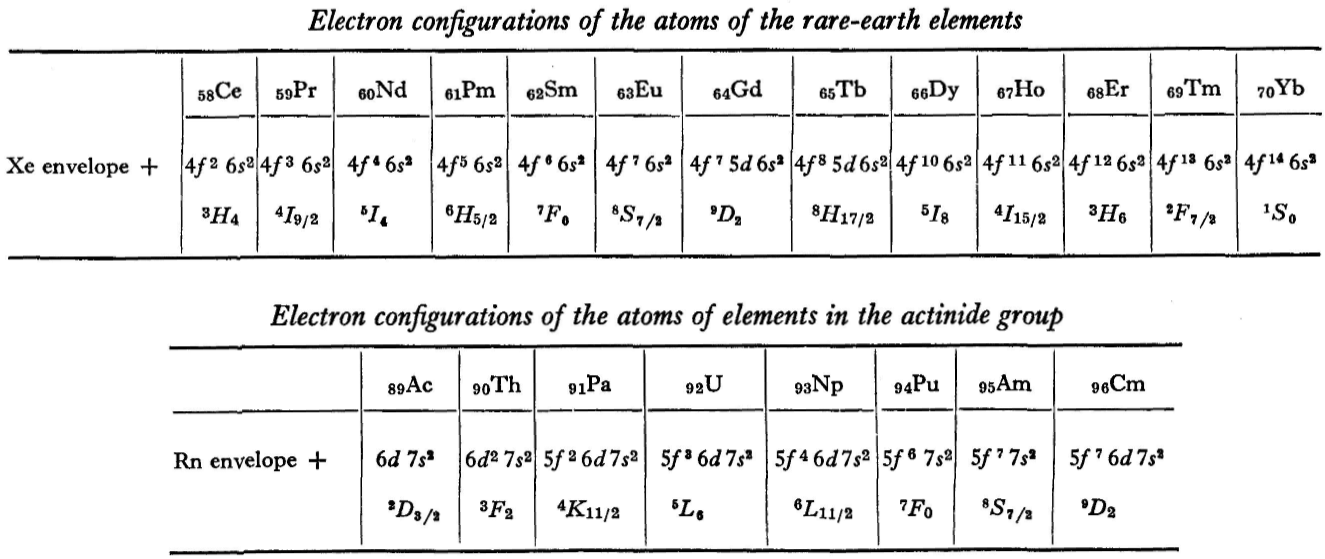
René Vernon writes: I have joined up their one note and three tables. (Curium was the last known element at their time of writing; transcurium elements are shown in parentheses.):
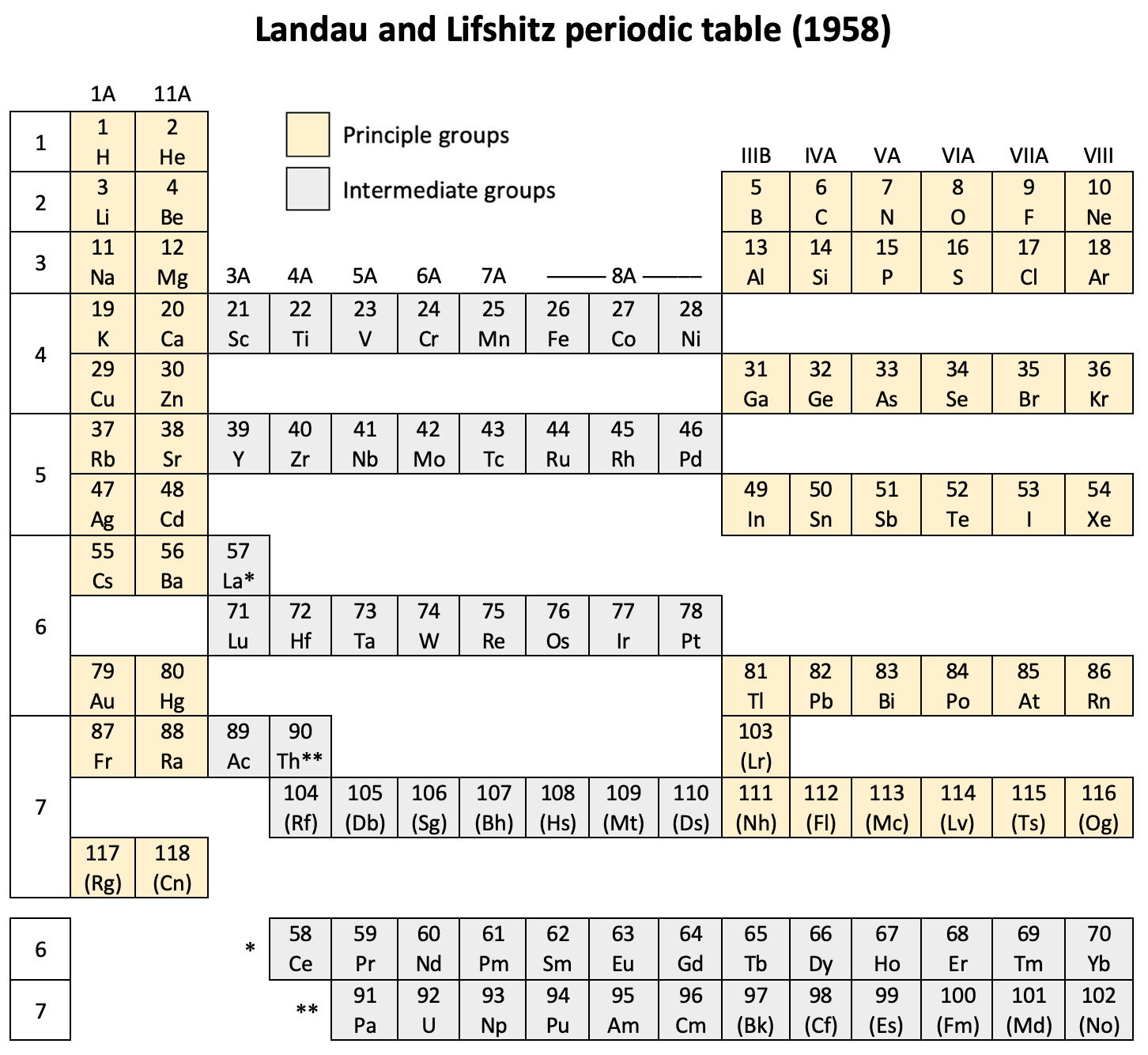
| Year: 1958 | PT id = 1263 |
Weaver & Foster's Laminar Chart of the Elements
Weaver EC & Foster LS 1960, Chemistry For Our Times. 3rd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, p. 382
René Vernon writes:
An earlier version of this table appeared in JChemEd in 1949. The authors then wrote:
"It is apparently difficult to give a proper idea of electronic configuration in two dimensions without spreading out vertically or horizontally, and thereby sacrificing the order of atomic number, or compactness, or both. In three dimensions it is entirely feasible, but the first reaction is to discard three dimensions as too awkward. The laminar chart here proposed seems to the authors to possess the advantages of both the two dimensional and three dimensional charts and to have none of their disadvantages.
"A minor feature of the table, introduced for reasons of expediency, is the artificial break between the first and the second main shell. Use is made of this space to print the traditional group headings, I A, III A, IVB, etc., which are firmly entrenched in the literature, and still find active use as classifying labels. Other objects in making the artificial break were to minimize the resemblance between hydrogen and the alkali metals and to emphasize helium's character as an inert gas (completed 1s subshell), rather than, as might otherwise be supposed, a member of the alkaline earth family.
"CONTOUR LAMINAR TABLE
"By another modification, constructing the Periodic Chart in the form of contour laminae, it is possible to represent actual energy levels without the necessity of referring to auxiliary tables. This is done by proportioning the rises between each subshell to correspond to the Pauling energy diagram. Thus, although the subshells having the same principal quantum number will be on the same contour lamina, they will not be on the same planar level. The recognition of these contour laminae is facilitated by the use of a different color for each one. A table of this type will then be more physically correct than the previous laminar models, and it is a question as to which form has the most practical utility.
"We believe that the laminar periodic tables, in either the original or a modified form, will greatly facilitate systematic teaching of the properties of the chemical elements. Students indoctrinated with the new system cannot fail to obtain a clearer and more lasting conception of the fundamental principles of inorganic chemistry."
Note the 4f and 5f series have been split into dyads of seven apiece. This is consistent with Shchukarev (1974, p. 118) who wrote that the filling sequence among the 4f metals is periodic, with two periods. Thus, after the occurrence of a half-full 4f subshell at europium and gadolinium, the filling sequence repeats with the occurrence of a full subshell at ytterbium and lutetium (Rokhlin 2003, pp. 4–5). A similar, but weaker, periodicity (Wiberg 2001, pp. 1643–1645) is seen in the actinoids, with a half-full 5f subshell at americium and curium, and a full subshell at nobelium and lawrencium.
Note that Zn, Cd, Lu and Hg have no electron numbers above them since the underlying shells were filled at Cu, Cd, Yb, and Au respectively.
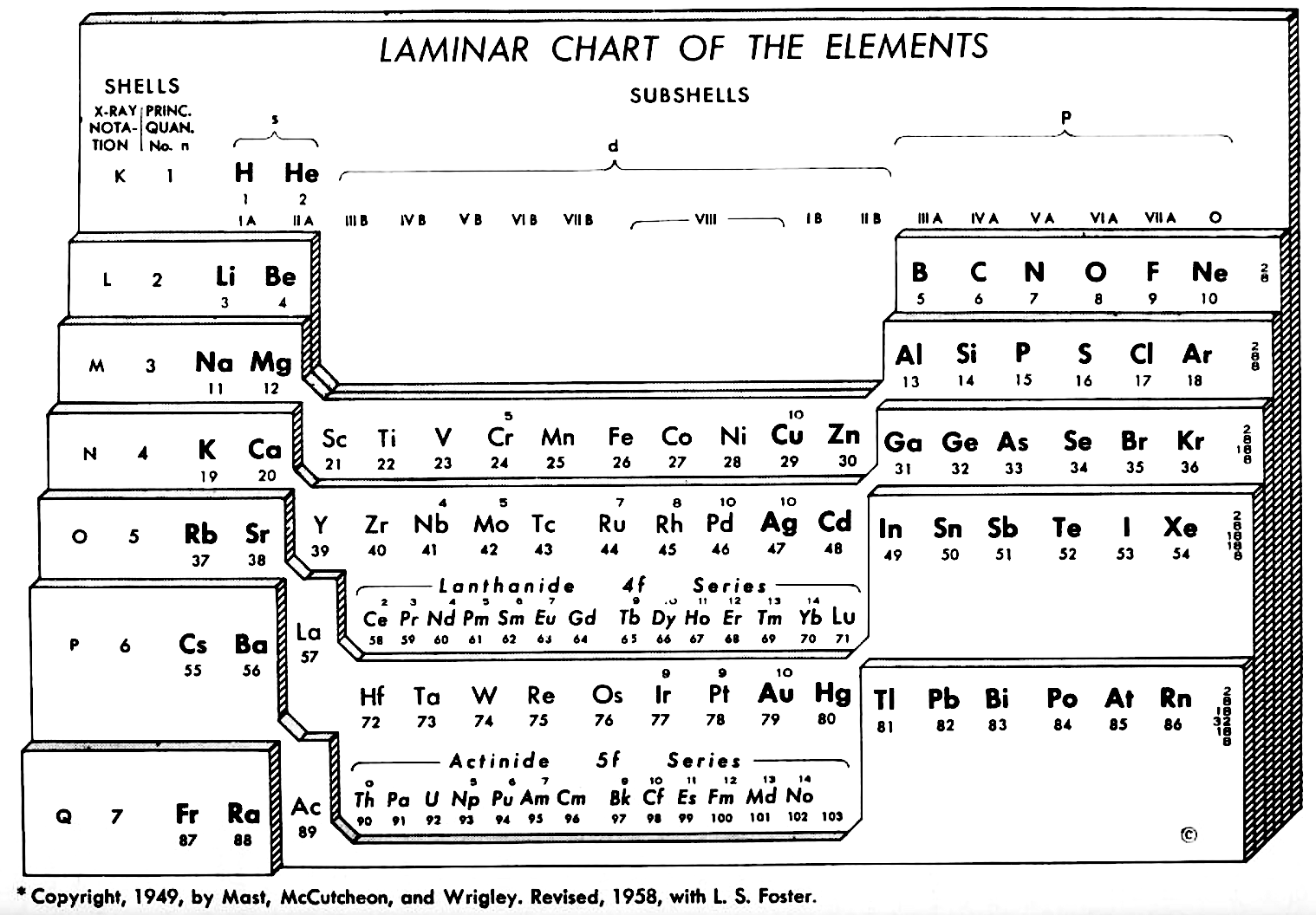
| Year: 1960 | PT id = 1012 |
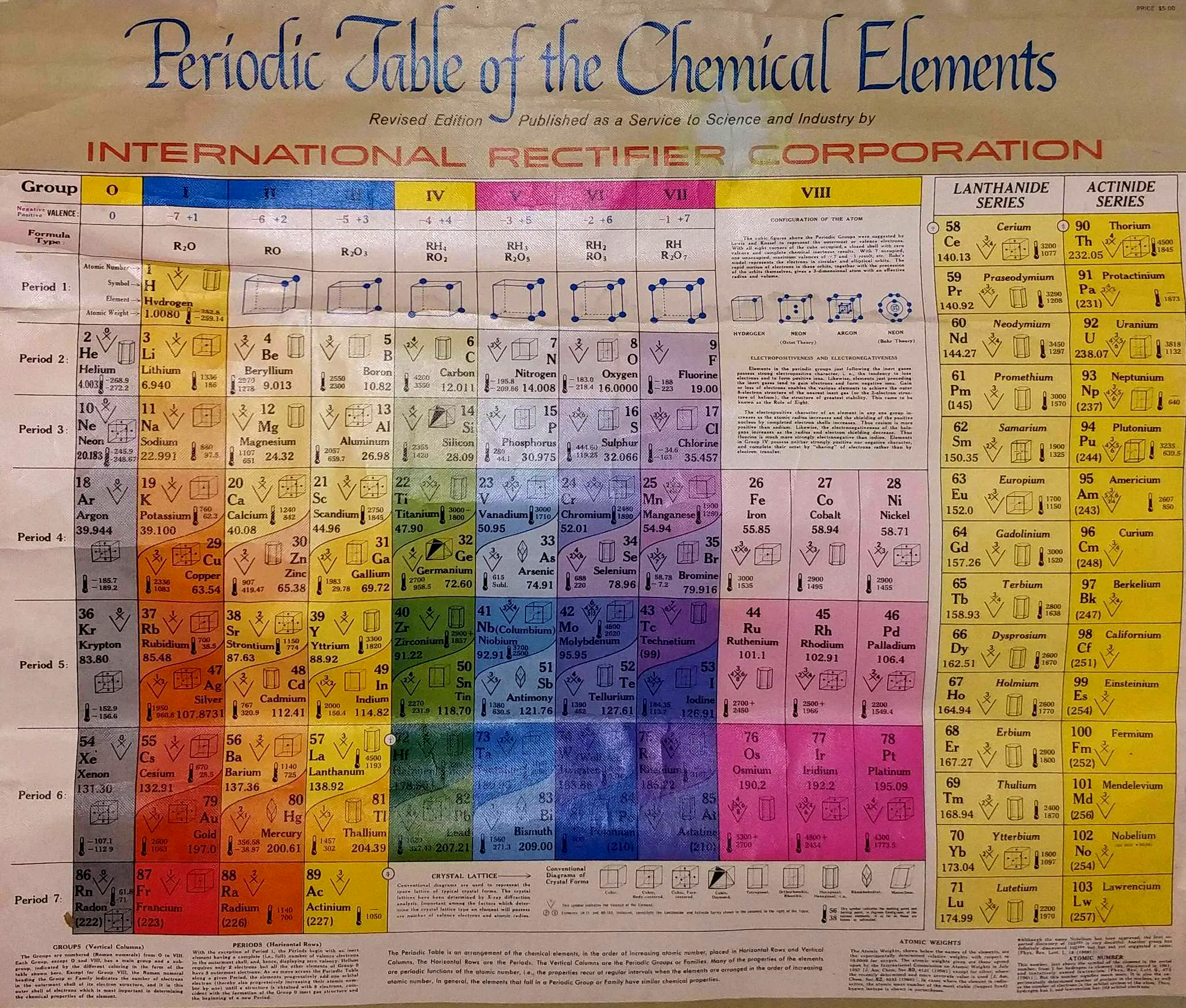
International Rectifier Corporation Periodic Table
International Rectifier Corporation was an American power management technology company manufacturing analog and mixed-signal ICs, advanced circuit devices, integrated power systems, and high-performance integrated components for computing. It is now part of Infineon Technologies.
The periodic table below was produced in the late 1950s to early 1960s. The earliest version we can find on the web dates from 1960.
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1962 | PT id = 1177 |
Scott & Kendal Periodic Table
René Vernon shows an extract from Scott E.C. & Kendal F.A., The Nature of Atoms & Molecules: A General Chemistry. Harper & Row, New York, 1962 pp 385, categorising the metals.
Rather than providing a holistic treatment of the nonmetals, the authors take a group-by-group approach.
Items of interest: Al over Sc; the split between groups 3 and 3; and the inclusion of Pt with the soft metals.
On the right is my add-on for the nonmetals, plus extracts from the literature speaking to the analogies between the four metal and four nonmetal categories.
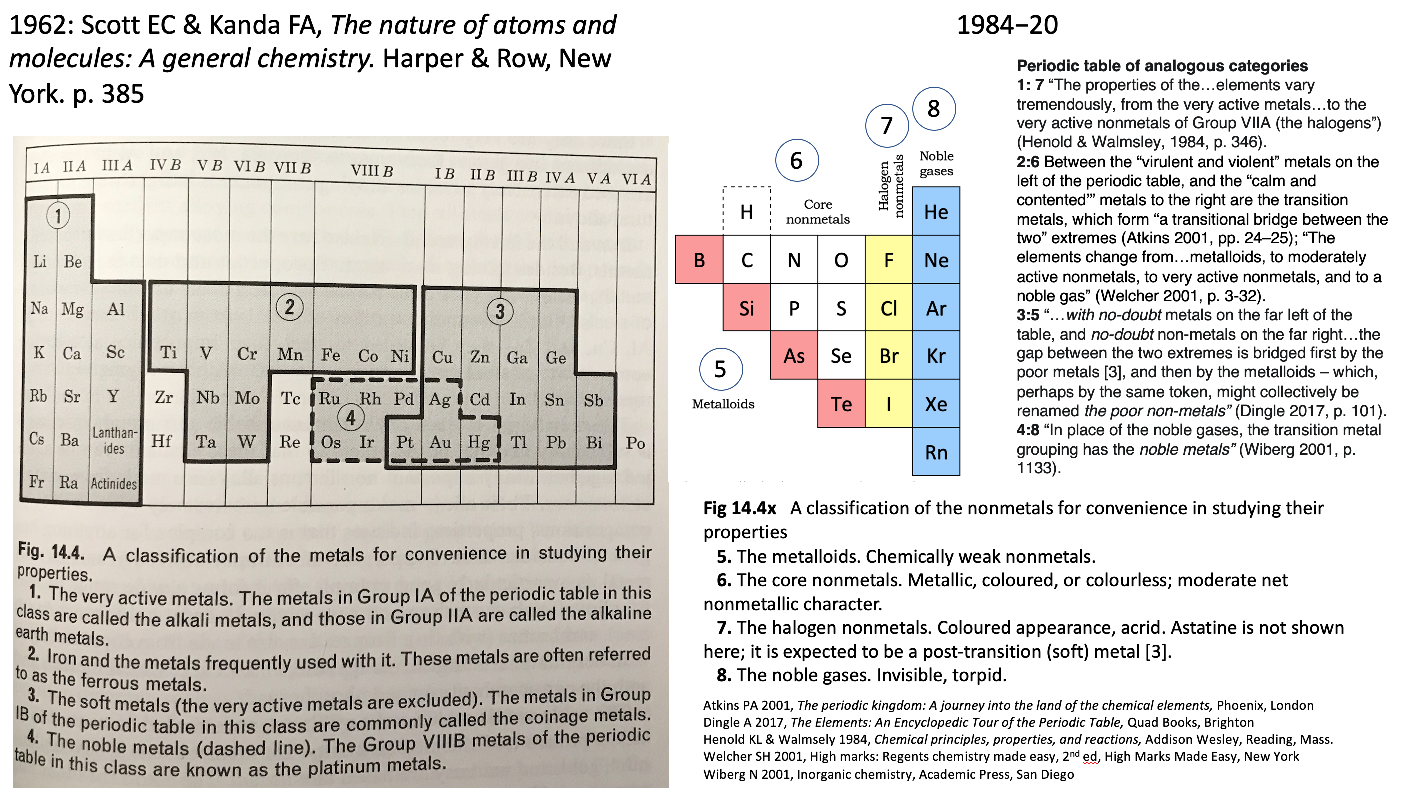
| Year: 1963 | PT id = 1249 |
Hutton's Periodic Table of The Elements
Hutton, K 1963, Chemistry: The Conquest of Materials, Penguin Books. Harmondsworth, Middlesex, pp. 38–39
René Vernon writes:
"Hutton shows:
Hutton refers to group 6A (Cr, Mo, W) as the "steel hardening" elements".
| Year: 1964 | PT id = 1006 |
Haward's Periodic Table
Roger Hayward created this periodic table for the book: Pauling & Hayward, p4, The Architecture of Molecules, W H Freeman and Company, San Francisco (1964).
From The Pauling Blog:
"By the end of the 1950s, Roger Hayward had retired from his professional work as an architect at the same time that his career as an illustrator was reaching its peak. Hayward signed a contract in the early 1960s that helped to solidify his position as a technical artist. The contract that Hayward signed was with W.H. Freeman & Company, a San Francisco-based publishing house that rose out of relative obscurity primarily by publishing Linus Pauling's hugely popular textbook, General Chemistry."
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1964 | PT id = 1271 |
Ternström's Periodic Table
Ref: A Periodic Table, Torolf Ternström, J. Chem. Educ. 1964, 41, 4, 190
René Vernon writes:
"Ternström gives us a triple-combo table drawing on the advantages of:
The outcome resembles the left step form of Janet (1928).
Some interesting features of Ternström's formulation are:
| Year: 1966 | PT id = 1265 |
Rare Earth Pop Out Periodic Table
From Rare Earths, The Fraternal Elements by Karl A. Gschneidner Jr., United States Atomic Energy Commission Division of Technical Information Library of Congress Catalog Card Number: 65-60546 1964; 1966 (Rev.)
There is an interesting point made in the text concerning the term "Rare Earths":
"The name rare earths is actually a misnomer for these elements are neither rare nor earths. They are metals, and they are quite abundant. Cerium, which is the most abundant, ranks 28th in the abundances of the naturally occurring elements and is more plentiful than beryllium, cobalt, germanium, lead, tin, or uranium. The least abundant naturally occurring rare earth, thulium, is more plentiful than cadmium, gold, iodine, mercury, platinum, or silver. Indeed, 25% of the elements are scarcer than thulium."
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1969 | PT id = 1146 |
Mendeleevian Conference, Periodicity and Symmetries in the Elementary Structure of Matter
Atti del Convegno mendeleeviano : periodicità e simmetrie nella struttura elementare della materia : Torino-Roma, 15-21 settembre 1969 / [editor M. Verde] Torino : Accademia delle Scienze di Torino ; Roma : Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei, 1971 VIII, 460 p.
Google Translate: Proceedings of the Mendeleevian Conference: periodicity and symmetries in the elementary structure of matter: Turin-Rome, 15-21 September 1969 / [editor M. Verde] Turin: Turin Academy of Sciences; Rome: National Academy of the Lincei, 1971 VIII, 460 p.
From the Internet Archive, the scanned book. Papers are in Italian & English.
For the 100th Anniversary of Mendeleev's iconic periodic table, a conference was held to look at (review) the elementary structure of matter. The 1960s saw huge developments in particle physics, including the theory of quarks. Papers were presented by many notable scientists including John Archibald Wheeler and the Nobel laureates: Emilio Segrè & Murray Gell-Mann.Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1969 | PT id = 1010 |
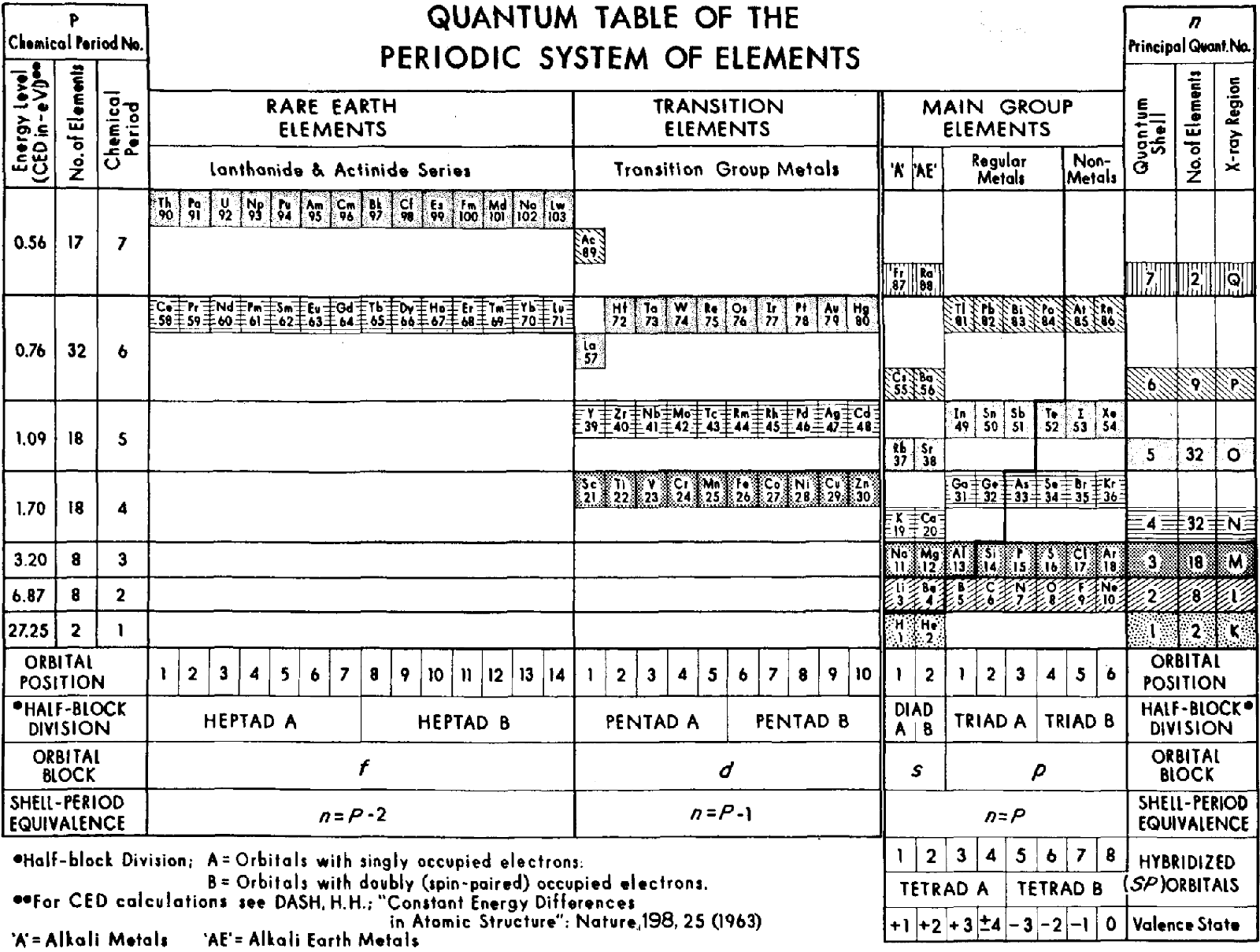
Dash's Quantum Table of the Periodic System of Elements
Harriman H. Dash, A quantum table of the periodic system of elements, International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, vol. 3, no. S3A, supplement: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Atomic, Molecular, and Solid?state Theory and Quantum Biology, 13/18 January 1969, pp. 335–340.
The abstract reads:
"The shortcomings of the long form of the periodic table of the chemical elements and the evident need for updating this format are briefly reviewed. To the question 'what format?' quantum physics provides an unequivocal answer. The foundations for the design of a quantum table are outlined. These are based on the principal quantum number as derived from the Schroedinger wave equation, the law of second order constant energy differences, and the coulomb–momentum interaction. These concepts are all combined into a single format which optimally and explicitly relates periodicity to atomic structure and the physical, chemical, and biological properties of the elements. This relationship emphasizes the unity and universality of all sciences."
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1969 | PT id = 1270 |
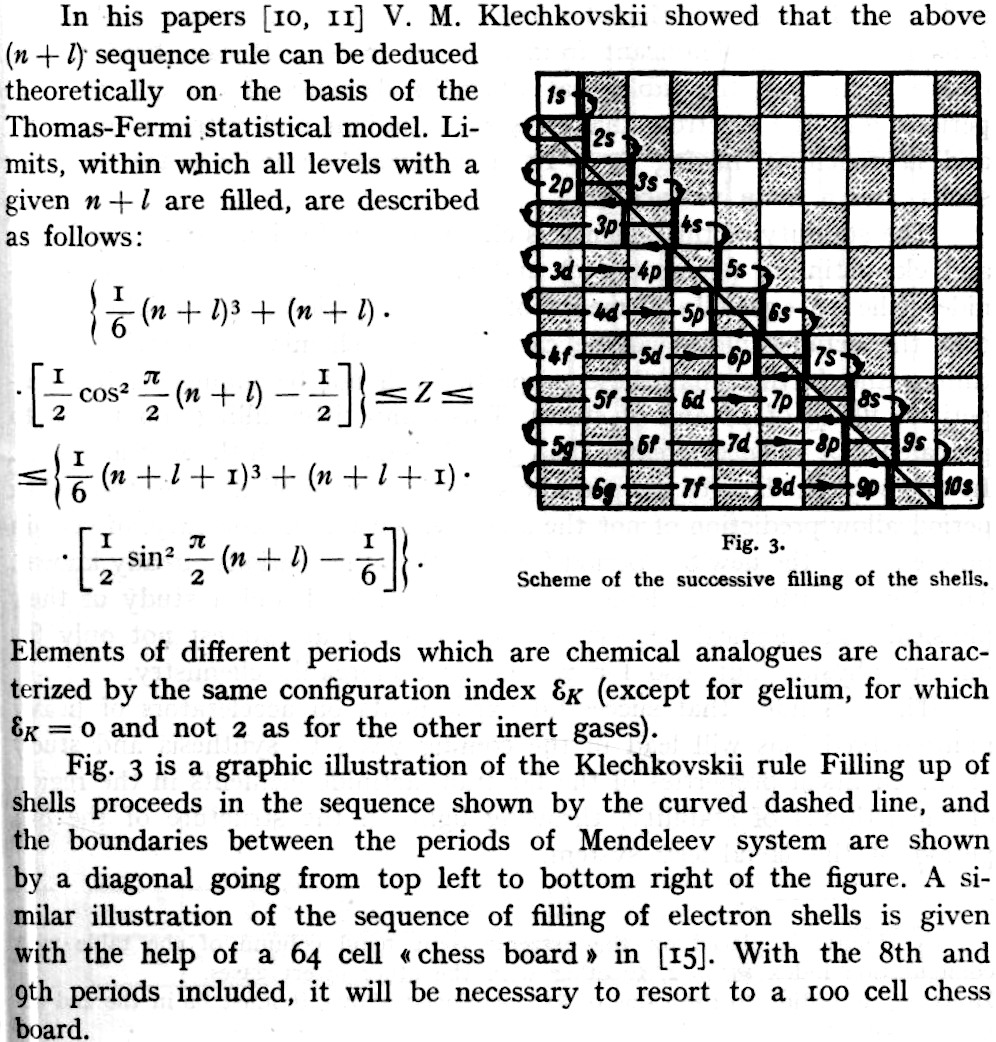
Seel-Klechkovskii Version of Madelung's Rule for Orbital Filling
Seel F., Bild der Wissenschaft, 6, 44 (1969), a monthly popular scientific journal.
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1969 | PT id = 1273 |
Martin's Crystal Structure Periodic Table
Ref: Martin JW 1969, Elementary Science of Metals, Wykeham Publications, London
René Vernon writes:
Note the unusual placement of La-Ac in two places, under Y and before Ce-Th. On another aspect, Martin writes:
"The non-metals, which occupy the top right-hand corner of the Periodic Table... form about one-sixth of all elements, and they are characterized by having melting-points and boiling points below about 500°C, and by having their solid and liquid phases not conducting electricity. About two-thirds of all elements are metals, and a further one sixth have properties intermediate between those of metals and non-metals."
His approach to the question of which elements are metals and non-metals, and which are intermediate may be the most useful "rough-and-ready" rubric I've seen. It is remarkable for its use of four criteria.
Perhaps we can then parse the elements as follows
Non-metals (16) = 15.5%
Fluids: H, N, O, F, Cl, Br; He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn 2
Solids: P, S, Se*, IIntermediate (16) = 15.5%
Metalloids: B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te
Near metalloids: C, At 3
Sub-metalloids: Al, Ga, In, Tl; Sn, Pb; Bi; PoMetals (71) = 68.9%
Be,^ Zn^
All the rest^ Borderline intermediate
Dingle (2017, The Elements: An Encyclopedic Tour of the Periodic Table, Quad Books, Brighton, p. 101) puts the situation this way:
"...the gap between the two extremes [of metals and nonmetals] is bridged... by the poor metals, and... the metalloids – which, perhaps by the same token, might collectively be renamed the poor non-metals.”
Redrawn by Vernon:
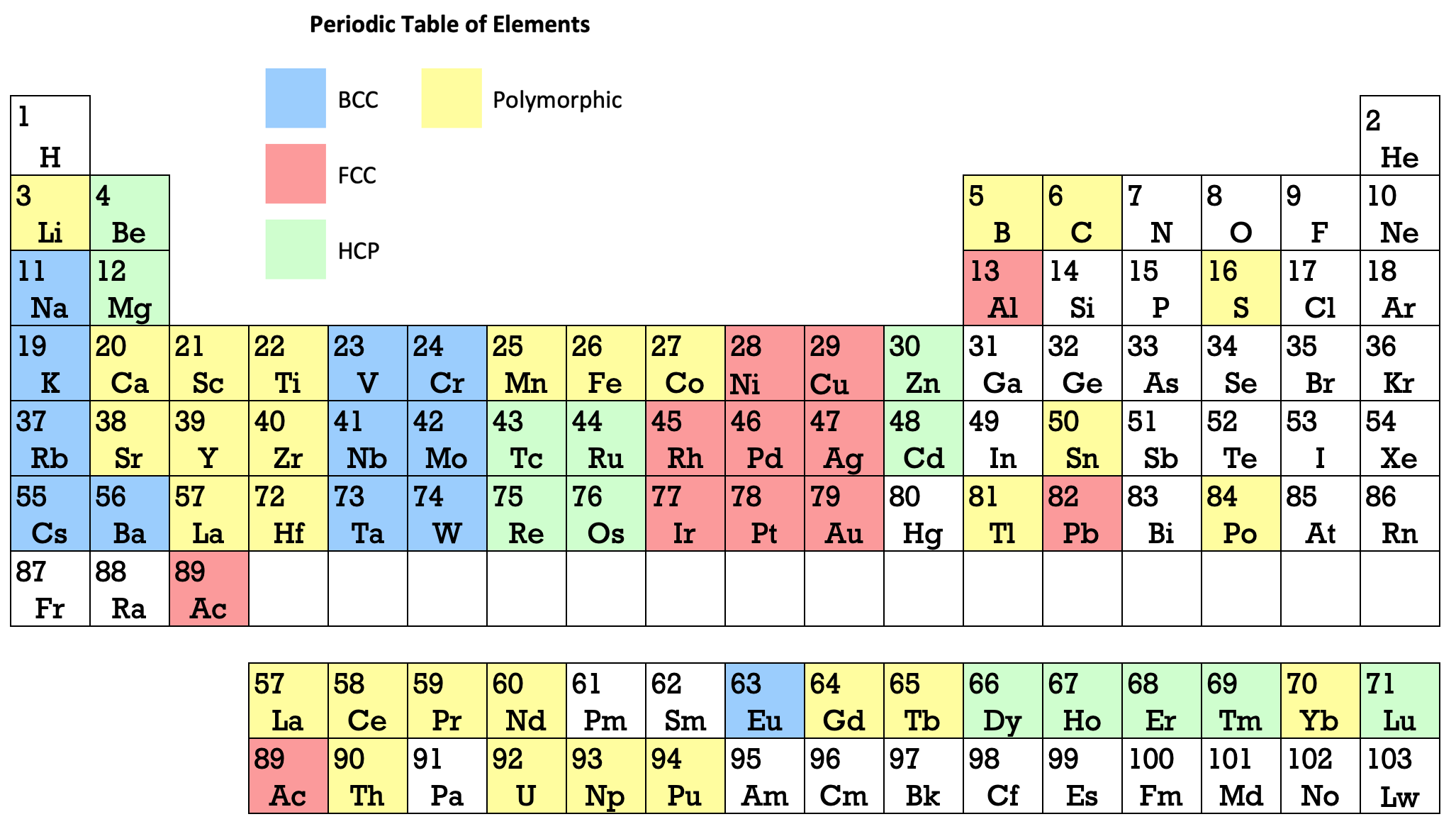
Thanks to René for the tip!
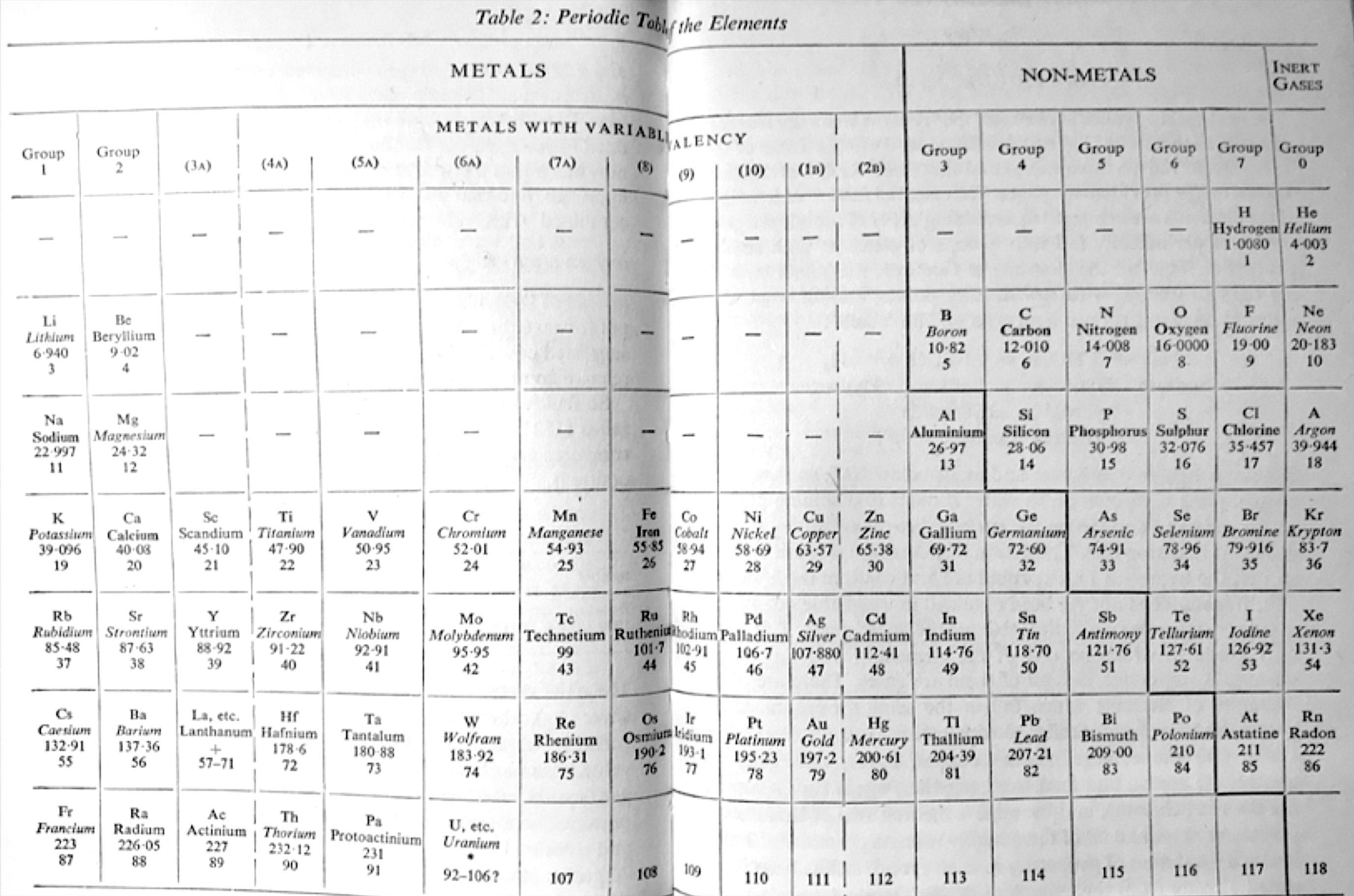
| Year: 1970 | PT id = 1007 |
Pauling's "General Chemistry" Periodic Table
From Linus Pauling's General Chemistry (3rd Ed.). Notice that the noble gases apear twice, at the beginning and the end of each period.
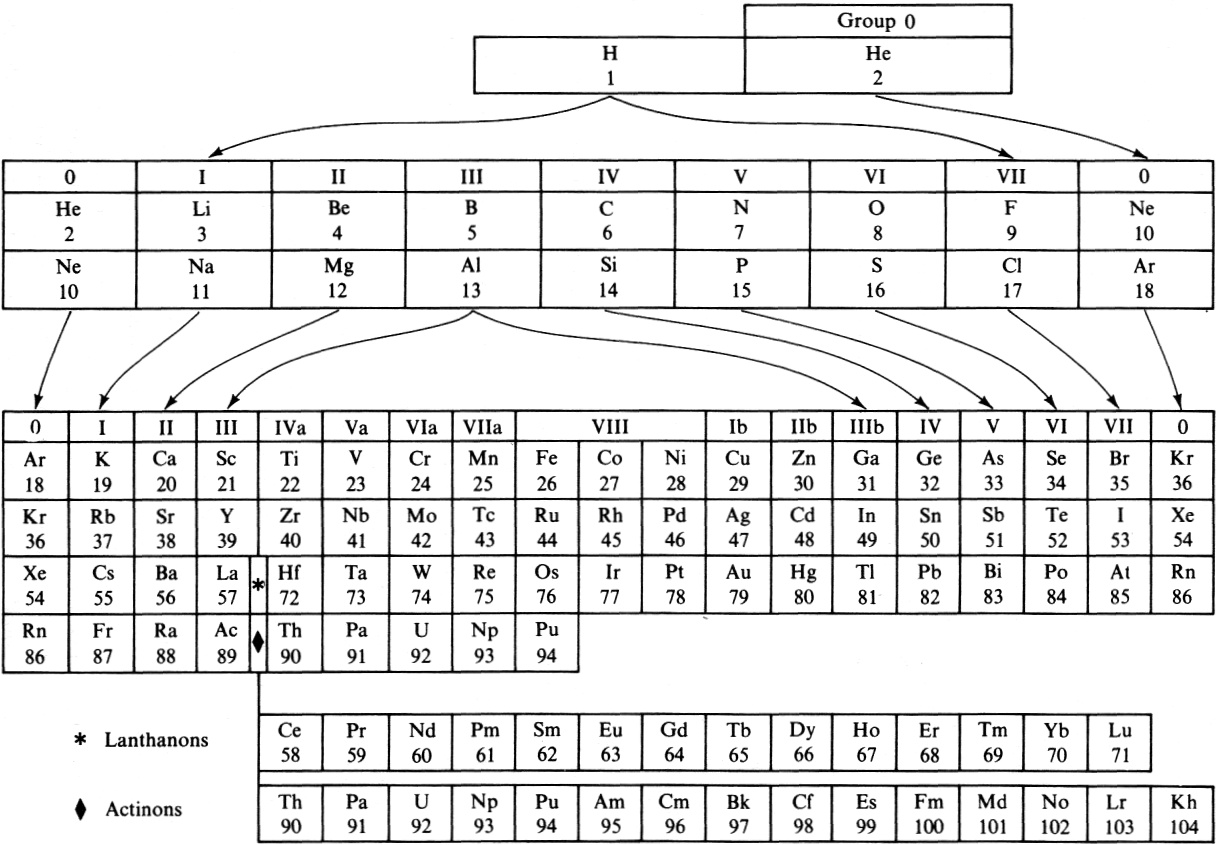
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1982 | PT id = 49 |
Cement Chemist's Periodic Cube
Periodic table designed in the style of a cube by J. Francis Young, Professor of Civil and Ceramic Engineering, University of Illinois. This table was published by Instruments for Research and Industry and includes instructions for assembly into a 3-D model.
More information, including high resolution files, at the Science History Institute.
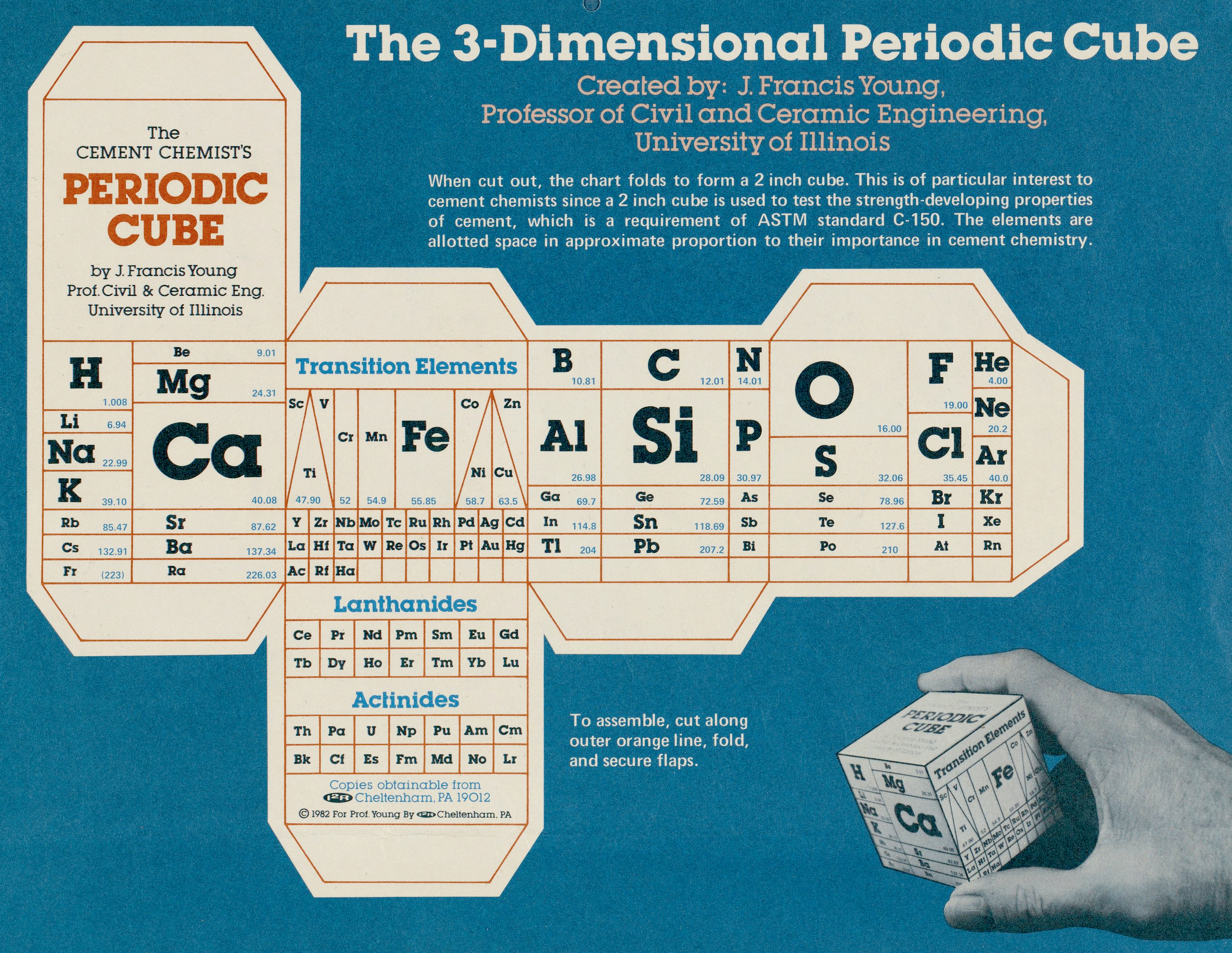
Thanks to René Vernon for the tip!
| Year: 1983 | PT id = 50 |
Periodic Pyramid
Periodic table designed in the style of a pyramid by Charles E. Gragg. This table was published by Instruments for Research and Industry and includes instructions for assembly into a 3-D model.
More information, including high resolution files, at the Science History Institute.

Thanks to René Vernon for the tip!
| Year: 1984 | PT id = 1258 |
Cherkesov: Two Periodic Tables
Cherkesov AI 1984, Ionization energy of 1-6 p-electrons and formation enthalpies of lutetium and lawrencium halides. Position of these elements in Periodic system, Radiokhimiya, vol. 26, no. 1, p. 53?60 (in Russian), https://inis.iaea.org/search/search.aspx?orig_q=RN:16012913
René Vernon writes:
"Two Russian offerings, the first is Mendeleev style, including He over Be and the integration of the Ln and An into the main body of the table.
"The second is the first time I have seen a genuine right step table, albeit at the expense of the numbers going backwards, and the non-intuitive group numbering scheme. Bonus marks for out-of-the box thinking."
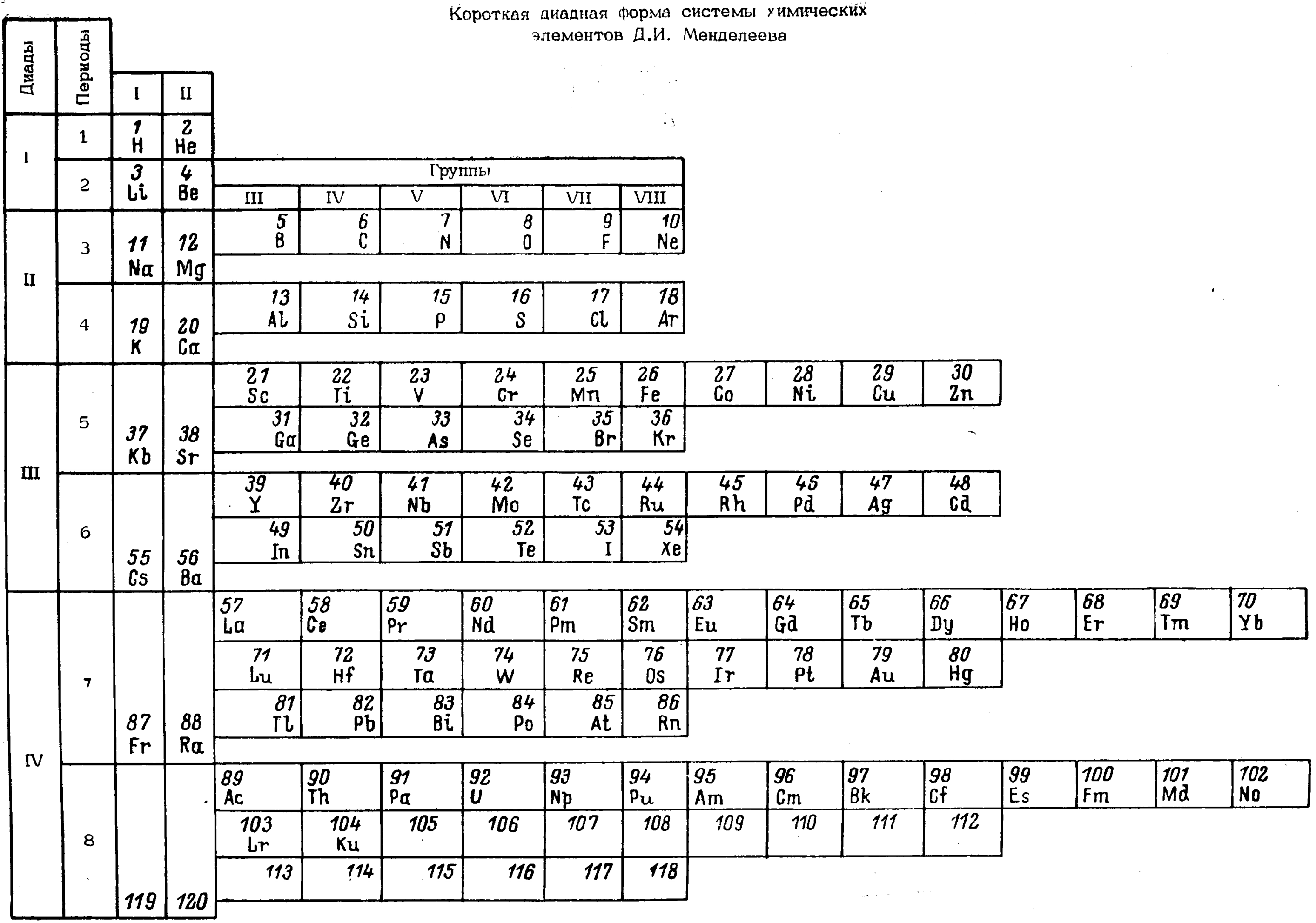
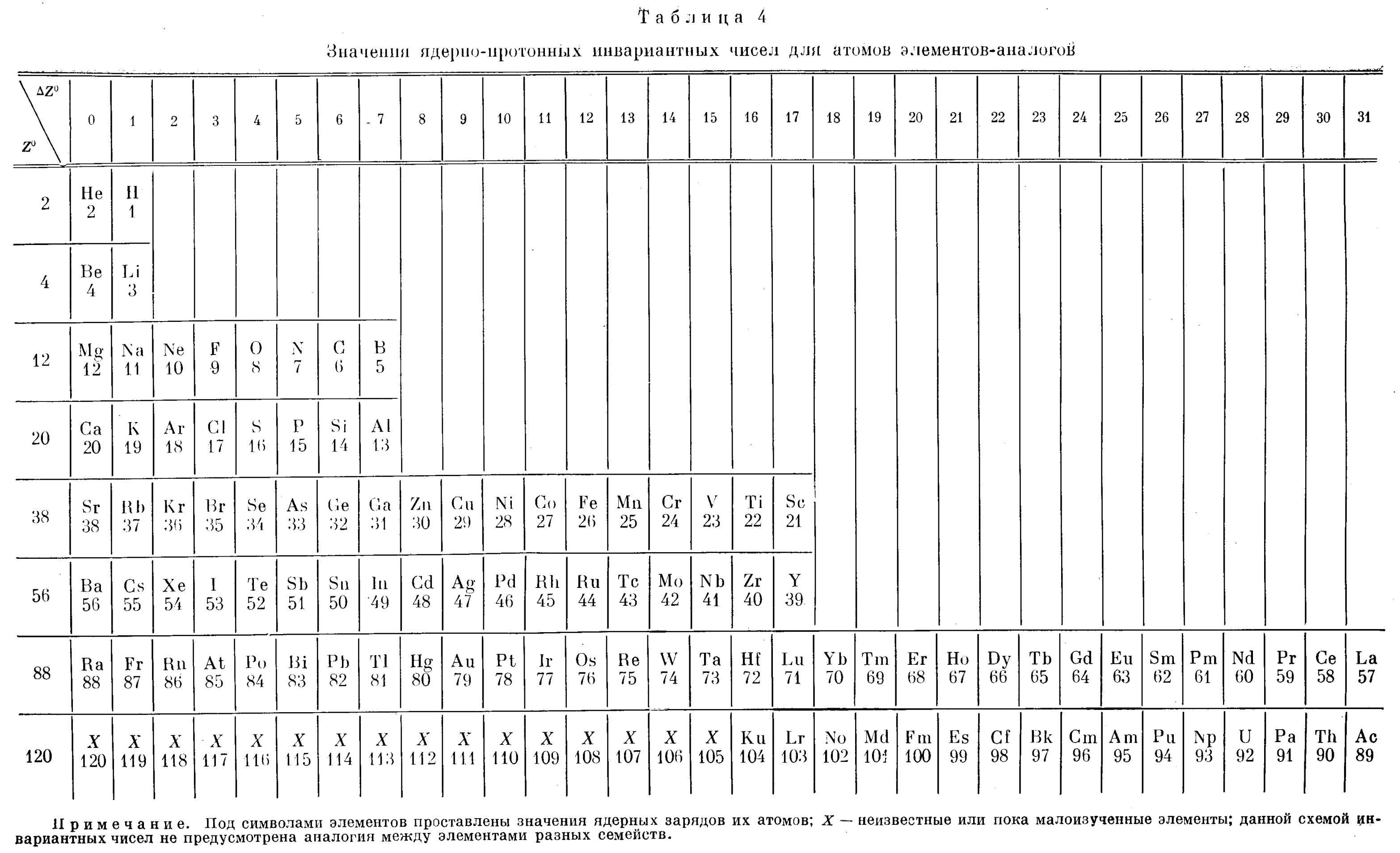
| Year: 1987 | PT id = 1115 |
Variation of Orbital Radii with Atomic Number
From Jour. Fac. Sci., Hokkaido Univ., Ser. IV. vol. 22, no. 2, Aug., 1987, pp. 357-385, The Connection Between the Properties of Elements and Compounds; Mineralogical-Crystallochemical Classification of Elements by Alexander A. Godovikov & Yu Hariya.
The analyses of the variations of the orbital atomic radii values (rorb) with the increase of the atomic number (Z) allow establishment of the following recurring regularities of their change:
Click image below to enlarge:
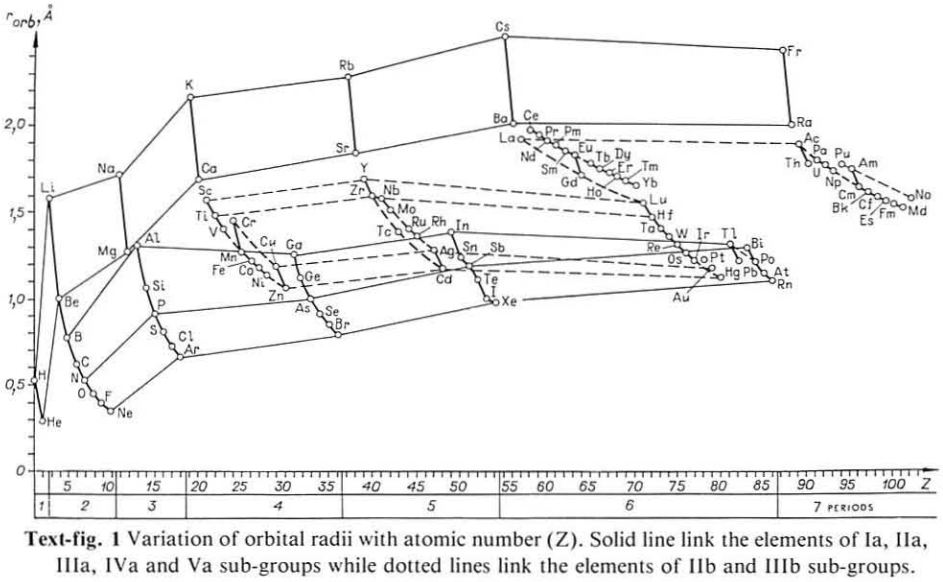
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1987 | PT id = 1116 |
Mineralogical-Crystallochemical Classification of Elements
From Jour. Fac. Sci., Hokkaido Univ., Ser. IV. vol. 22, no. 2, Aug., 1987, pp. 357-385, The Connection Between the Properties of Elements and Compounds; Mineralogical-Crystallochemical Classification of Elements by Alexander A. Godovikov & Yu Hariya.
Any mineralogical-crystallochemical classification of elements must provide answers to the following queries:
Click images below to enlarge:
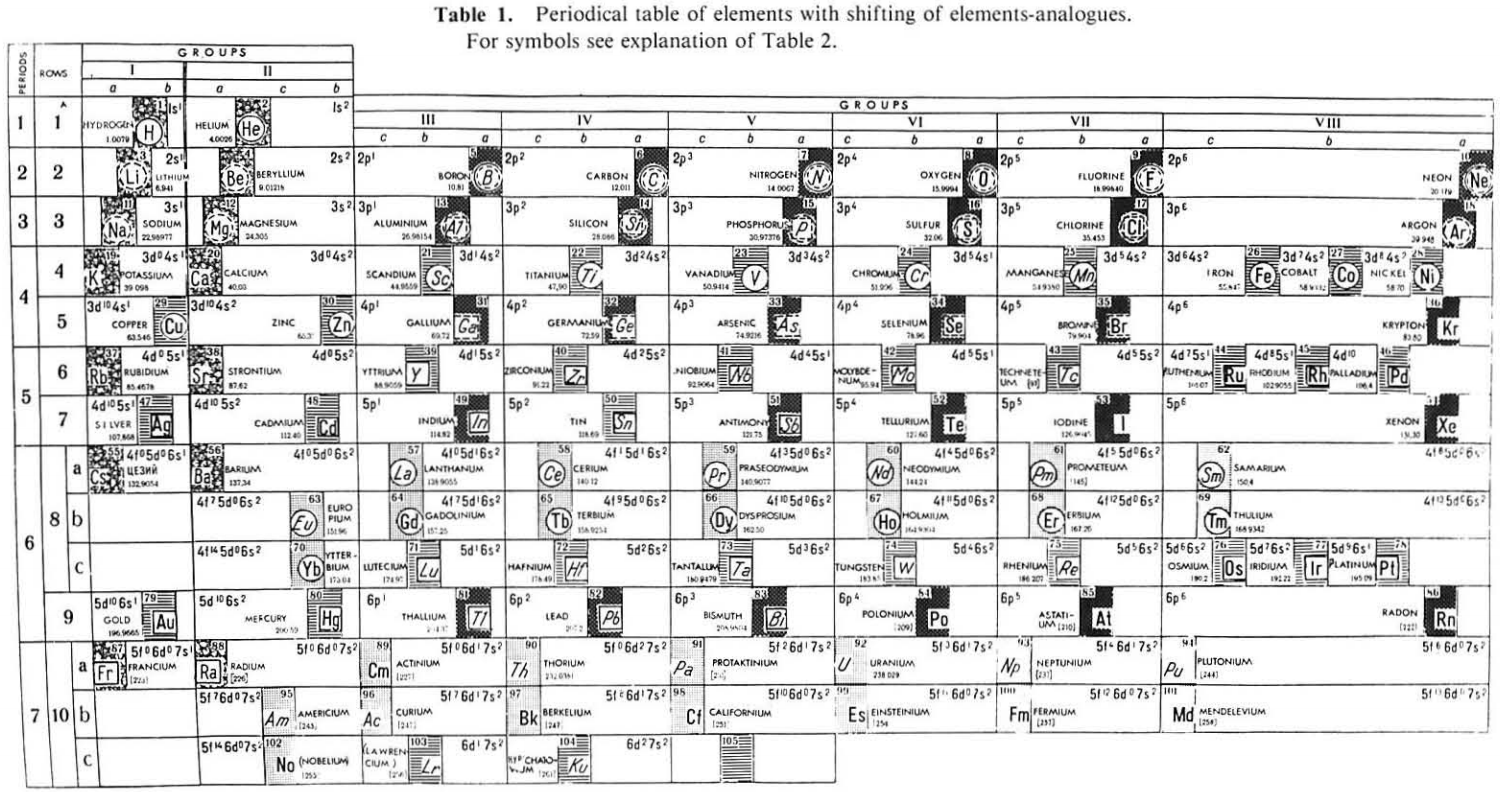

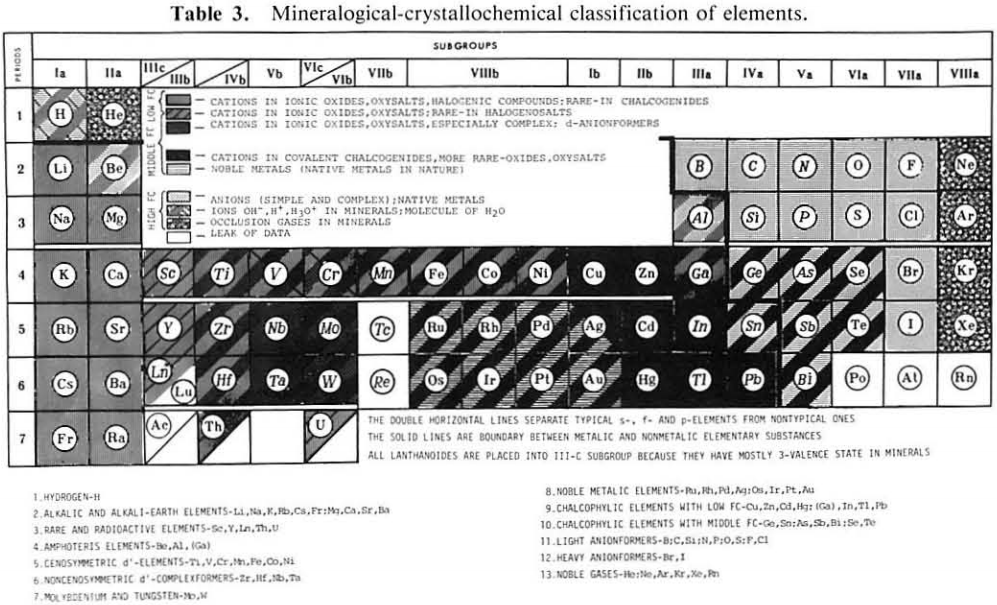
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 1993 | PT id = 1268 |
Huheey's Version of The Madelung Rule (For Orbital Filling)
Huheey, J.E., Keiter, E.A., Keiter, R.L.: Inorganic Chemistry: Principles of Structure and Reactivity. 4th edn. HarperCollins College Publishers (1993), p. 22
René Vernon comments: "A peculiar depiction of the Madelung Rule order of filling diagram."
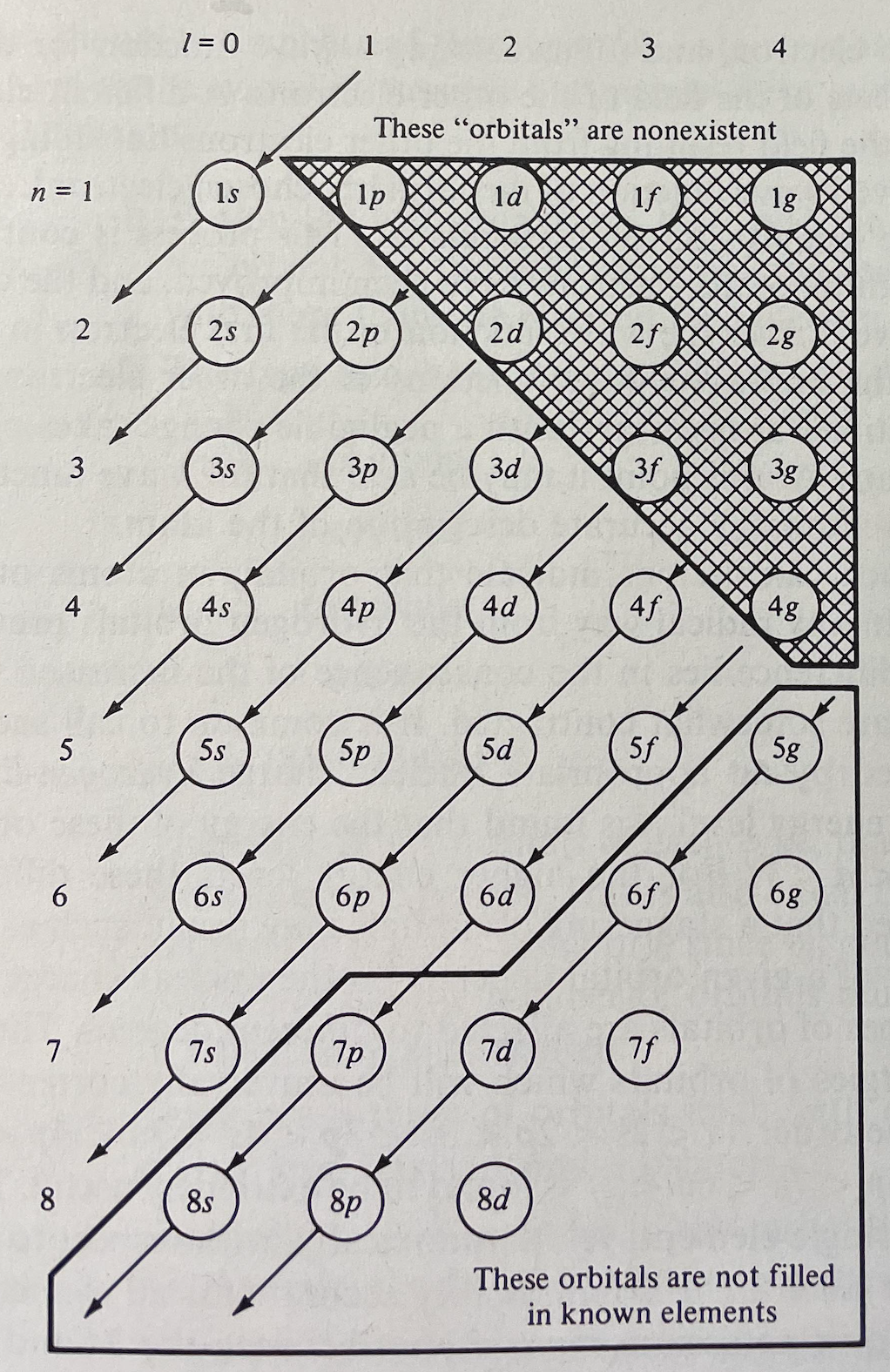
| Year: 1994 | PT id = 1159 |
Treplow's Periodic Table of The Atoms
R.S. Treplow, J. Chem. Educ. 1994, 71, 12, 1007: The Periodic Table of Atoms: Arranging the Elements by a Different Set of Rules.
"Although periodic tables differ greatly in their appearance, examination shows they are all designed according to a common set of conventions. This paper reviews those conventions and asks how the table would look under a different set of rules."
Ground-state multiplicity vs. atomic number for elements 1 to 103. Subblocks are labeled S, P, D & F. Lines connecting the dots show the "ideal" pattern. Atoms not on the lines are "nonideal" (where ideal refers to Madelung's rule):
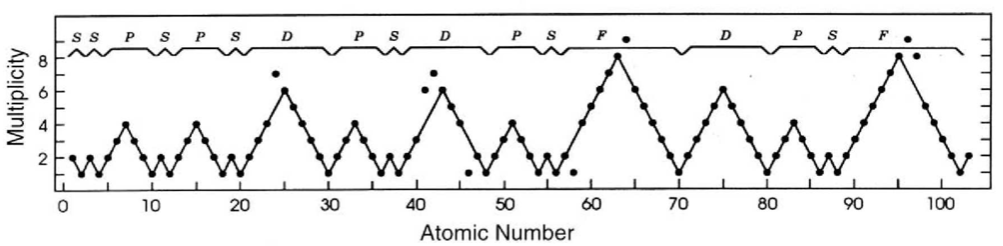
Thanks to René Vernon for his help.
| Year: 1995 | PT id = 1292 |
Considine's Polar Periodic Table
From: Considine DM (ed.) 1995, Van Nostrand’s Encyclopedia of Science, 8th ed. New York, p. 2376
René Vernon writes:
"A nice design but of quite limited practical utility for quick reference or detailed chemical analysis."

| Year: 2003 | PT id = 1150 |
Stable Isotopes, Periodic Table of
From Boeyens, JCA 2003, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 257, 33 a periodic table of the 264 stable isotopes arranged as an 11 x 24 matrix.
Click the image to enlarge:
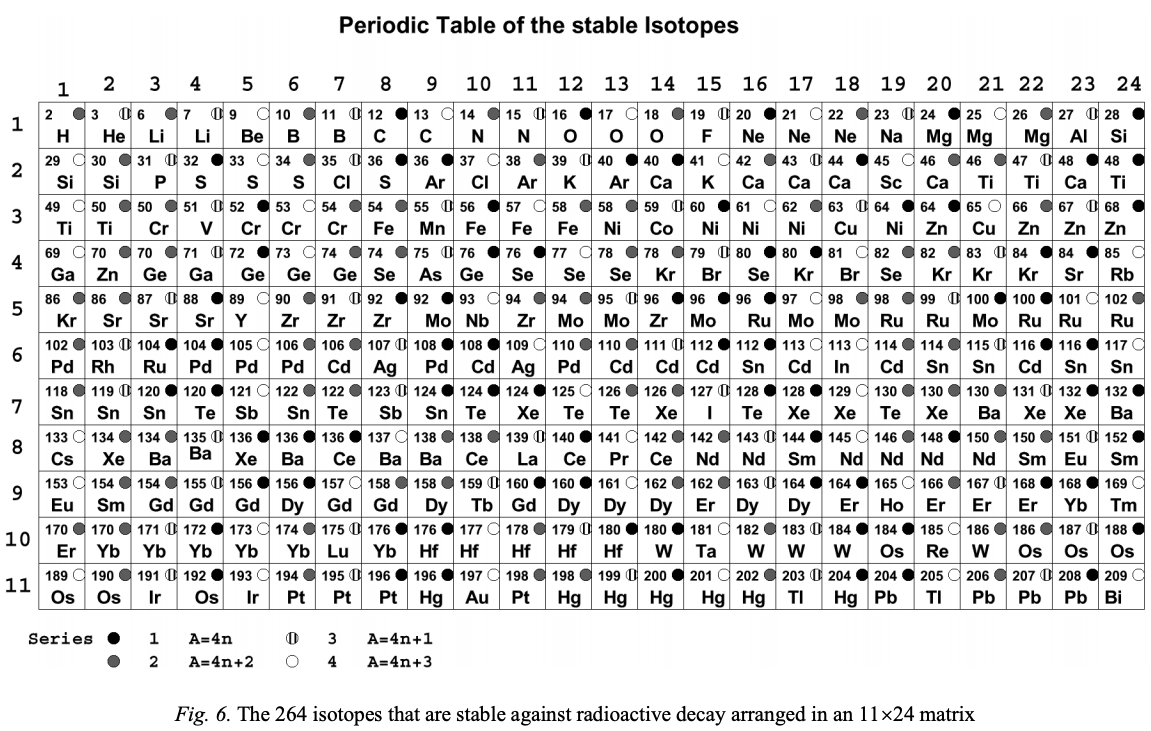
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 2007 | PT id = 1282 |
Seeger-Quadbeck Periodic Table
Seeger-Quadbeck H-J 2007, World of the Elements Elements of the World, Wiley-VCH, Wienheim, inside cover.
René Vernon, who provided the graphic, writes:
"An example of a rarely seen 32-column table. The categorisation scheme is interesting.

| Year: 2007 | PT id = 1021 |
Bent & Weinhold's 2D/3D Periodic Tables
From a paper by Henry Bent & Frank Weinhold, J. Chem. Educ., 2007, 84, 7, 1145 and here. The authors write in the abstract:
"The periodic table epitomizes chemistry, and evolving representations of chemical periodicity should reflect the ongoing advances in chemical understanding. In this respect, the traditional Mendeleev-style table appears sub-optimal for describing a variety of important higher-order periodicity patterns that have become apparent in the post-Mendeleevian quantal era. In this paper we analyze the rigorous mathematical origins of chemical periodicity in terms of the quantal nodal features of atomic valence orbitals, and we propose a variety of alternative 2D/3D display symbols, tables, and models.":
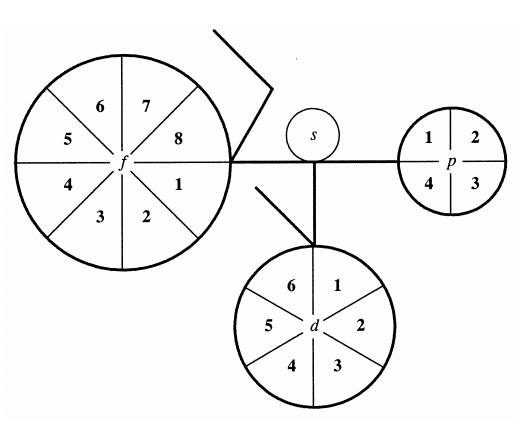
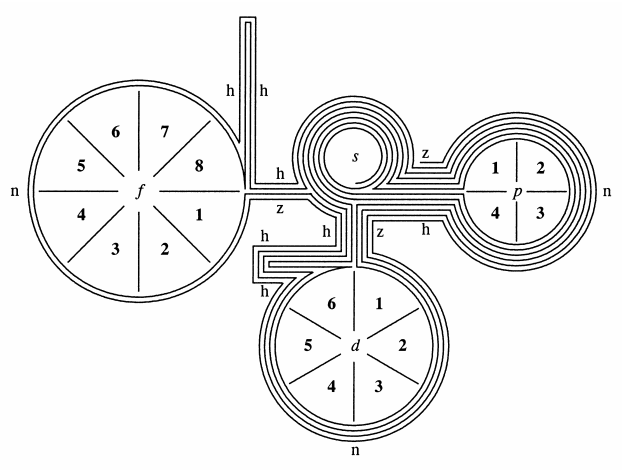
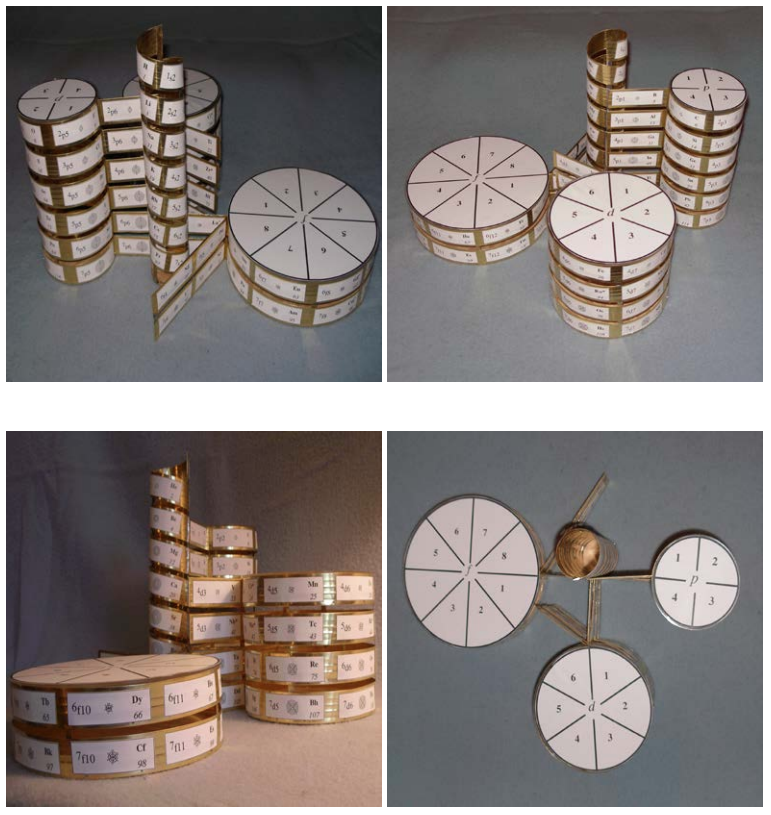
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 2018 | PT id = 1202 |
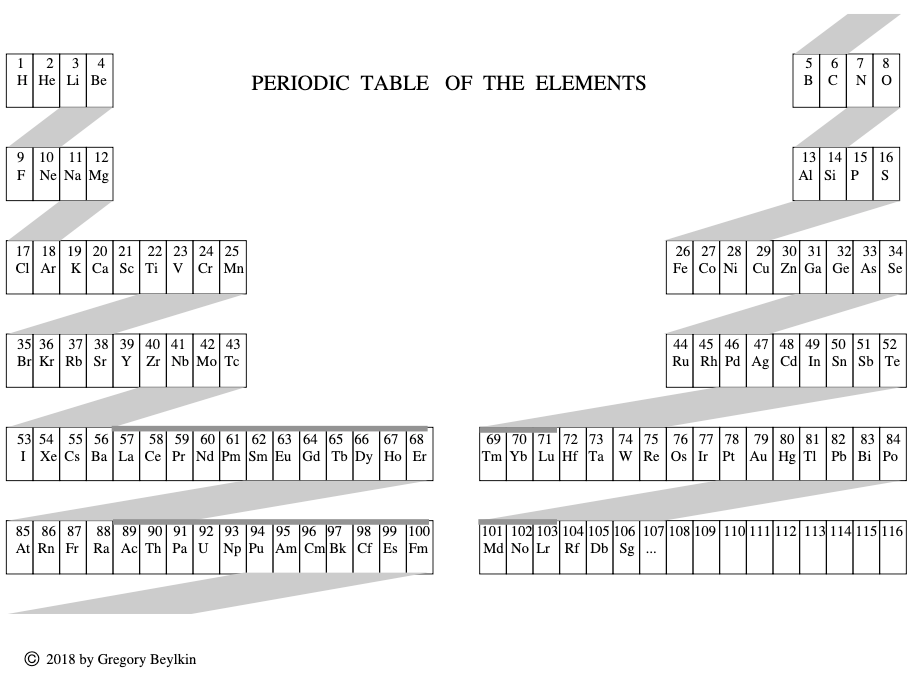
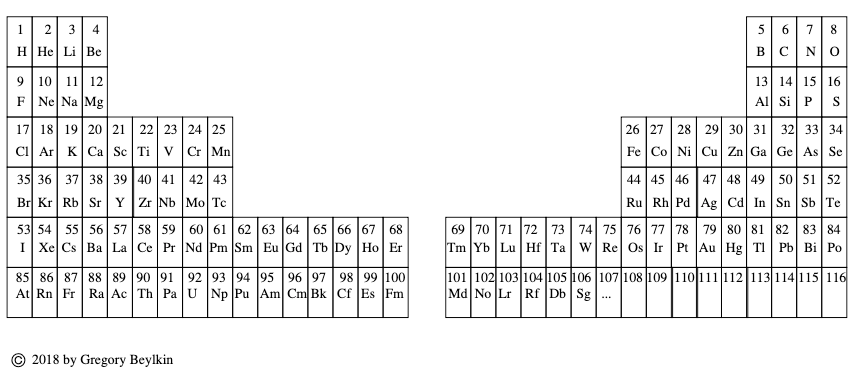
Beylkin's Periodic Table of The Elements
René Vernon writes: Beylkin's Periodic Table of The Elements has 4n2 periods, where n = 2,3..., and shows symmetry, regularity, and elegance, more so than Janet's left step table.
Beylkin (an applied mathematician) writes:
"Let us take a continuous strip of paper and, on one side of the strip, write all the elements in the order of their atomic numbers. We then form a spiral with the strip such that the two most chemically distinct groups, the group of halogens (in which we include hydrogen) and the group of noble gases, are properly aligned. By flattening the strip on a plane and folding it in the middle, we obtain the new periodic table..."
Other features:
There are four new(ish) groups: Ti-Zr-Ce-Th, V-Nb-Pr-Pa, Cr-Mo-Nd-U and Mn-Tc-Pm-Np. For the actinide elements of these groups, the resemblance of the earlier actinides to their lighter transition metal congeners is well known. For the lanthanide elements, Johansson et al. (2014) wrote a nice article about Ce and its cross-road position. For Pr, Nd, and Pm, all of these are known in multiple oxidations states (+2, +3, +4 excl. Pm, and +5 for Pr only), just as the transitions metals are so known.
| Year: 2018 | PT id = 1261 |
Kurushkin's 32-Column Periodic Table & Left-step Periodic Table United
Dr Mikhail V. Kurushkin, 32-column Periodic Table & Left-step Periodic Table United: https://bernalinstitute.com/events/bernal-seminar-by-dr-mikhail-v-kurushkin-itmo-universityrussia/
ABSTRACT
The pursuit of optimal representation of the Periodic Table has been a central topic of interest for chemists, physicists, philosophers and historians of science for decades (Leigh, 2009; Scerri, 2009). Should the Periodic Table of Chemical Elements first and foremost serve the needs of chemists as implied by its name? Or should it start from considerations of before quantum mechanics and thus be more appealing to physicists (Scerri, 2010, 2012b)? Is there a representation which overcomes this problem? The Periodic Table is from a fundamental point of view a graphic representation of periodicity as a phenomenon of nature. While the 32-column Periodic Table, popularized by Glenn T. Seaborg, is considered by chemists the most scientifically correct representation (Scerri, 2012a), physicists apparently prefer the Left-step Periodic Table above all (Scerri, 2005; Stewart, 2010). Alternatively, it is suggested that a rigorously fundamental representation of periodicity could only take the form of a spiral as, evidently, the abrupt periods of 2-D Periodic Tables contradict the gradual increase of atomic number, and the spiral representation reconciles this debate (Imyanitov, 2016). An optimal representation is eagerly sought after both for the needs of philosophy of chemistry and chemical education as their never-ending dialogue secures a thorough methodology of chemistry. The aim of the present work is to show that the 32-column Periodic Table and the Left-step Periodic Table can co-exist in mutual tolerance in a form of what Philip Stewart has already called Kurushkin’s Periodic Table (Kurushkin, 2017), Figure 1 below.
René Vernon writes:
"Kurushkin reminds us that the Janet left step table (with Sc-Y-Lu-Lr, and He over Be), and the version of the table with the s-elements on the right (also with Sc-Y-Lu-Lr, and He over Be) are interchangeable.
"For an earlier paywall version which includes a short video see:
Kurushkin M 2018, Building the periodic table based on the atomic structure, Journal of Chemical Education, vol. 94, no. 7, pp. 976–979, https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jchemed.7b00242
"Kurushkin’s interchangeable approach extends to tables with group 3 as either Sc-Y-La-Ac or Sc-Y-Lu-Lr. See Vernon's Yin Yang of The Periodic Table https://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?PT_id=1252"
| Year: 2019 | PT id = 1027 |
Chemical Bonds, Periodic Table of
The Max Planck Society (M-P-G, Max-Planck-Gesellschaft) has an article about the hidden structure of the periodic system.
Guillermo Restrepo, MPI for Mathematics in the Sciences:
"A periodic table of chemical bonds: Each of the 94 circles with chemical element symbols represents the bond that the respective element forms with an organic residue. The bonds are ordered according to how strongly they are polarized. Where there is a direct arrow connection, the order is clear: Bonds of hydrogen, for example, are more polarized than bonds of boron, phosphorus, and palladium. The same applies to rubidium in comparison to caesium, which has particularly low polarized bonds and is therefore at the bottom of the new periodic table. If there is no direct arrow between two elements, they may still be comparable – if there is a chain of arrows between them. For example, the bonds of oxygen are more polarized than the bonds of bromine. Bonds represented by the same colour have the same binding behaviour and belong to one of the 44 classes.":

Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 2019 | PT id = 1028 |
Slightly Different Periodic Table
The Max Planck Society (M-P-G, Max-Planck-Gesellschaft) has an article about the hidden structure of the periodic system.
Guillermo Restrepo, MPI for Mathematics in the Sciences:
"A slightly different periodic table: The table of chemical elements, which goes back to Dmitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer, is just one example of how objects – in this case the chemical elements – can be organized in such a system. The researchers from Leipzig illustrate the general structure of a periodic table with this example: The black dots represent the objects ordered by the green arrows. Using a suitable criterion, the objects can be classified into groups (dashed lines) in which the red arrows create a sub-order":
Thanks to René for the tip!
| Year: 2019 | PT id = 1046 |
Group 3 of The Periodic Table
There are several ways in which the 'common/modern medium form' periodic table are shown with respect to the Group 3 elements and how the f-block is shown. Indeed, there is even some dispute about which elements constitute Group 3. There are three general approaches to showing Group 3:
(See Scerri's take and Thyssen's view on this matter.)
So, which one of the three options is 'better'?
The general feeling amongst the knowledgeable is that leaving a gap is not an option, so it comes down to:
Sc, Y, La, Ac vs. Sc, Y, Lu, Lr
René Vernon has looked as the properties of the potential Group 3 elements, including: densities, 1st ionisation energies, ionic radii, 3rd ionisation energies, melting points & electron affinity:
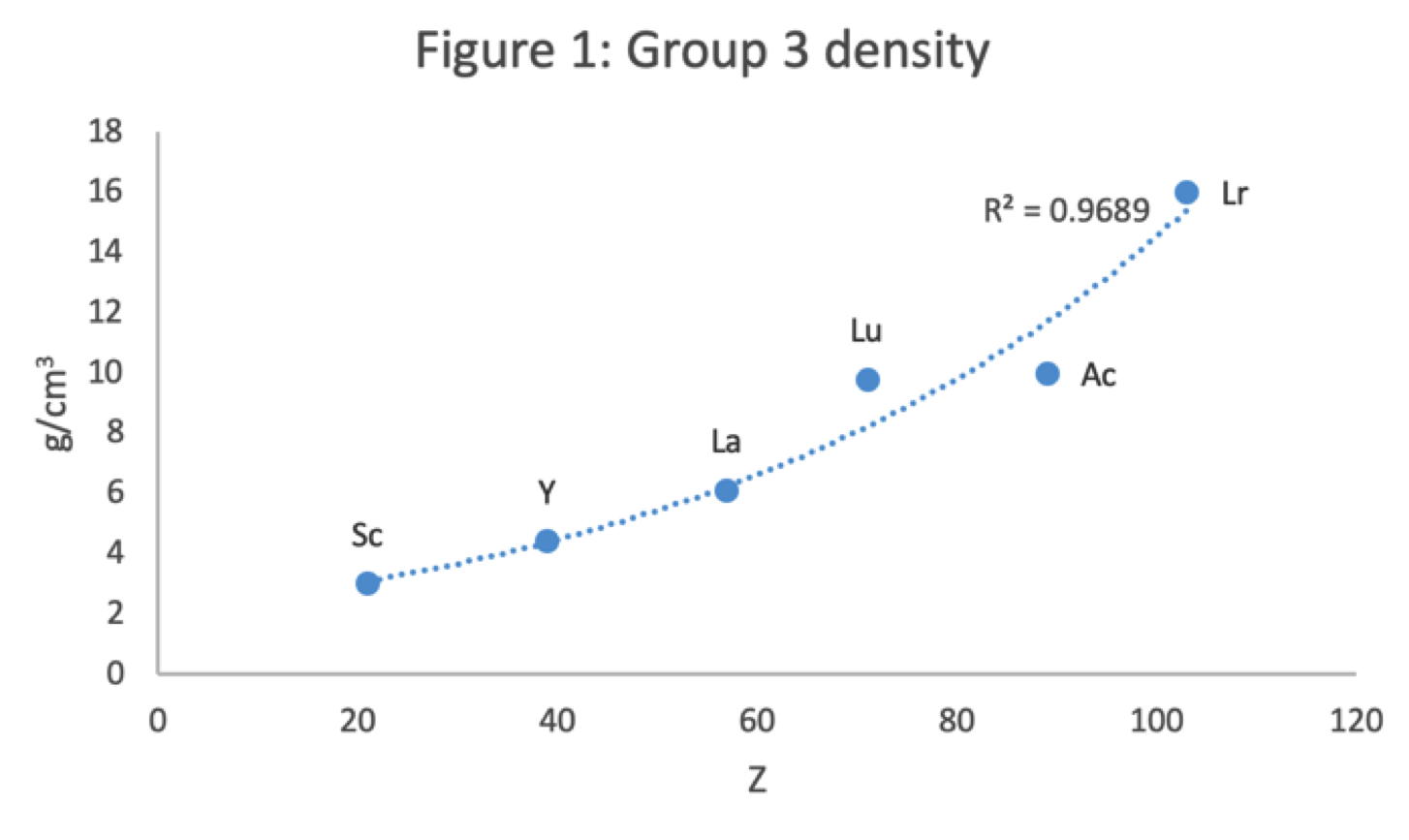
Figure 1 shows that a Z plot of the density values for Sc, Y, La, Lu Ac and Lr follows a smooth trendline.
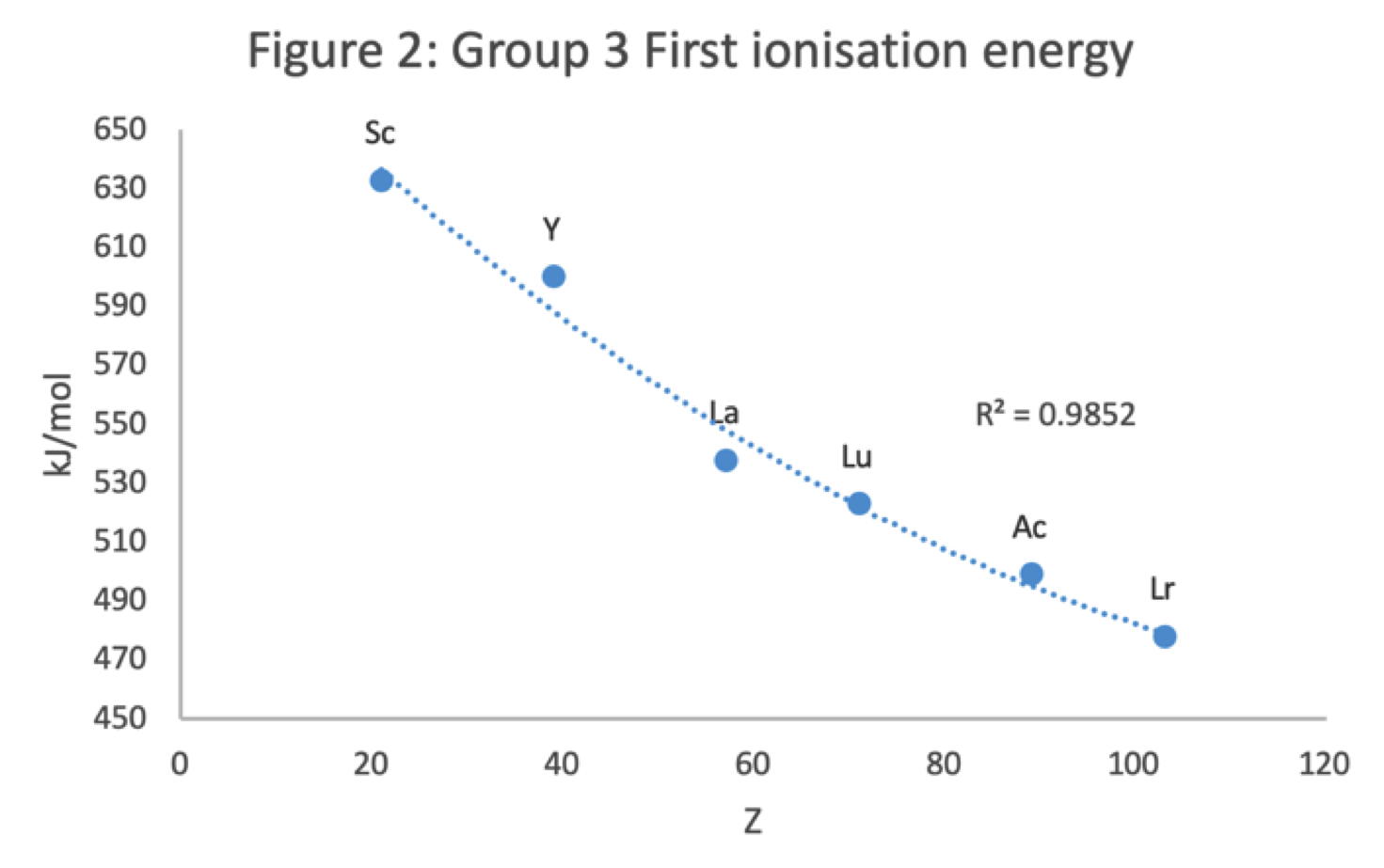
Figure 2 shows that a Z plot of the first ionization energy values follows a smooth trendline.
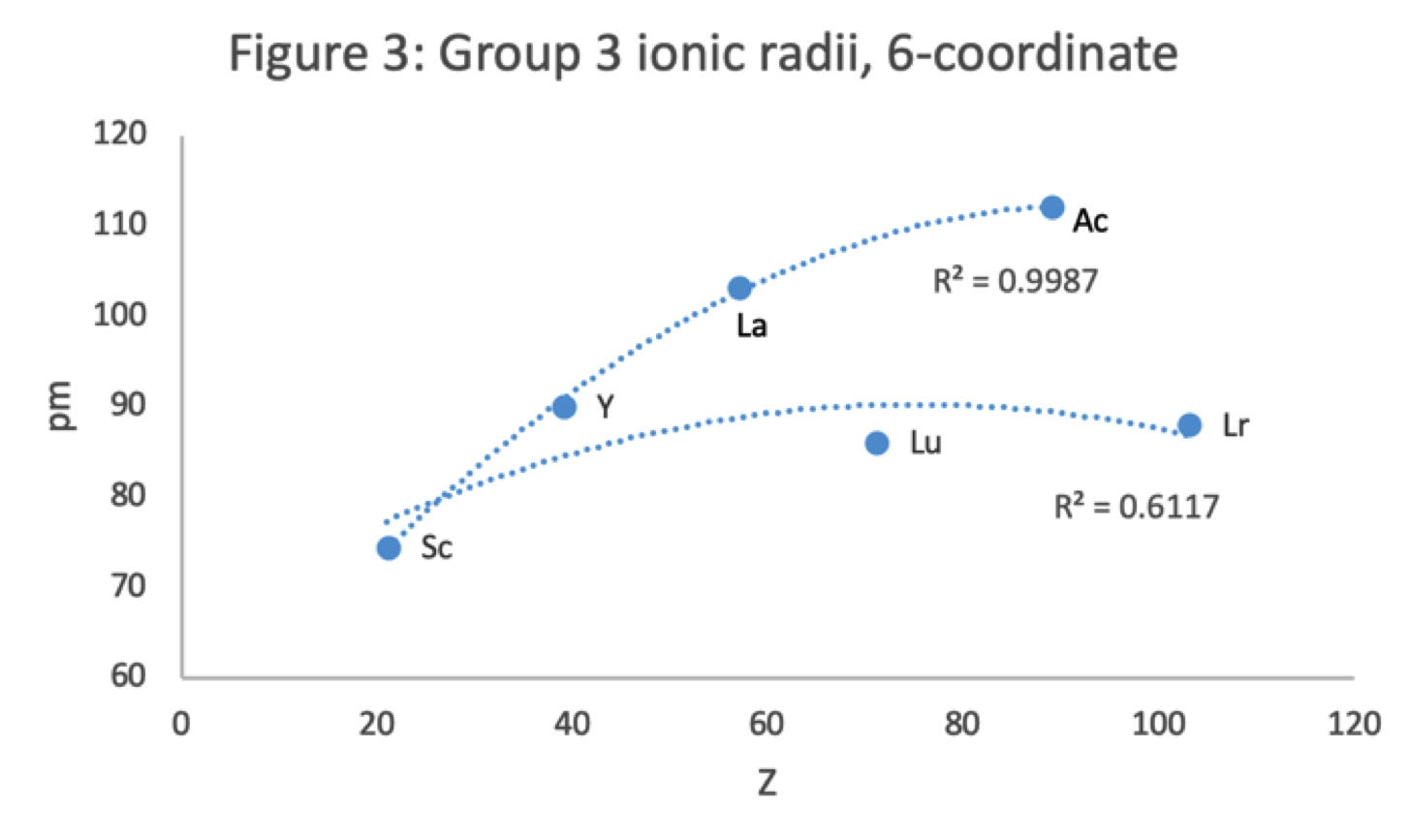
Figure 3 shows that a Z plot of the 6-coordinate ionic radii for the subject elements bifurcates after Y into an -La-Ac tranche (R2 = 0.99) and a -Lu-Lr branch (0.61). The trendline for -La-Ac is smoother.
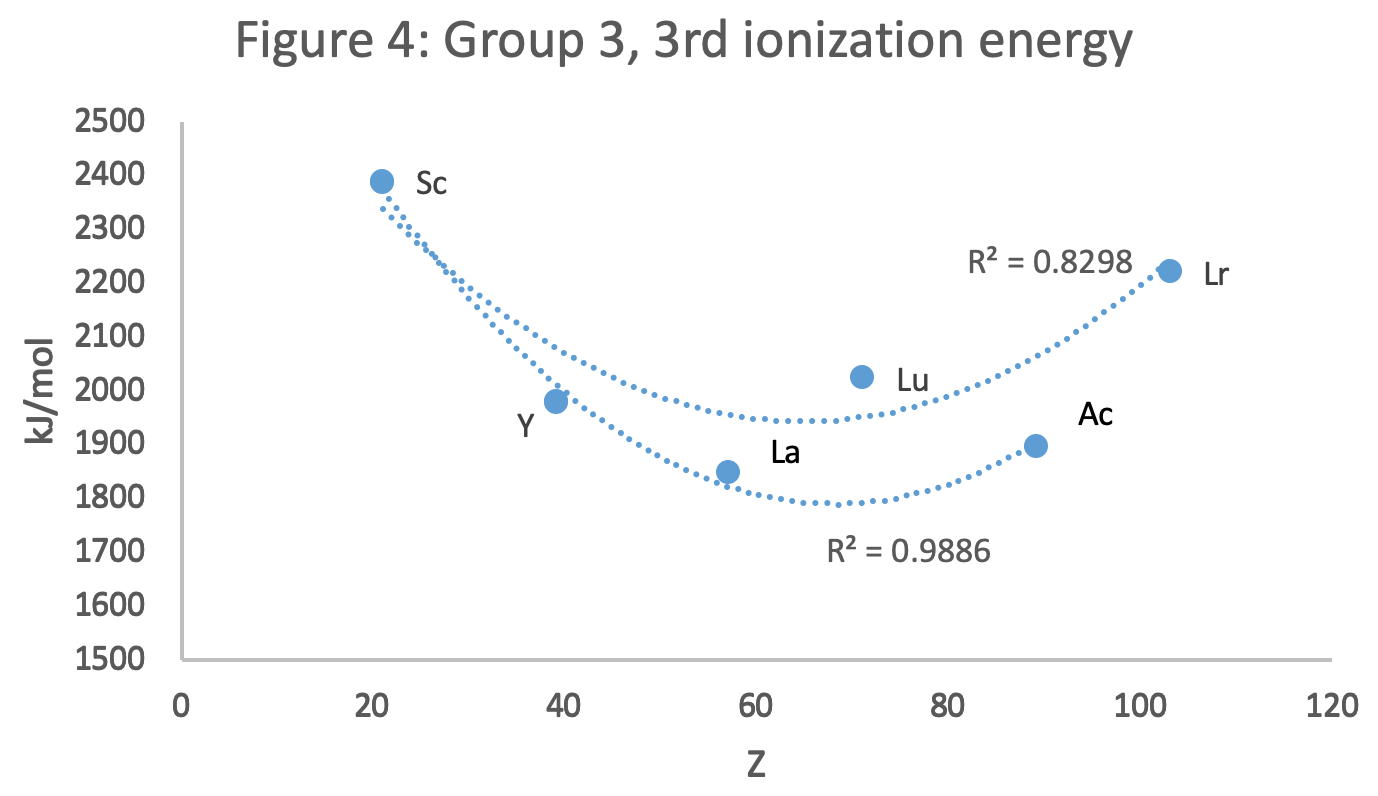
Figure 4 shows a Z plot of 3rd ionisation energy values bifurcating after Y into a -Lu-Lr tranche (R2 = 0.83) and a -La-Ac branch (0.98). The trendline for -La-Ac is smoother.
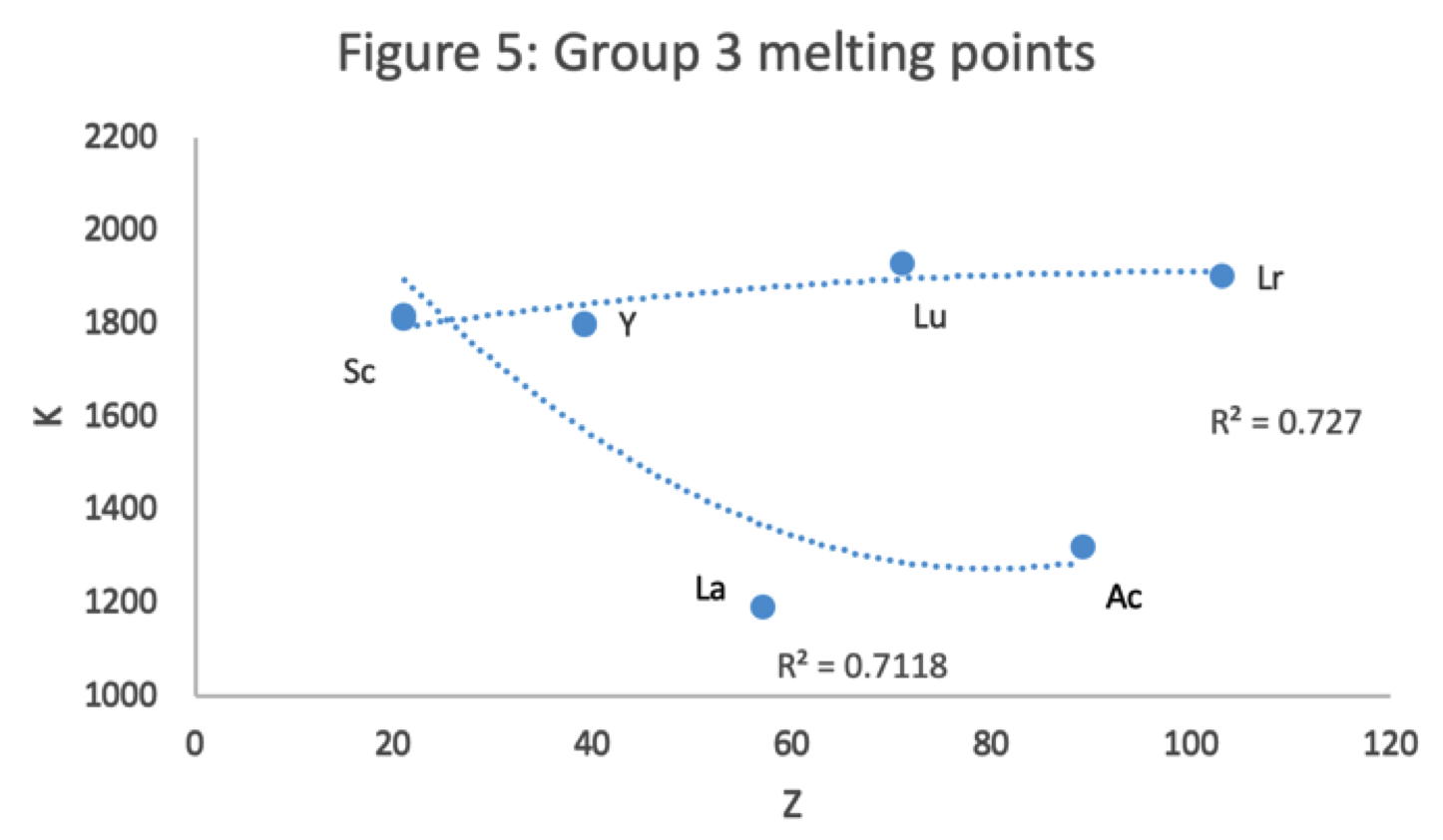
Figure 5 shows that a Z plot of the melting points bifurcates after Y into an -Lu-Lr (R2 = 0.72) tranche and a -La-Ac (0.71) branch. While the fit values for the two options are comparable, -Lu-Lr is preferred since Y and La show a greater departure from trend.
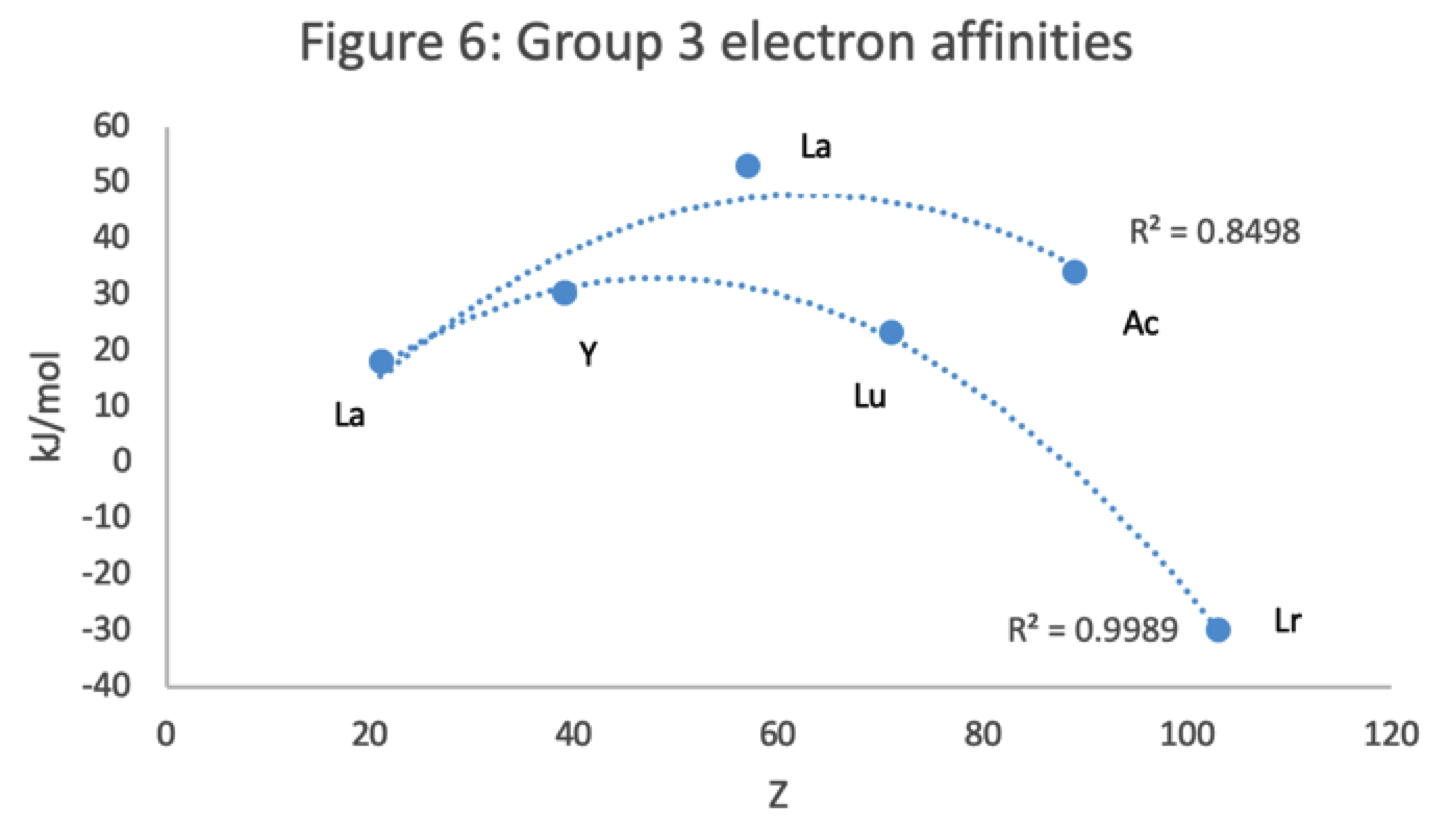
Figure 6 has a Z plot of electron affinity values bifurcating after Y into an -La-Ac tranche (R2 = 0.85) and a -Lu-Lr branch (0.99).[iii] The trendline supports Lu-Lr. The trend-lines by themselves are inconclusive: two show no difference; two support -La-Ac; two support -Lu-Lr.
Upon reviewing the data, René's comment is that: "The net result is that the two options seem inseparable" and he proposes that IUPAC adopt the following periodic table numbering system:
Professor Sir Martyn Poliakoff's [of the Periodic Videos YouTube channel & Nottiningham University] take on this matter:
| Year: 2019 | PT id = 1178 |
Abundance by Atomic Number, Z
An article in De Gruyter Conversations: The Periodic Table & The Lanthanides by Simon Cotton has this interesting chart of elemental abundance with respect to 106 atoms of Si.
The image source is http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/09/Elemental_abundances.svg
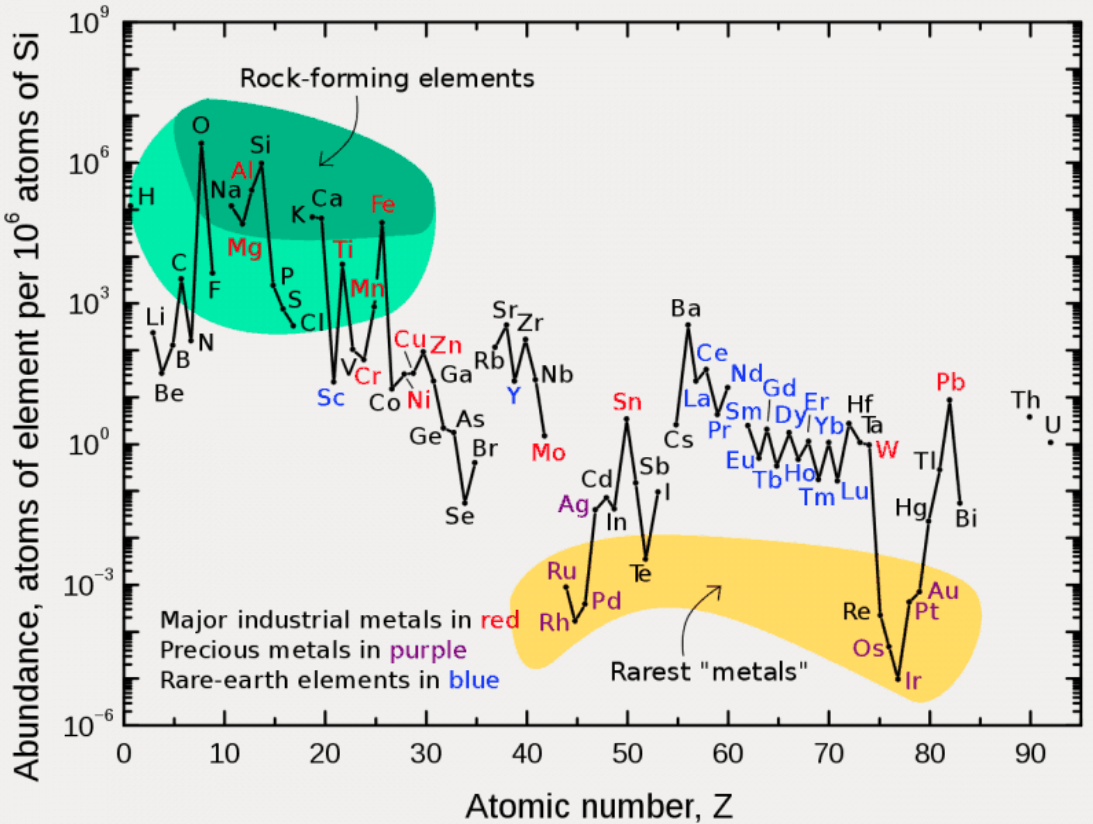
Thanks to René Vernon for the tip.
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1114 |
Vernon's Periodic Table showing the Idealized Solid-State Electron Configurations of the Elements
René Vernon writes:
"I've attached a periodic table showing the solid-state electron configurations of the elements. Among other things, it provides a first order explanation as to why elements such as Ln (etc.) like the +3 oxidation state.
"The table includes two versions of the f-block, the first starting with La-Ac; the second with Ce-Th. The table with the first f-block version has 24 anomalies [with respect to Madelung's rule]; the table with the second f-block version has 10 anomalies.
"In the case of the Sc-Y-La-Ac form, I wonder if such a solid-state table is more relevant these days than a table based on gas phase configurations, which has about 20 anomalous configurations.
"Partly we use gas phase configurations since, as Eric Scerri mentioned to me elsewhere, configurations were first obtained (~100 years ago?) from spectroscopy, and this field primarily deals with gas phase atoms. That said, are gas phase configurations still so relevant these days – for this purpose – given the importance of solid-state physics?
"I've never been able to find a periodic table of solid-state electron configurations. Perhaps that has something to do with it? Then again, surely I'm not the first person to have drawn one of these?"
Click image below to enlarge:
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1117 |
Correlation of Electron Affinity (F) with Elemental Orbital Radii (rorb)
From Jour. Fac. Sci., Hokkaido Univ., Ser. IV. vol. 22, no. 2, Aug., 1987, pp. 357-385, The Connection Between the Properties of Elements and Compounds; Mineralogical-Crystallochemical Classification of Elements by Alexander A. Godovikov & Yu Hariya and expanded by René Vernon who writes.
René Vernon writes:
I was delighted to read about two properties that account for nearly everything seen in the periodic table.
Two properties
While researching double periodicity, I happened upon an obscure article, which simply correlates electron affinity with orbital radius, and in so doing reproduces the broad contours of the periodic table. Having never thought much about the value or significance of EA, and its absence of easily discernible trends, I was suitably astonished. The authors left out the Ln and An and stopped at Bi. They were sitting on a gold mine but provided no further analysis.Development
I added the data up to Lr, updated the EA values, and have redrawn their graph. It is a thing of beauty and wonderment in its simplest sufficient complexity and its return on investment. I've appended 39 observations, covering all 103 elements.
Observations
Conclusion
So there it is, just two properties account for nearly everything.
Click images below to enlarge:
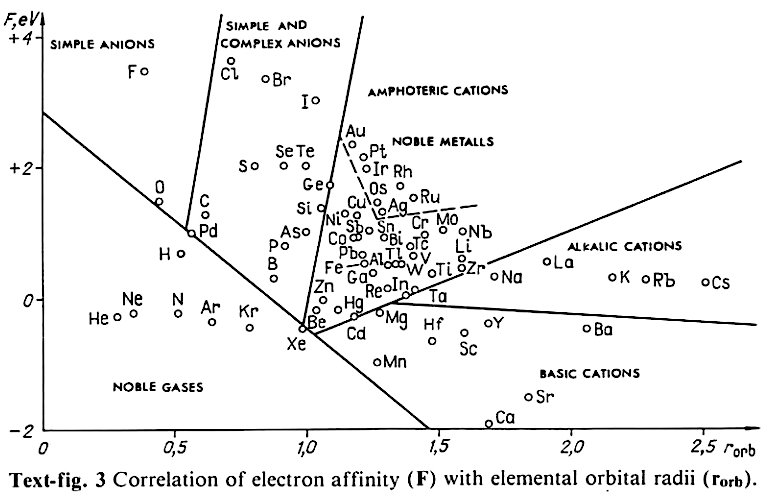
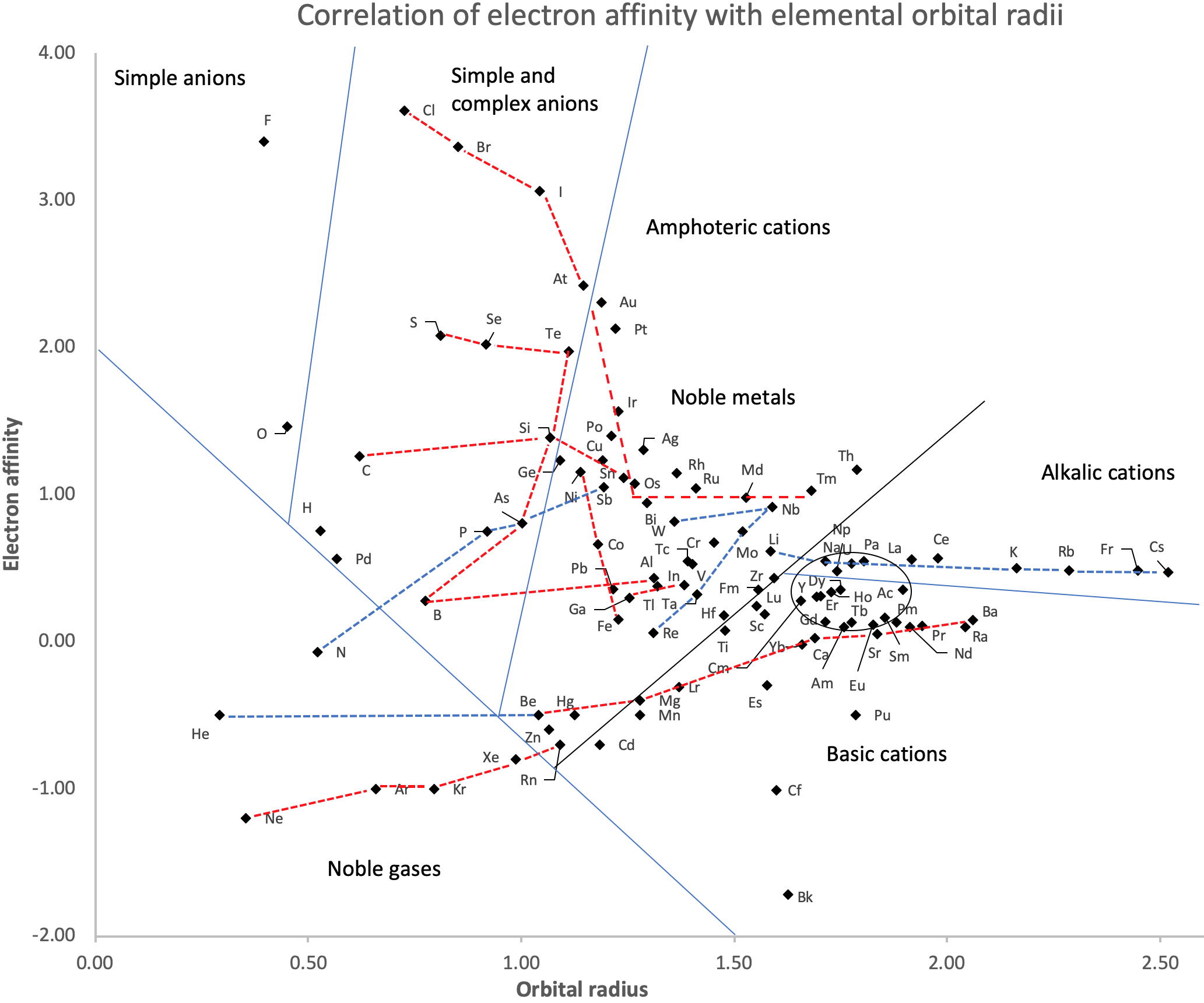
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1147 |
Periodic Ziggurat of The Elements
By René Vernon, the Periodic Ziggurat of the Elements. Click to enlarge:
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1157 |
Molar Magnetic Susceptibilities, Periodic Table of
Periodic Table of Molar Magnetic Susceptibilities by René Vernon, who writes:
I had read that the lanthanides were characterised by their magnetic properties, but never fully appreciated what this means. To this end, here is a table of Molar Magnetic Susceptibility (MMS) values (χ) for the elements, where MMS is a measure of how much a material will become magnetised in an applied magnetic field.
Formally, MMS is the ratio of magnetisation M (magnetic moment per unit volume) to the applied magnetising field of intensity H, allowing a simple classification into two categories of most materials responses to an applied magnetic field:
Alignment with the magnetic field, χ > 0, gives rise to paramagnetism
Alignment against the magnetic field, χ < 0, gives rise to diamagnetismSix observations:
1. The average value for each block is:
2. Lanthanides having unpaired 4f metals (Ce to Tm) have magnetic susceptibilities two to four orders of magnitude larger than those of "normal" metals.
3. Mn (511), Pd (540), O (3415) [this is actually the triplet diradical molecule O2] & Bi (-280) stand out. [A magnetic cross would be good for repelling a bismuth vampire.]
4. MMS reduces going down all groups of the d-block. The average reduction going from 4d to 5d is 50%.
5. In group 3 there is a reduction of 48% on going from Y to La. If Lu is instead placed under Y the reduction is 2%.
6. There are at least six, rather than three, ferromagnetic metals.
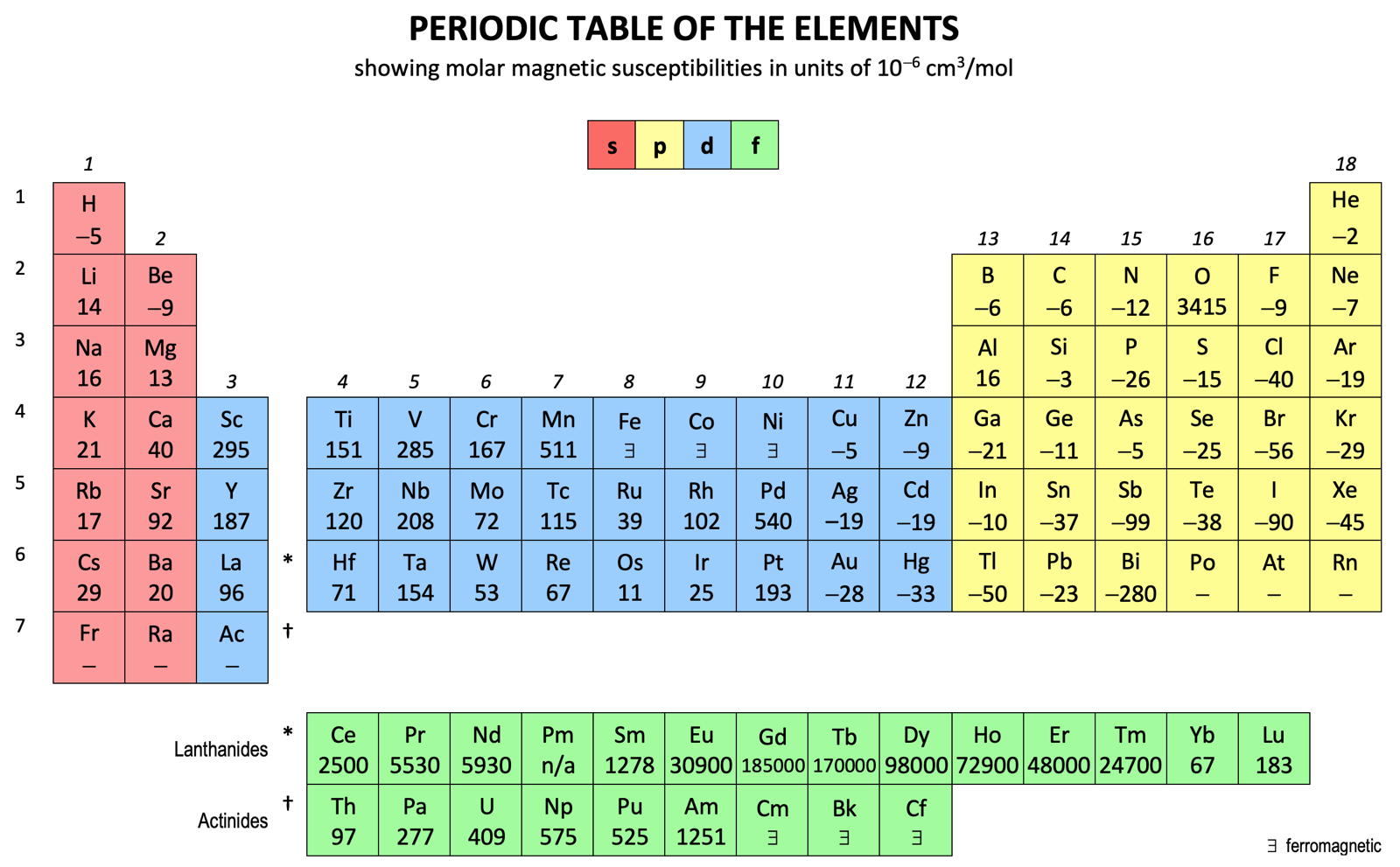
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1161 |
Vernon's Periodic Treehouse
René Vernon's Periodic Treehouse of the Elements, fearuring the World's longest dividing line between metals and nonmetals.
René writes:
I can't remember what started me off on this one. It may have been Mendeleev's line, as shown on the cover of Bent's 2006 book, New ideas in chemistry from fresh energy for the periodic law.
There are a few things that look somewhat arbitrary, so I may revisit these:
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1165 |
Vernon's (Partially Disordered) 15 Column Periodic Table
A formulation by René Vernon, who writes:
"Here is a 15-column table which is a hybrid of a Mendeleev 8-column table and an 18-column standard table. The key relocations are the p-block nonmetals to the far left; and the coinage and post-transition metals under their s and early d-block counterparts.
"Taking a leaf out of Mendeleev's playbook, I ignored atomic number order when this seemed appropriate. It's refreshing to see the traditional horizontal gaps between blocks disappear. (DIM did not like these.)
"Since Dias (2004, see references below) reckoned a periodic table is a partially ordered set forming a two-dimensional array, I believe I now have a partially ordered table that is partially disordered twice over.
"The table has some curious relationships. Equally, some relationships seen in the standard form are absent. The Group 2, 3, and aluminium dilemmas disappear. This confirms my impression that such dilemmas have no intrinsic meaning. Rather, their appearance or non-appearance is context dependent."
Notes & references below.
Groups 1 to 4 have either a C or F suffix where C (nonmetal) is after the importance of carbon to our existence; and F (metal) is for the importance of iron to civilisation.
Groups 1C and 1F present the greatest contrast in nonmetallic and metallic behaviour.
Coactive Nonmetals: They are capable of forming septenary heterogeneous compounds such as C20H26N4O10PSSe.
Group 2C: Helium is shaded as a noble gas. "Heliox" is a breathing gas mixture of helium and oxygen used in saturation diving, and as a medical treatment for patients with difficulty breathing.
Group 3C: Boron over nitrogen looks odd. Yet one boron atom and one nitrogen atom have the same number of electrons between them as two adjacent carbon atoms. The combination of nitrogen and boron has some unusual features that are hard to match in any other pair of elements (Niedenzu & Dawson 1965).
Boron and phosphorus form a range of ring and cage compounds having novel structural and electronic properties (Paine et al. 2005).
Metalloids. I treat them here as nonmetals given their chemistry is predominately that of chemically weak nonmetals.
Metals: The labels electropositive; transition; and electronegative are adapted from Kornilov (2008).
Group 1F: Monovalent thallium salts resemble those of silver and the alkali metals.
An alloy of cesium (73.71%), potassium (22.14%) and sodium (4.14%) has a melting point of –78.2°C (–108.76°F) (Oshe 1985).
Silver, copper, and gold, as well as being the coinage metals, are borderline post-transition metals.
Group 2F: Beryllium and magnesium are not in fact alkaline earths. Beryllium is amphoteric rather than alkaline; magnesium was isolated in impure form from its oxides, unlike the true alkaline earths. The old ambiguity over whether beryllium and magnesium should go over calcium or zinc has gone.
Nobelium is here since +2 is its preferred oxidation state, unlike other actinoids.
Group 3F: Aluminium is here in light of its similarity to scandium (Habishi 2010).
InGaAsP is a semiconducting alloy of gallium arsenide and indium phosphide, used in lasers and photonics.
There is no Group 3 "issue" since lanthanum, actinium, lutetium and lawrencium are in the same family.
Gold and aluminium form an interesting set of intermetallic compounds known as Au5Al2 (white plague) and AuAl2 (purple plague). Blue gold is an alloy of gold and either gallium or indium.
Lanthanoids: The oxidation state analogies with the transition metals stop after praseodymium. That is why the rest of lanthanoids are footnoted in dash-dot boxes.
Actinoids: The resemblance to their transition metal analogues falters after uranium, and peters out after plutonium.
Group 4F: It's funny to see titanium—the lightweight super-metal—in the same group as lead, the traditional "heavy" metal.
This is the first group impacted by the lanthanoid contraction (cerium through lutetium) which results in the atomic radius of hafnium being almost the same as that of zirconium. Hence "the twins".
The chemistry of titanium is significantly different from that of zirconium and hafnium (Fernelius 1982).
Lead zirconate titanate Pb[ZrxTi1–x]O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) is one of the most commonly used piezo ceramics.
Group 5: Bismuth vanadate BiVO4 is a bright yellow solid widely used as a visible light photo-catalyst and dye.
Steel Friends: The name is reference to their use in steel alloys. They have isoelectronic soluble oxidizing tetroxoanions, plus a stable +3 oxidation state. (Rayner-Canham 2020).
Ferromagnetic Metals: The horizontal similarities among this triad of elements (as is the case among the PGM hexad) are greater than anywhere in the periodic table except among the lanthanides (Lee 1996). The +2 aqueous ion is a major component of their simple chemistry (Rayner-Canham 2020).
Group 8: "Rubiferous metals" (classical Latin rubēre to be red; -fer producing) is from the reddish-brown colour of rust; the most prevalent ruthenium precursor being ruthenium trichloride, a red solid that is poorly defined chemically but versatile synthetically; and the red osmates [OsO4(OH)4]?2 formed upon reaction by osmium tetroxide with a base.
Group 9: "Weather metals" comes from the use of cobalt chloride as a humidity indicator in weather instruments; rhodium plating used to "protect other more vulnerable metals against weather exposure as well as against concentrated acids or acids fumes" (Küpfer 1954); and the "rainbow" etymology of iridium.
Group 10: "Catalytic metals" is after a passage in Greenwood and Earnshaw, "They are... readily obtained in finely divided forms which are catalytically very active." (2002). Of course, many transition metals have catalytic properties. That said, if you asked me about transition metal catalysts, palladium and platinum would be the first to come to mind. Group 10 appear to be particularly catalytic.
References:
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1168 |
Shukarev's Periodic System (redrawn by Vernon)
Shukarev SA 1975, "On the image of the periodic system with the use of fifth move of late a-elements", Collection of Scientific and Methodological Articles on Chemistry. M.: Higher School, no 4, pp 3-12 (in Russian). Redrawn and commented upon by René Vernon:
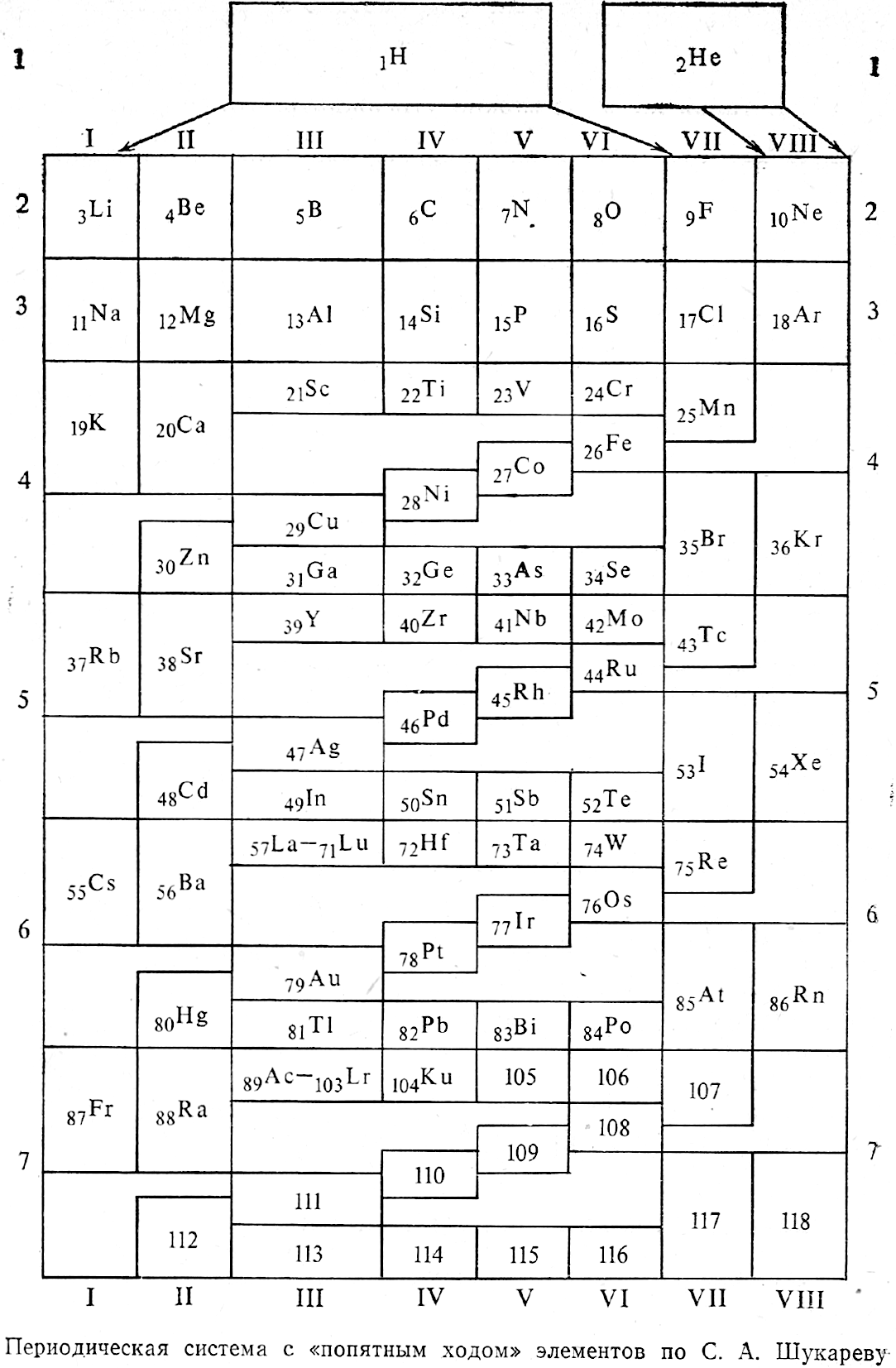
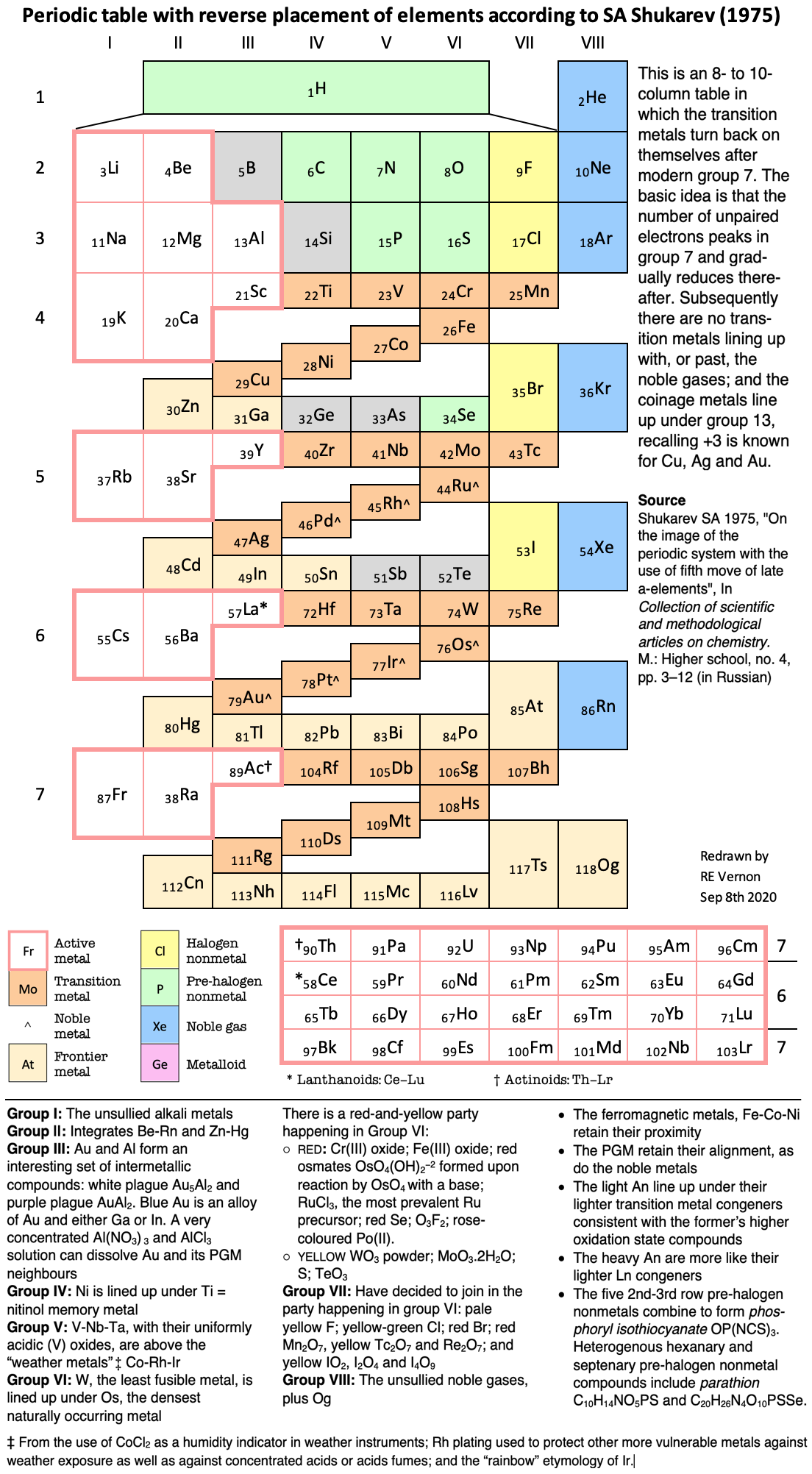
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1170 |
Zig-Zag Line, Periodic Table
Periodic Table showing the (regular) zig-zag line by René Vernon who writes:
"It is curious that the full extent of the line has never been properly mapped (to my knowledge).
"Elements on the downside of the line generally display increasing metallic behaviour; elements on the topside generally display increasing nonmetallic behaviour.
"When you see the line you will usually see only about a quarter of it. The line actually runs all the way across the periodic table, as shown, for a total of 44 element box sides.
"Interpretations vary as to where the line runs. None of these is better than any other of them, provided the interpretation is explained to you. The thick black line (at least in the p-block) is the most common version. The metalloids tend to lie to either side of it.
"Polonium and astatine are shown here as post-transition metals although either or both of them are sometimes shown as metalloids (or, in the case of astatine, as a halogen). Polonium conducts electricity like a metal and forms a cation in aqueous solution. In 2013, astatine was predicted to be a centred cubic-metal Condensed Astatine: Monatomic and Metallic This prediction has been cited 35 times, with no dissenters. Astatine also forms a cation in aqueous solution. Oganesson is shown as having (as yet) unknown properties.
"The dashed lines show some alternative paths for the zigzag line.
"The lower one treats the metalloids as nonmetals since metalloid chemistry is predominately nonmetallic. The lower line and the upper line are sometimes shown together used when the metalloids are treated as neither metals nor nonmetals."
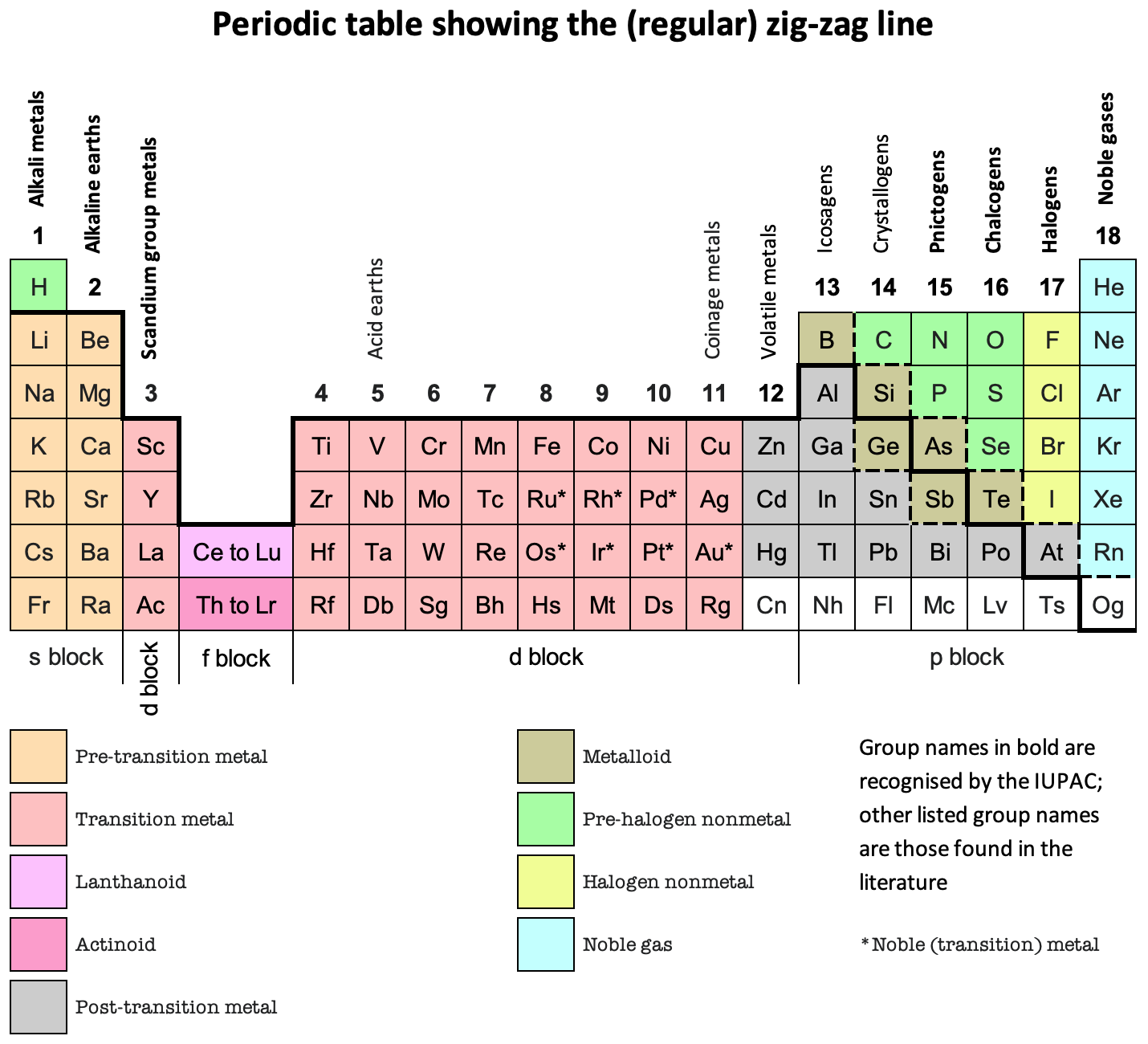
And in Janet Left-Step form:
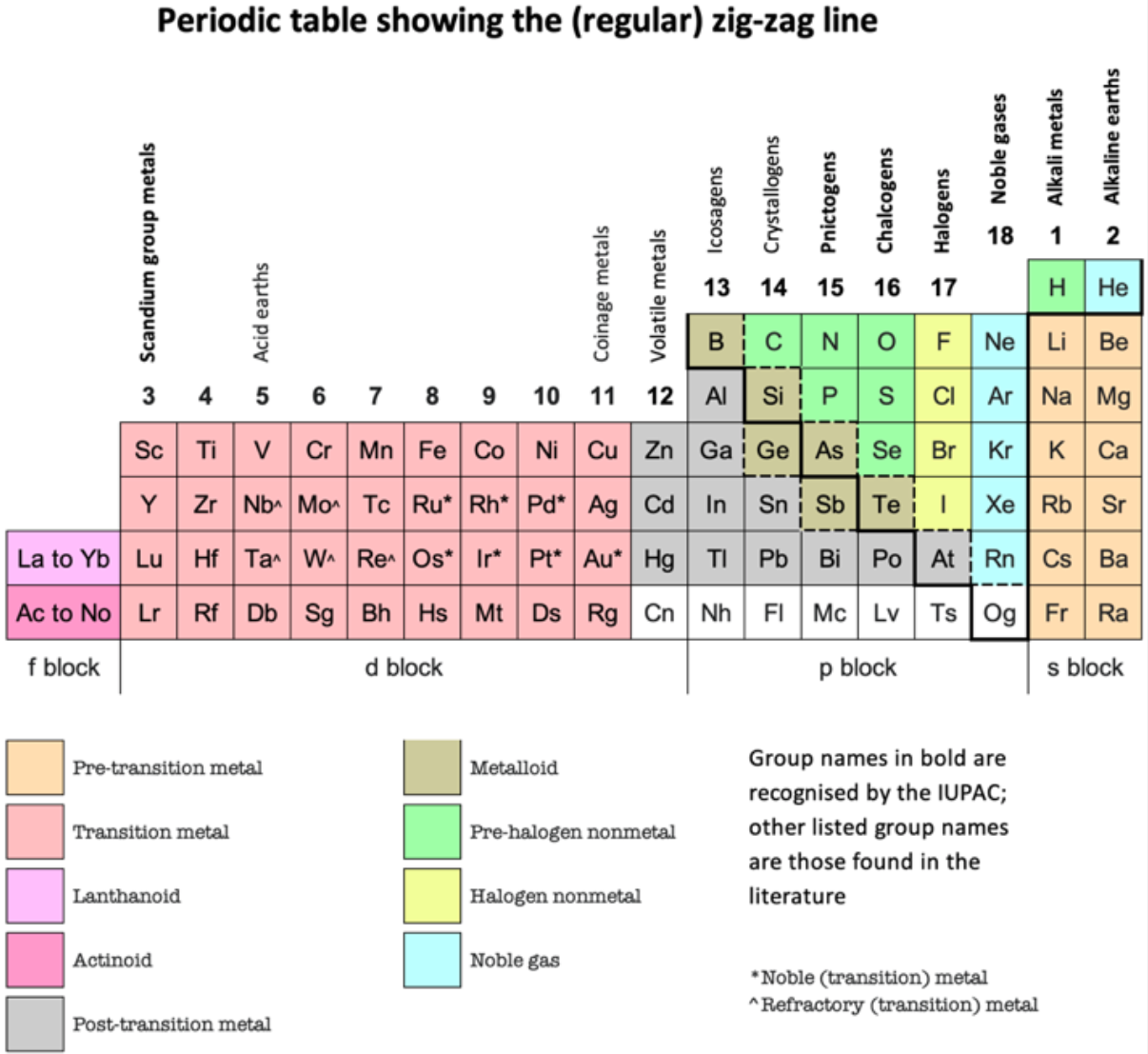
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1171 |
16 Dividing Lines Within The Periodic Table
René Vernon points out that there are 16 dividing lines within the periodic table.
A-Z Dividing Lines:
48-crash line: Named after the dramatic reduction in physical metallic character after group 11, Cd being Z = 48. Group 12 show few transition metal attributes and behave predominantly like post-transition metals.
Big bang line: H makes up about 73% of the visible universe.
Corrosive line: O, F, Cl = most corrosive nonmetals.
d-Block fault line: Group 3 show little d-block behaviour; group 4 is the first in which characteristic d-block behaviour occurs.
Deming line: Demarcates the metalloids from the pre-halogen nonmetals. The "reactive" nonmetals to the right of the metalloids each have a sub-metallic appearance (C, O, Se, I).
Edge of the world line: No guesses for this one.
Klemm line: Klemm, in 1929, was the first to note the double periodicity of the lanthanides (Ce to Lu). Lockyer line: After the discoverer of He, the first element not found on Earth.
Ørsted line: After the magnetic effects believed to be responsible for Mn having a crystalline structure analogous to white P; Tc: First radioactive metal; Re: Last of the refractory metals; "most radioactive" of the naturally occurring elements with stable isotopes. Fe: First of the ferromagnetic metals; Ru: First noble metal; Os: Densest of naturally occurring metals. The number of unpaired d electrons peaks in group 7 and reduces thereafter.
Platypus line: Tl shows similarities to Rb, Ag, Hg, Pb.
Poor metal line: Most metals (80%) have a packing factor (PF)3 68%. Ga: Has a crystalline structure analogous to that of iodine. BCN 1+6.* PF 39.1%. Melts in your hand. In: Partly distorted structure due to incompletely ionised atoms. BCN 4+8. PE 68.6%. Oxides in preferred +3 state are weakly amphoteric; forms anionic indates in strongly basic solutions. Tendency to form covalent compounds is one of the more important properties influencing its electro-chemical behaviour. Sn: Irregularly coordinated structure associated with incompletely ionised atoms. BCN 4+2. PF 53.5%. Oxides in preferred +2 state are amphoteric; forms stannites in strongly basic solutions. Grey Sn is electronically a zero band gap semimetal, although it behaves like a semiconductor. Diamond structure. BCN 4. PF 34.0%. Pb: Close-packed, but abnormally large inter-atomic distance due to partial ionisation of Pb atoms. BCN 12. PF 74%. Oxide in preferred +2 state is amphoteric; forms anionic plumbates in strongly basic solutions. Bi: Electronic structure of a semimetal. Open-packed structure (3+3) with bonding intermediate between metallic and covalent. PF 44.6%. Trioxide is predominantly basic but will act as a weak acid in warm, very concentrated KOH. Can be fused with KOH in air, resulting in a brown mass of potassium bismuthate.
Seaborg line: No f electrons in gas phase La, Ac and Th atoms.
Triple line: N = gas; S = solid; Br = liquid.
Zigzag lobby: H needs no intro. Li: Many salts have a high degree of covalency. Small size frequently confers special properties on its compounds and for this reason is sometimes termed 'anomalous'. E.g. miscible with Na only above 380° immiscible with molten K, Rb, Cs, whereas all other pairs of AM are miscible with each other in all proportions. Be: Has a covalent component to its otherwise predominately metallic structure = low ductility. Lowest known Poisson's ratio of elemental metals. Amphoteric; predominately covalent chemistry atypical of group 2. Some aspects of its chemical properties are more like those of a metalloid.
Zigzag line: Eponymous metal-nonmetal dividing line.
Zintl line: Hypothetical boundary highlighting tendency for group 13 metals to form phases with a various stoichiometries, in contrast to group 14+ that tend to form salts with polymeric anions.
* BCN = bulk coordination number
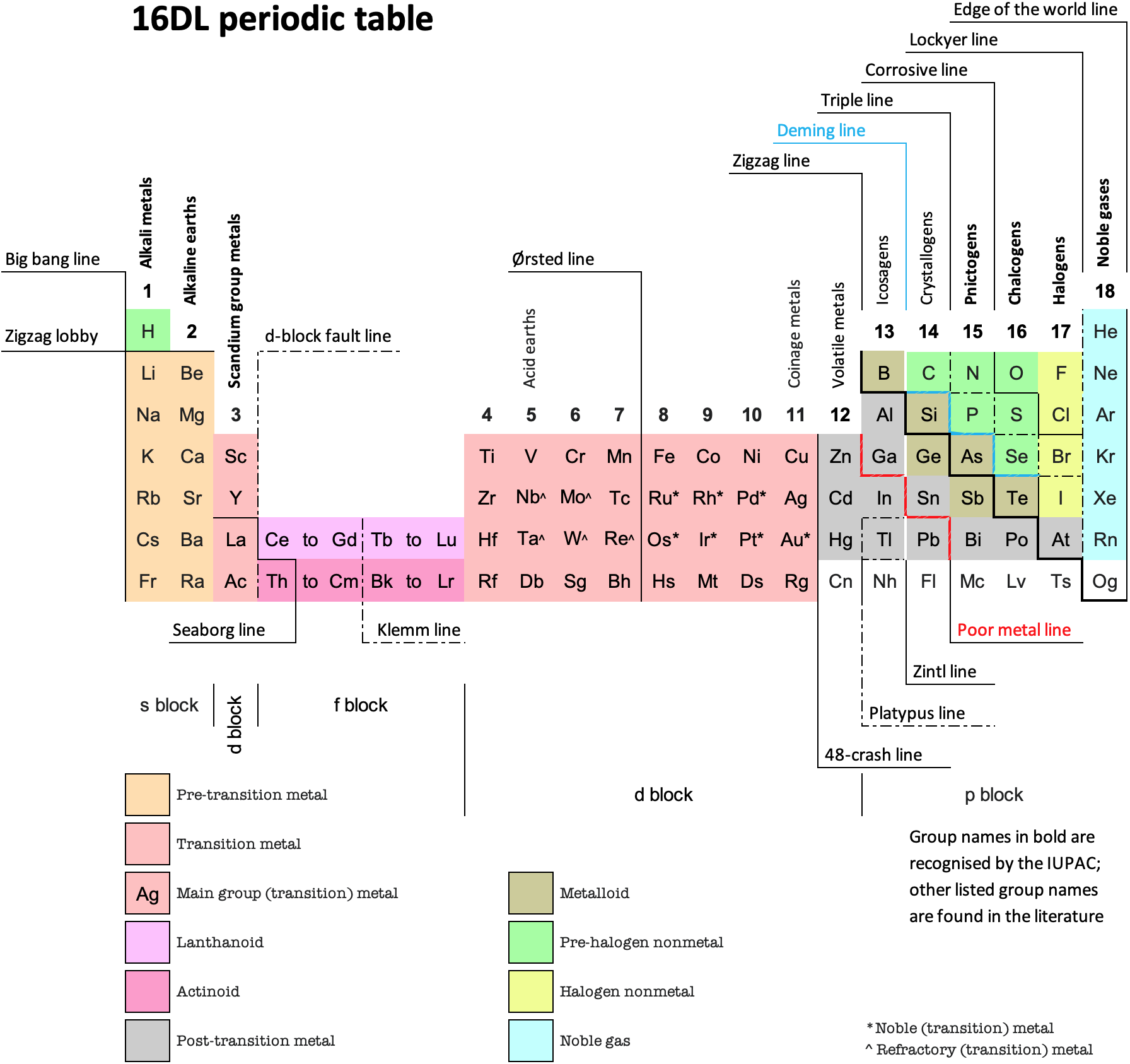
| Year: 2020 | PT id = 1174 |
Split s-, p- & d-Block Periodic Table
René Vernon presents a periodic table formulation with split s-, p- & d-blocks.
The details: Group 3 as B-Al-Ga-In-Tl
Al over Sc has some history, which seems to have been forgotten.
Here are some other tables with B-Al-Sc-Y-La:
What was it that these luminaries knew about B-Al-Sc-Y-La-Ac that is deemed to be no longer relevant, and why is that the case?
Deming (1947, Fundamental Chemistry, 2nd ed. p. 617) located Al with the pre-transition metals in groups 1?2. Cox (2004, Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd ed. p. 185) refers to the pre-transition metals as those in groups 1 and 2, and Al. Here's that 2019 periodic table (by me), recording oxidation number trends, further suggesting B and Al are better placed over Sc.
In this vein, Rayner-Canham (2020, The periodic table: Past, present, and future, pp. 178–181) writes:
"It was Rang in 1893 who seems to have been the first, on the basis of chemical similarity, to place boron and aluminum in Group 3.
"Such an assignment seems to have been forgotten until more recent times. Greenwood and Earnshaw have discussed the way in which aluminum can be considered as belonging to Group 3 as much as to Group 13 particularly in its physical properties. Habashi has suggested that there are so many similarities between aluminum and scandium that aluminum's place in the Periodic Table should actually be shifted to Group 3.
"In terms of the electron configuration of the tripositive ions, one would indeed expect that Al3+ (electron configuration, [Ne]) would resemble Sc3+ (electron configuration, [Ar]) more than Ga3+ (electron configuration, [Ar]3d10). Also of note, the standard reduction potential for aluminum fits better with those of the Group 3 elements than the Group 13 elements (Table 9.2) – as does its melting point.
"In terms of their comparative solution behavior, aluminum resembles both scandium(III) and gallium(III). For each ion, the free hydrated cation exists only in acidic solution. On addition of hydroxide ion to the respective cation, the hydroxides are produced as gelatinous precipitates. Each of the hydroxides redissolve in excess base to give an anionic hydroxo-complex, [M(OH)4]–... There does seem to be a triangular relationship between these three elements. However, aluminum does more closely resemble scandium rather than gallium in its chemistry. If hydrogen sulfide is bubbled through a solution of the respective cation, scandium ion gives a precipitate of scandium hydroxide, and aluminum ion gives a corresponding precipitate of aluminum hydroxide. By contrast, gallium ion gives a precipitate of gallium(III) sulfide. Also, scandium and aluminum both form carbides, while gallium does not."
To answer my own question as to why group 3 as B-Al-Sc-Y-La-Ac has been forgotten.
I suspect what happened is that it was historically known that group 3 was better represented as B-Al-Sc-Y-La-[Ac]. Then, with the advent and rise of modern electronic structure theory, B-Al- got moved to the p-block because, after all, they were p-block elements, never mind the damned chemistry. And La stayed in the d-block since it was the first element to show 5d electron, and 4f did not show until Ce. And Lu stayed where it was since even thought it was learnt that the f shell become full at Yb, rather than Lu, nothing changed about the chemistry of Lu. Nowadays, this has all been forgotten.
The modern periodic table is a chemistry-physics hybrid.
Lu in group 3 demands He over Be. La in group 3 demands B-Al over Sc. Neither option gets up. The more important consideration is to teach the history and have students and chemists appreciate both perspectives.
| Year: 2021 | PT id = 1181 |
Understanding Periodic and Non-periodic Chemistry in Periodic Tables
Cao C, Vernon RE, Schwarz WHE and Li J (2021). Front. Chem. 8:813. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00813
Abstract:
The chemical elements are the "conserved principles" or "kernels" of chemistry that are retained when substances are altered. Comprehensive overviews of the chemistry of the elements and their compounds are needed in chemical science. To this end, a graphical display of the chemical properties of the elements, in the form of a Periodic Table, is the helpful tool. Such tables have been designed with the aim of either classifying real chemical substances or emphasizing formal and aesthetic concepts. Simplified, artistic, or economic tables are relevant to educational and cultural fields, while practicing chemists profit more from "chemical tables of chemical elements."
Such tables should incorporate four aspects:
(i) typical valence electron configurations of bonded atoms in chemical compounds (instead of the common but chemically atypical ground states of free atoms in physical vacuum);
(ii) at least three basic chemical properties (valence number, size, and energy of the valence shells), their joint variation across the elements showing principal and secondary periodicity;
(iii) elements in which the (sp)8, (d)10, and (f)14 valence shells become closed and inert under ambient chemical conditions, thereby determining the "fix-points" of chemical periodicity;
(iv) peculiar elements at the top and at the bottom of the Periodic Table.
While it is essential that Periodic Tables display important trends in element chemistry we need to keep our eyes open for unexpected chemical behavior in ambient, near ambient, or unusual conditions. The combination of experimental data and theoretical insight supports a more nuanced understanding of complex periodic trends and non-periodic phenomena.
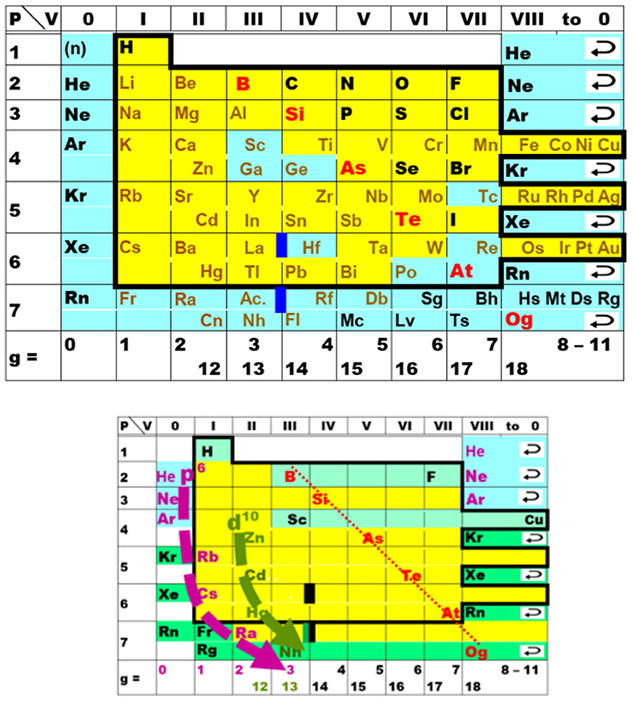
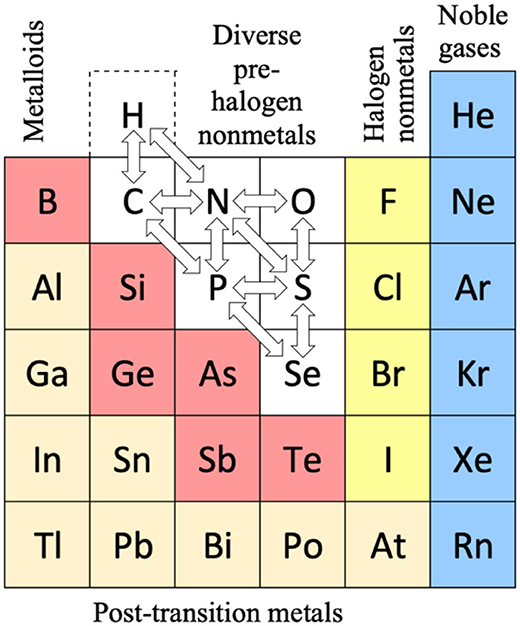
Thanks to René Vernon for the tip.
| Year: 2021 | PT id = 1183 |
Crustal Abundance vs. Electronegativity
A chart by René Vernon of Elemental Abundance (g/kg log10) vs. Electronegativity, H to Bi.
René writes:
Below is a remarkable XY chart where x = electronegativity and y = crustal abundance (log10). It stops at the end of the s-process, at Bi. The abundance figures are from the CRC Hanbook of Physics and Chemistry (2016-2017).
I say remarkable as I had little idea what the chart would end up looking like when I started plotting the values.
As well as its coloured regions, I've marked out track lines for six of the main groups and one for group 3.
Observations
The rose-coloured arc on the left encompasses the pre-transition metals i.e. the alkali and alkaline earth metals and aluminium, followed by, in the orange rectangle, the rare earth metals. Opposite these regions, along the southern boundary of the green paddock, are the halogens.
In the pale yellow field sheltered by the pre-transition metals and the REM, are the 3d transition metals and, in the white corral, are 4d and 5d base transition metals. Opposite these regions, in the green paddock, are the core nonmetals H, C, N, O, P and S, with Se as an outlier.
Following in the grey blob are the post-transtion or poor metals, immediately adjacent to the bulk of the metalloids or poor nonmetals.
Finally, in the light blue patch, the noble metals are complemented by the noble gases frolicking in the open.
Abundance tends to decrease with increasing Z. Notable exceptions are Li, B, N and Si.
Curiosities
Comment
I was intrigued by the article referring to Ni and Ar, and the suggestion of Ar becoming somewhat anionic, albeit in extreme conditions (140 GPa, 1500 K)
References
Correlations
I wasn't looking for these but they at least exist as follows:
My references are:
Thus the abundance of the metals in the crust tends to fall with increasing EN.
An answer from L. Bruce Railsback, creator of the Earth Scientist's Periodic Table https://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?PT_id=142:
"I think I can answer one of the questions. 'Why is Si good at forming a planetary crust?' – because it's so bad at staying in the core. Silicon isn't sufficiently metallic to stay in the core. Even in the mantle and crust, it doesn't go into non-metal solids well: in cooling magmas, it's only a lesser member of the early-forming minerals (e.g., Mg2SiO4, forsterite, where it's outnumbered two to one). The mineral only of Si as a cation, SiO2 (quartz), is the LAST mineral to form as a magma cools, in essence the residuum of mineral-forming processes. At least some this thinking is at Bowen's Reaction Series and Igneous Rocks at http://railsback.org/FundamentalsIndex.html#Bowen"
Which Electronegativity Scale?
The wide variety of methods for deriving electronegativities tend to give results similar to one another.
| Year: 2021 | PT id = 1184 |
van Spronsen's Periodic Table: Update
René Vernon writes:
I'd never before realised how clever van Spronsen's 1969 Periodic Table is. It seems to be the ultimate logical electronic version, informed by the actual filling sequence in the gas phase atoms, rather than the idealised sequence.
So, H-He are over Li-Be.
Group 3 is Sc-Y-La-Ac since that is where the d-shell starts filling. In the rest of the d-block, there are (4+1) x d5 and (4+2) x d10.
The f-block starts with Ce, as that is where the f-shell starts filling. Notice the high degree of regularity with the 4 x f7 and the 4 x f14, and how Th is treated i.e. as 5f0.
After DIM's 8-column form, I believe the periodic family tree now looks like this:
Three split-blocks
1a. He over Ne; B-Al over Sc-Y-La-Ac = old school form
1b. H-He over F-Ne; ditto = e.g. Soddy 1914?, Kipp 1942?Two split blocks
2a. He over Ne; group 3 as Sc-Y-La-Ac = popular formOne split-block
3a. He over Ne; group 3 as Sc-Y-Lu-Lr = Lu form 3b. He over Be; group 3 as Sc-Y-La-La = forgotten van Spronsen formNo split blocks
4. He over Be = Janet equivalent
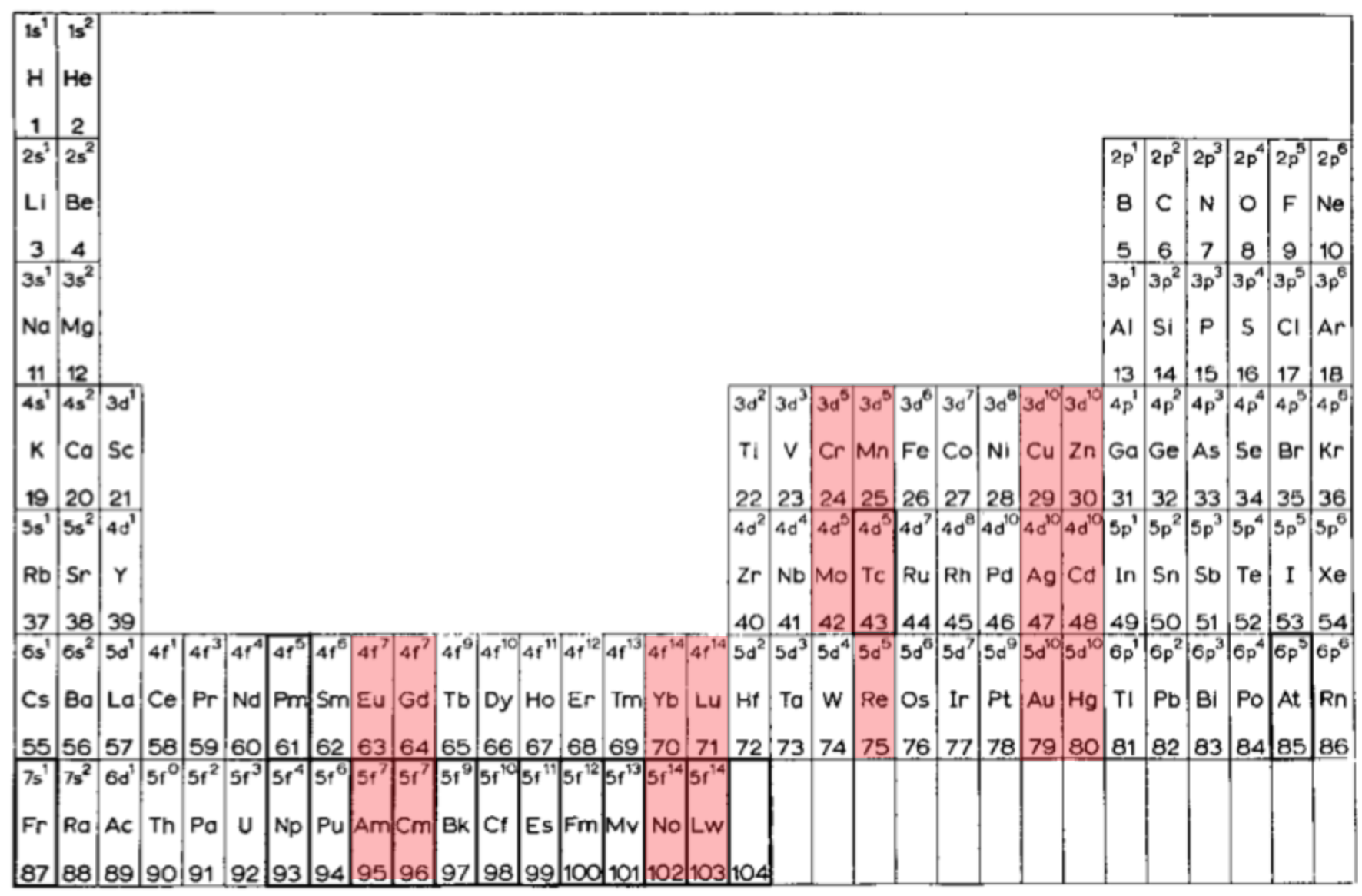
| Year: 2021 | PT id = 1190 |
Electronegativity: A Three-Part Wave
René Vernon points out that although there is a general trend in increasing electnegativity from Cs to F, there is actually an s-curve in the data.
Electronegativity across groups 1 to 18 appears to a show a three-part wave-like pattern.
There is a rise from group 1 to group 6, followed by a fall at group 7. I guess for group 7 that the EN for Mn is based on +2 and in this state Mn has five 3d electrons. The EN for Tc and Re are presumably based on +7, in which they notionally have underlying [Kr] and [Xe] cores.
There is rise from 7 to 8 (why?); a mesa from 8 to 11 (why?) that includes the PGM; and a fall at group 12. The fall may be influenced by group 12 having a full d shell; ditto group 13.
There is a rise from 13 to 18. Whereas in group 13 there is ionic chemistry in the form of the cations of Al to Tl this is not the case for C, Si, and Ge in group 14. Sn is reluctant to form a cation expect at pH < 1, and there is no Pb4+ cation.
The R2 value of 0.9739 is a best fit value for a second order polynomial. R2 for a straight line is 0.786
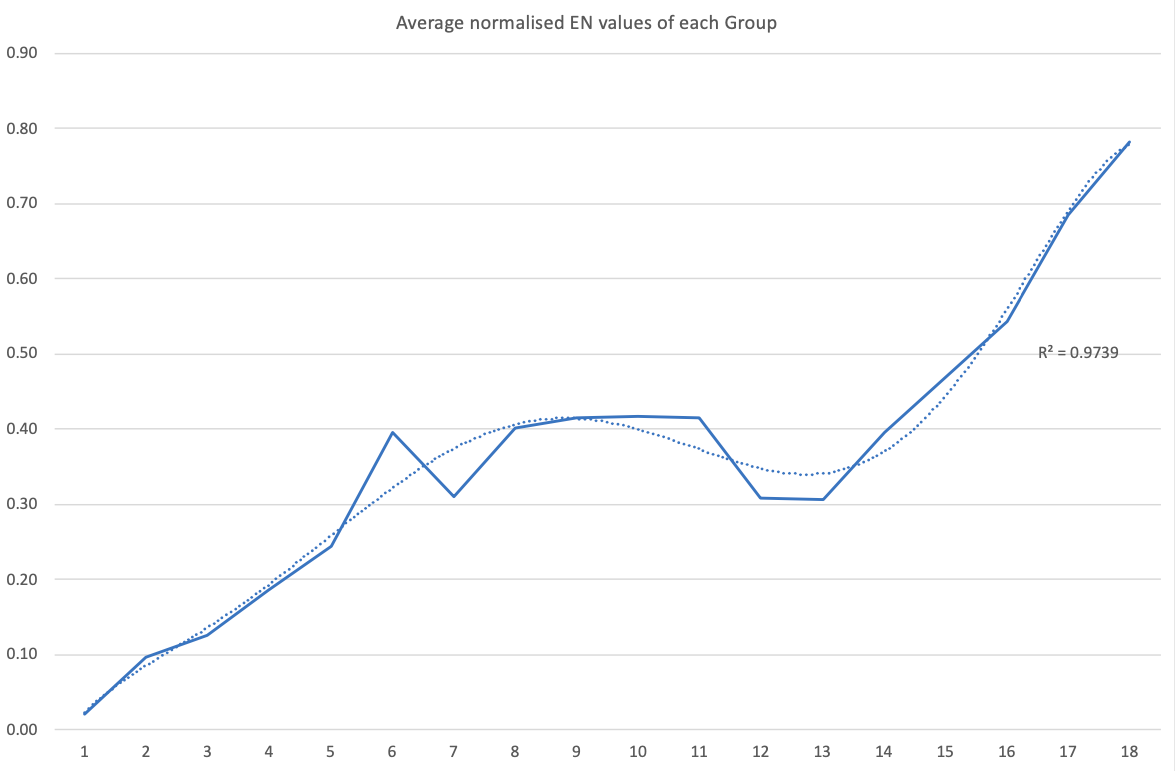
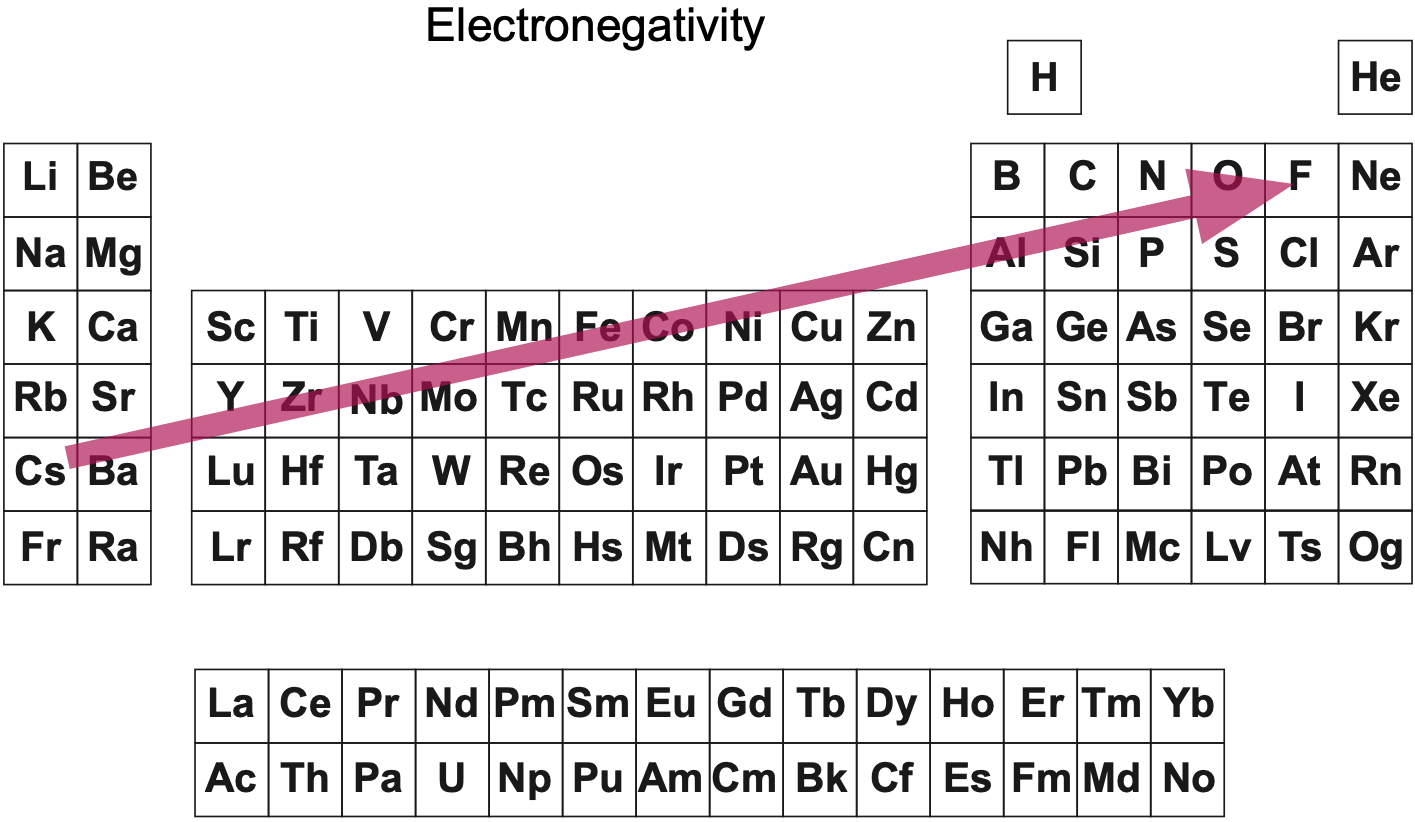
| Year: 2021 | PT id = 1203 |
Vernon's CSF Left-Step Periodic Table.
René Vernon's CSF Left-Step Periodic Table.
"I was prompted to switch to He-Be and [to develop a Janet type] left-step periodic table. I suggest it remediates concerns about H and He, and Lu in group 3.
Pros
Cons
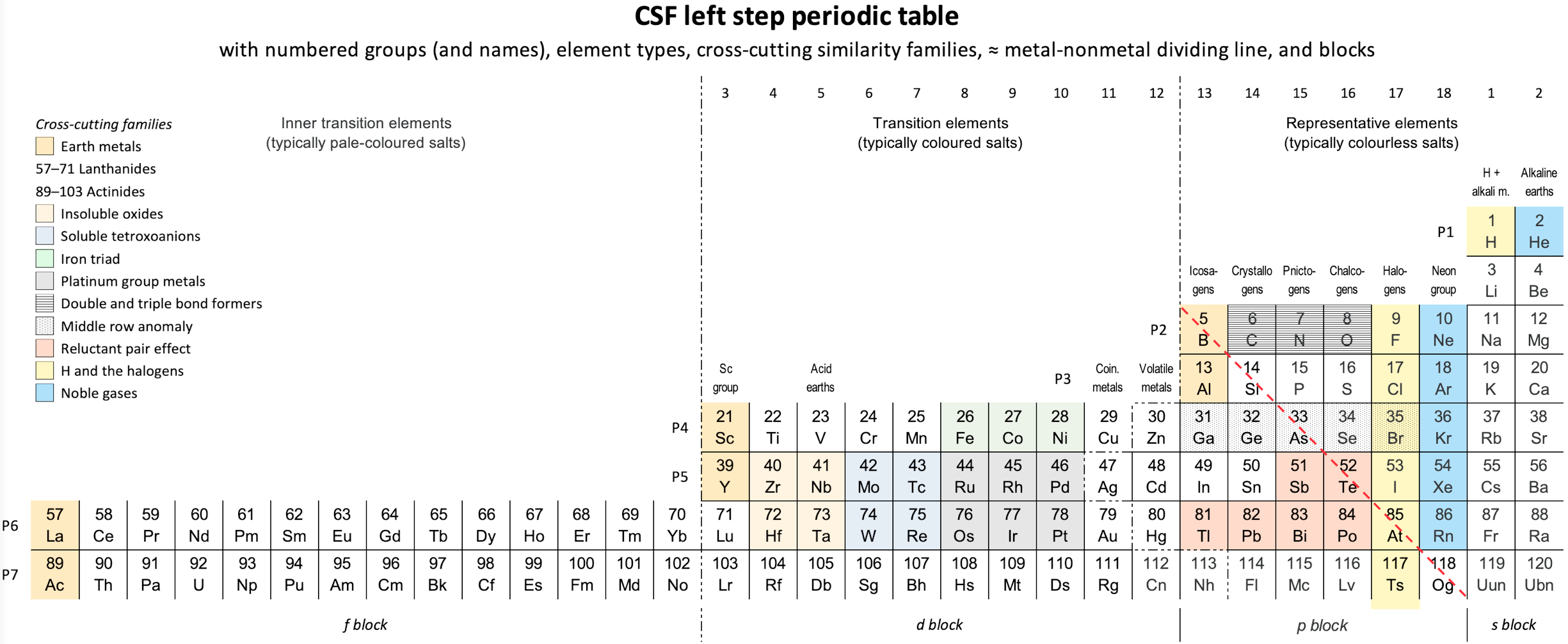
| Year: 2021 | PT id = 1210 |
Vernon's Eight-Fold Way Periodic Table
René Vernon suggests that the chemical elements can be grouped into eight classes: four metallic (Active, Transition, Post-Transition and Noble) and four non-metallic (Halogen, Biogen, Metalloid and Noble gas):
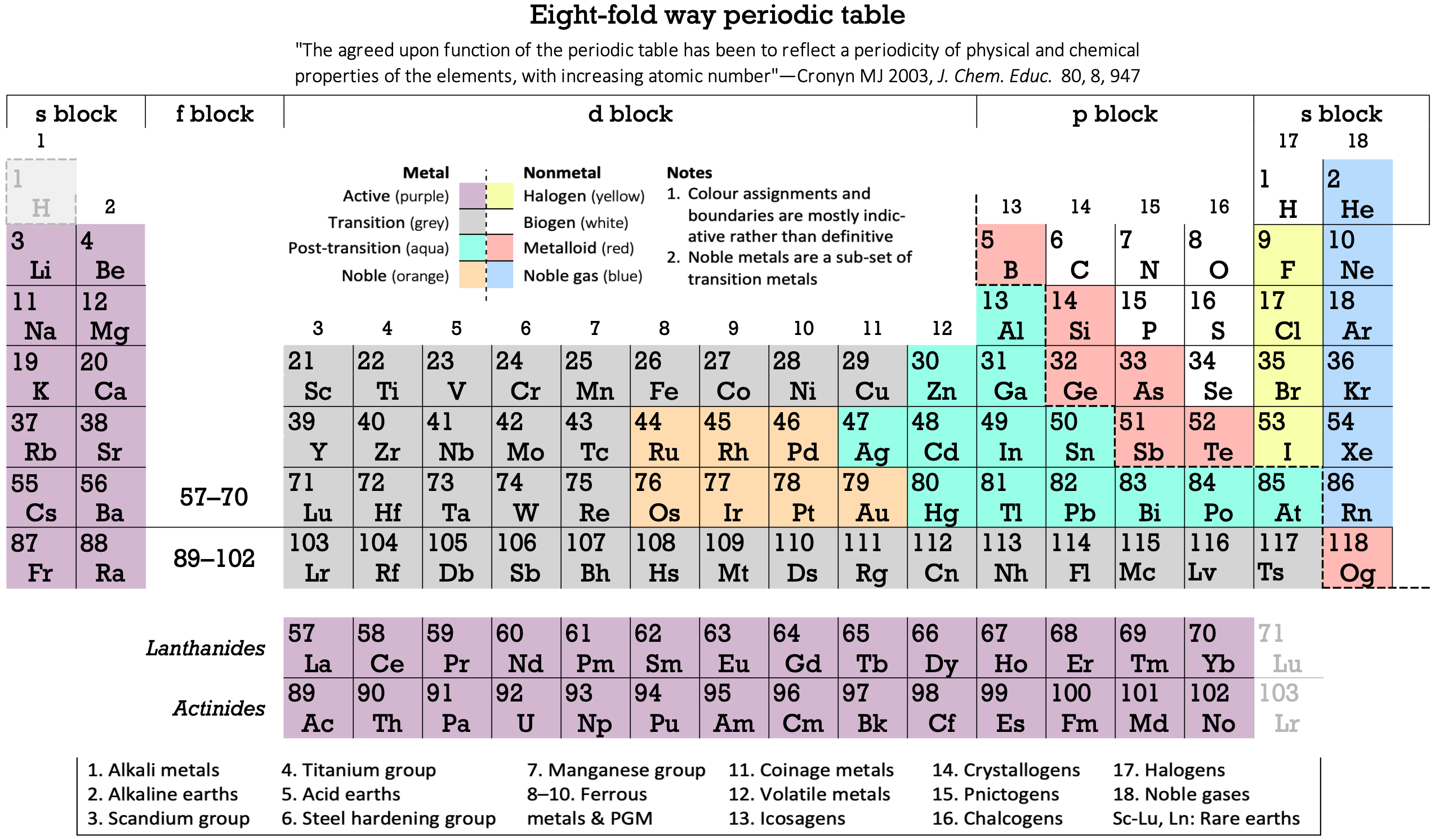
| Year: 2021 | PT id = 1244 |
Vernon's ABC Periodic Table
The Annotated Blocks & Categories (ABC) Periodic Table by René Vernon.
| Year: 2022 | PT id = 1241 |
Electronegativity Seamlessly Mapped Onto Various Formulations of The Periodic Table
A discussion on the Google Groups Periodic Table Discussion List, involving a René Vernon, Nawa Nagayasu & Julio Samanez (all contributors this database) lead to the development of the representations below, showing electronegativity seamlessly mapped onto a modified Left-Step Periodic Table:
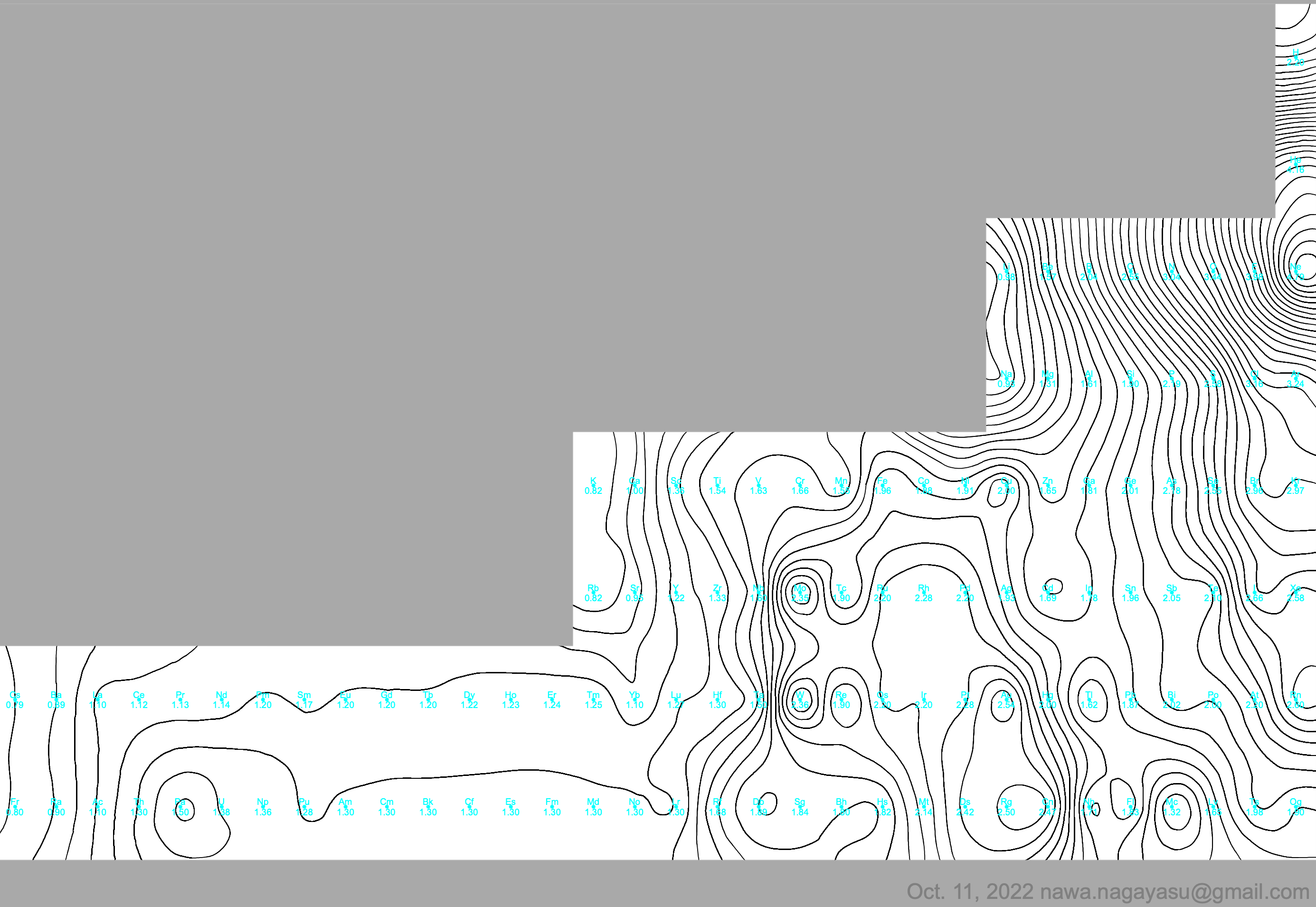
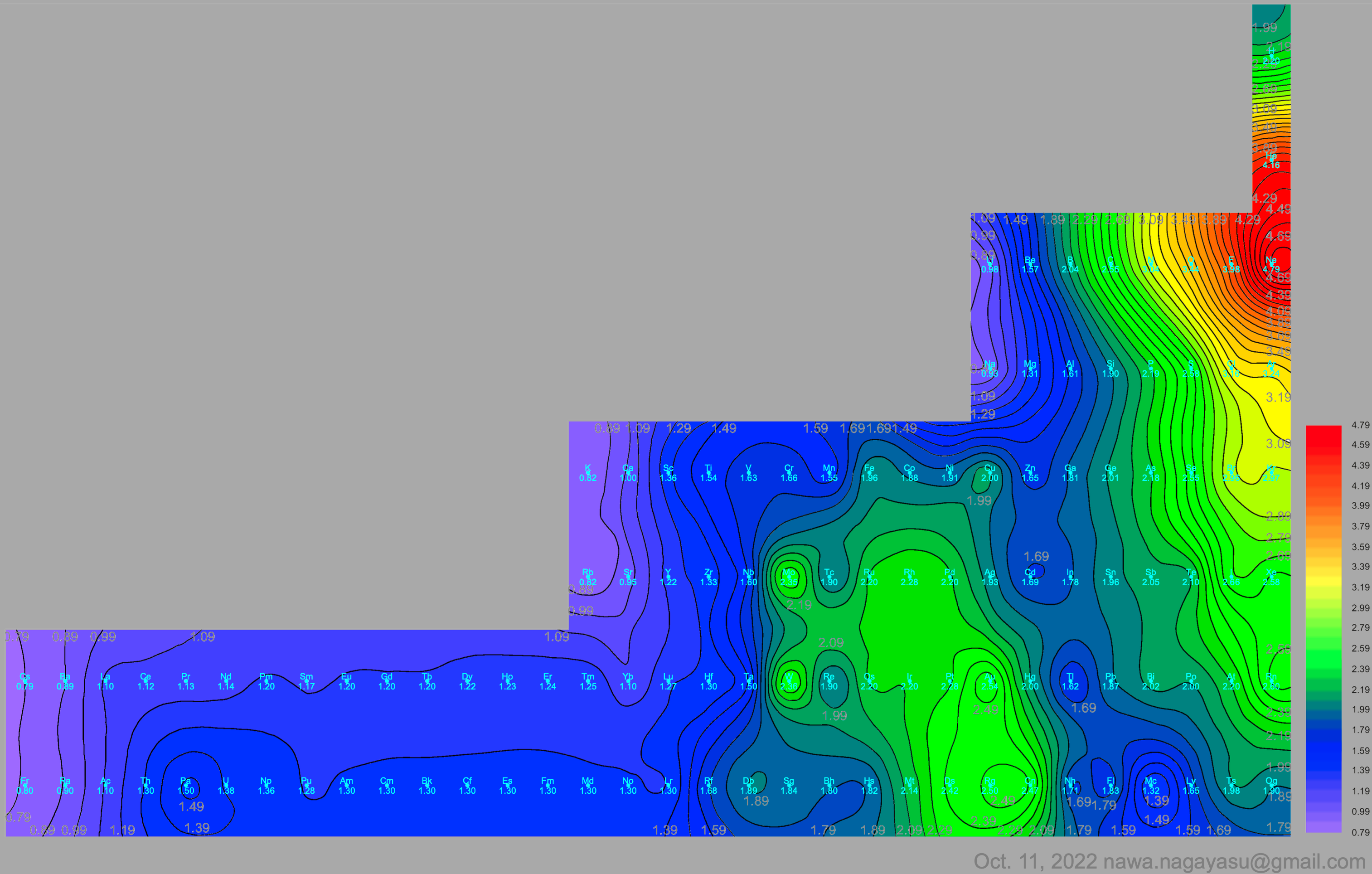
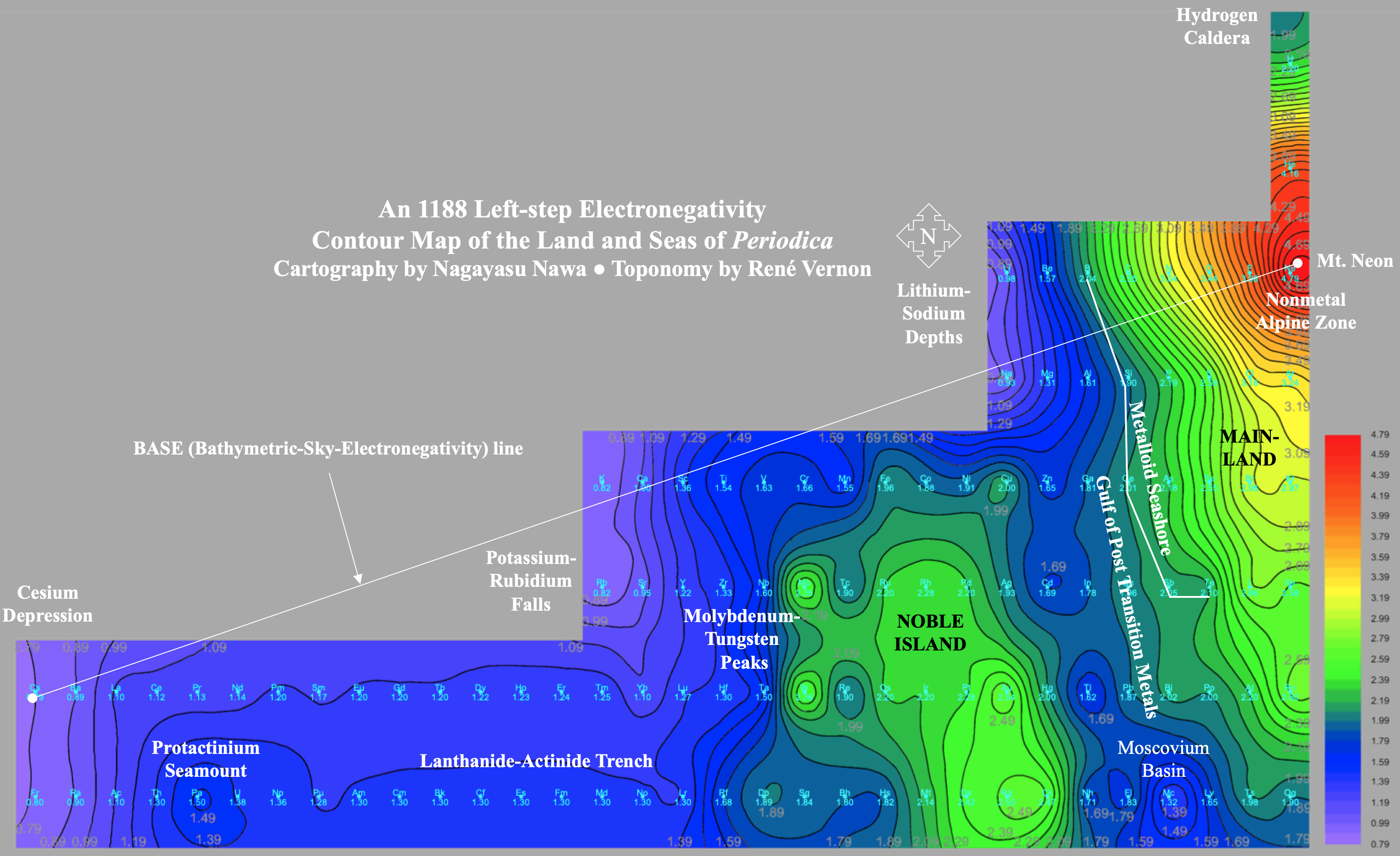
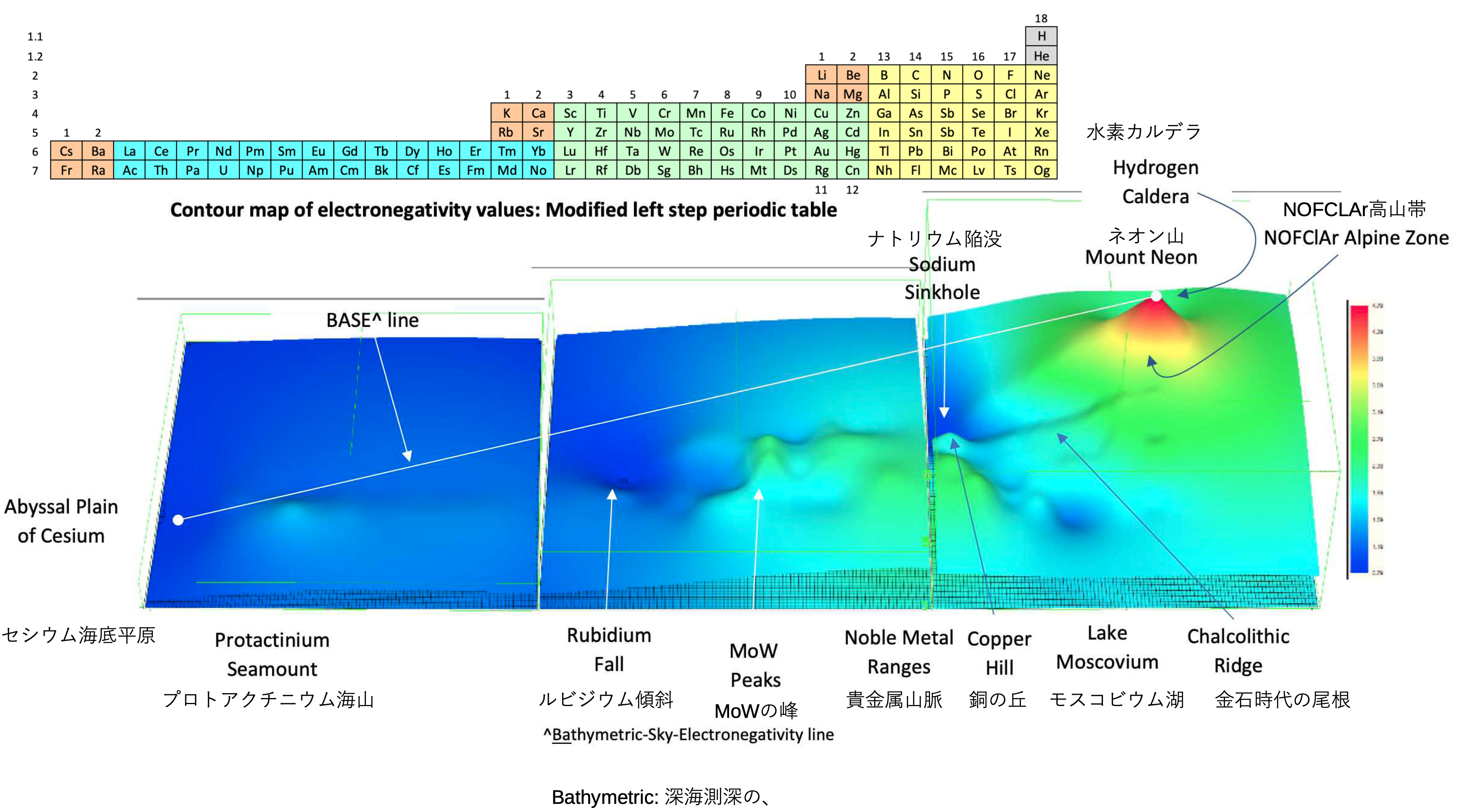
Nawa Nagayasu has mapped electronegativity to Mendeleeve's formulation:
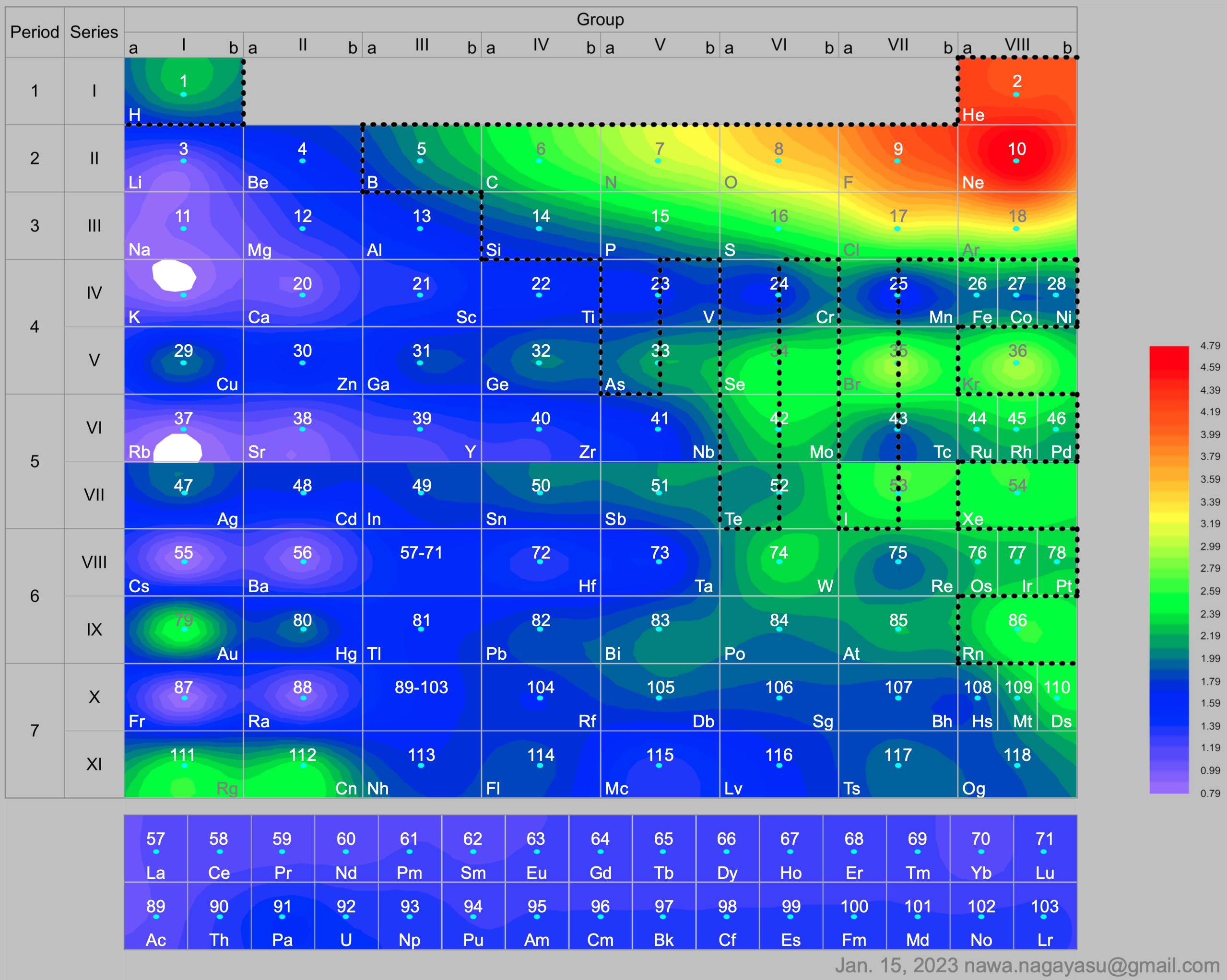
Nawa Nagayasu has mapped electronegativity onto other formulations, Julio's Binode Spiral:
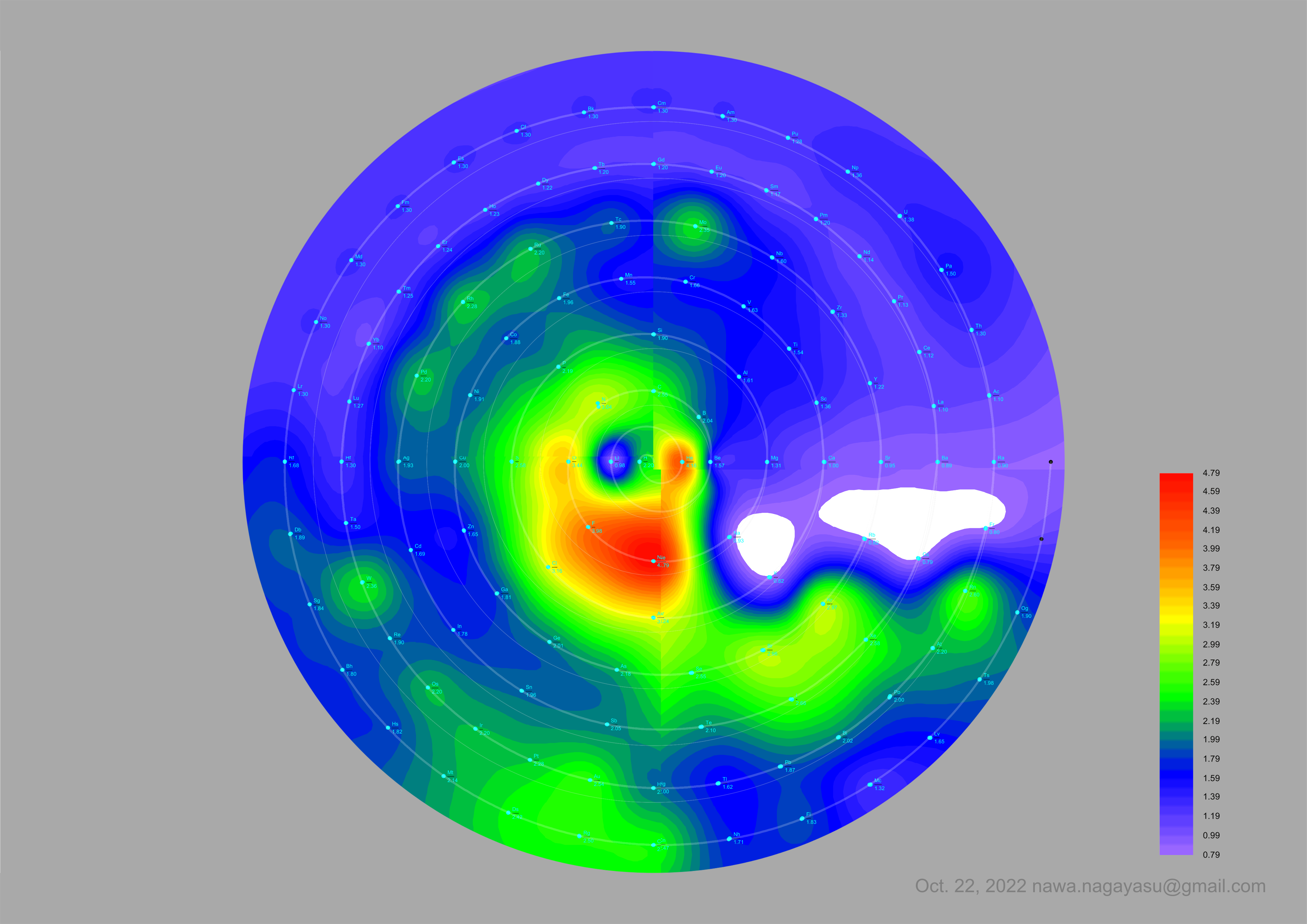
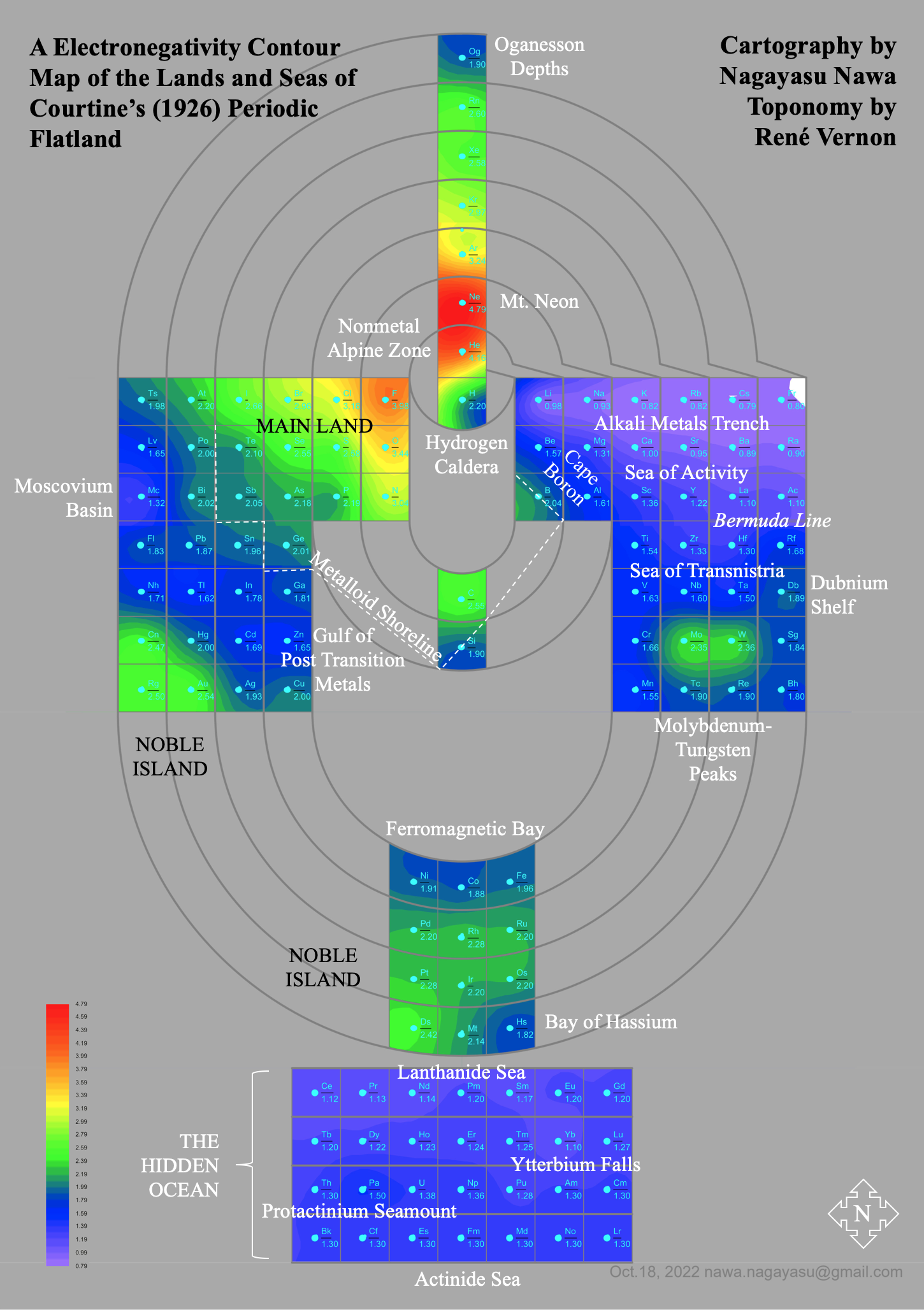
and the "conventional", short, medium and long forms of the periodic table with hydrogen above and between B & C which show the botom-right-to-top-left electronegativity trend:
René Vernon's 777 Periodic Wedding Cake:
Valery Tsimmerman's ADOMAH formulation:
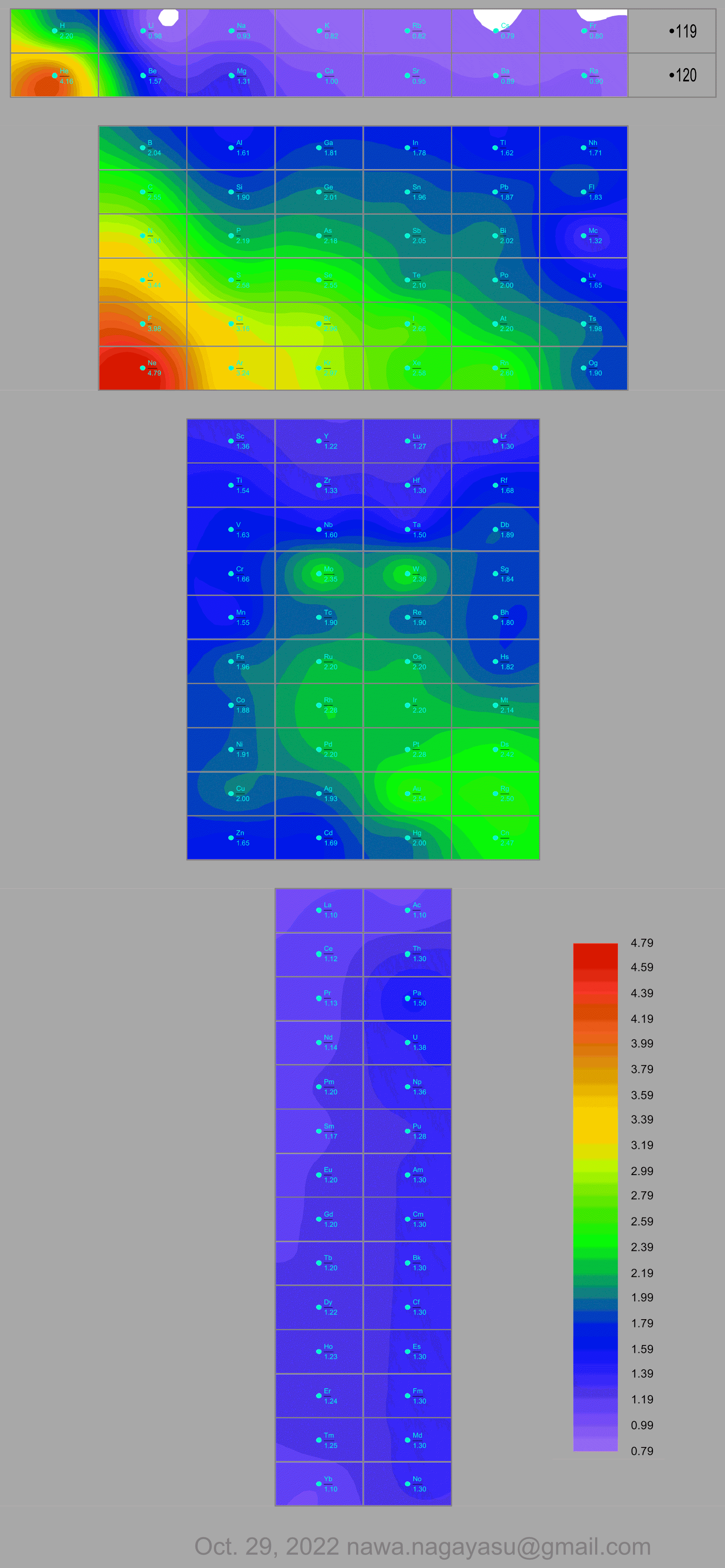
Valery Tsimmerman's ADOMAH tetrahedron (in a glass cube) formulation:
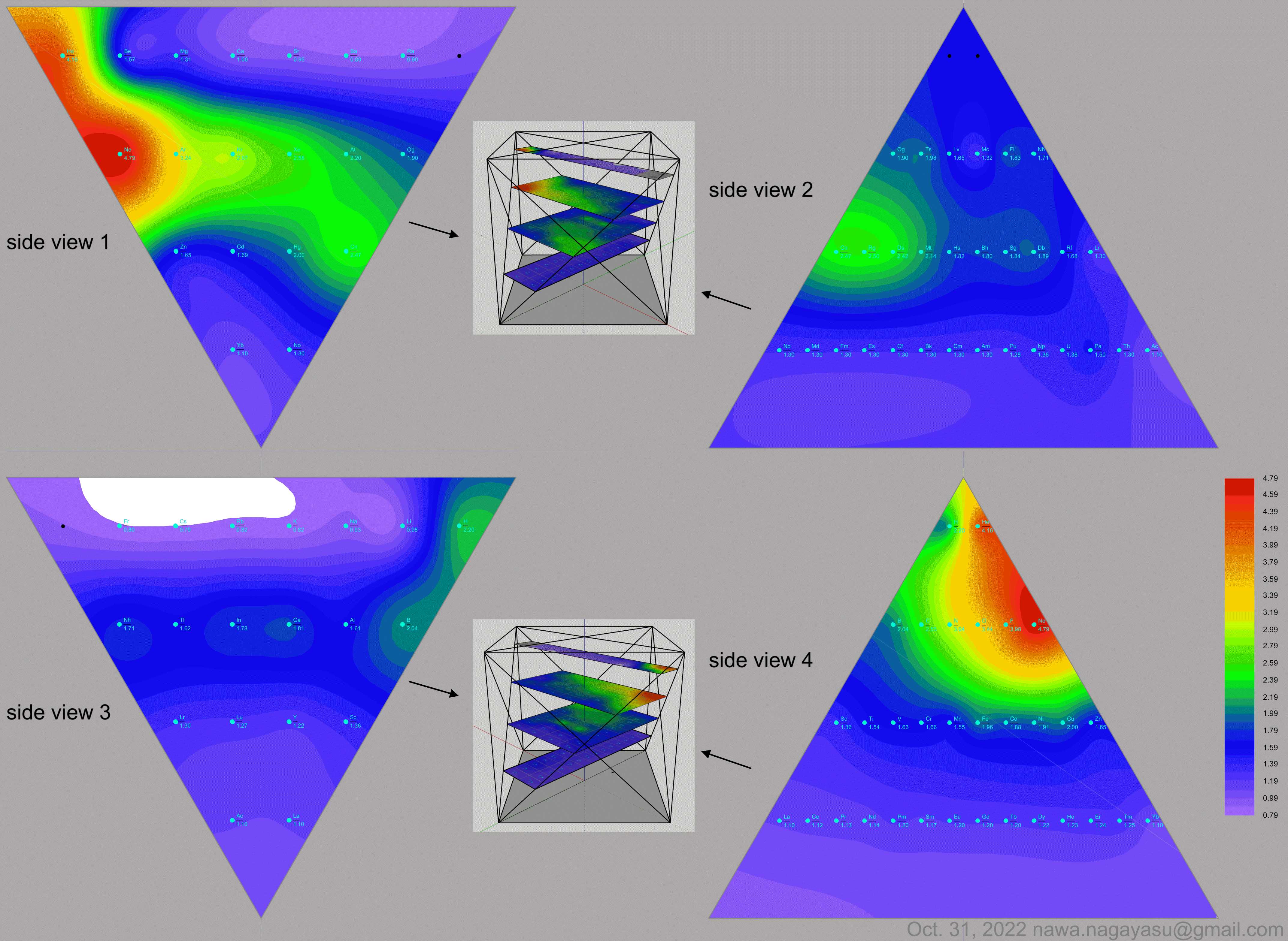
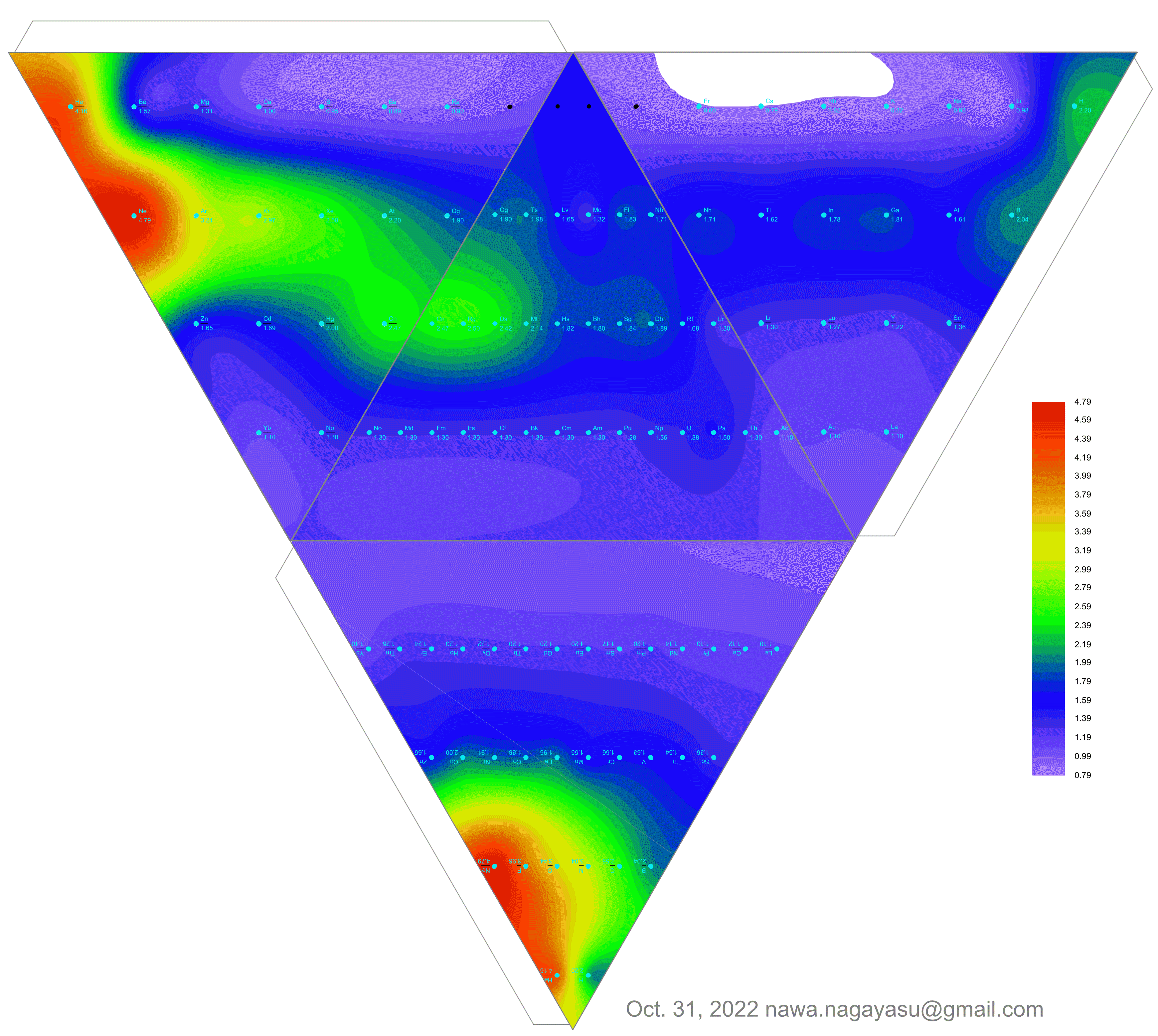
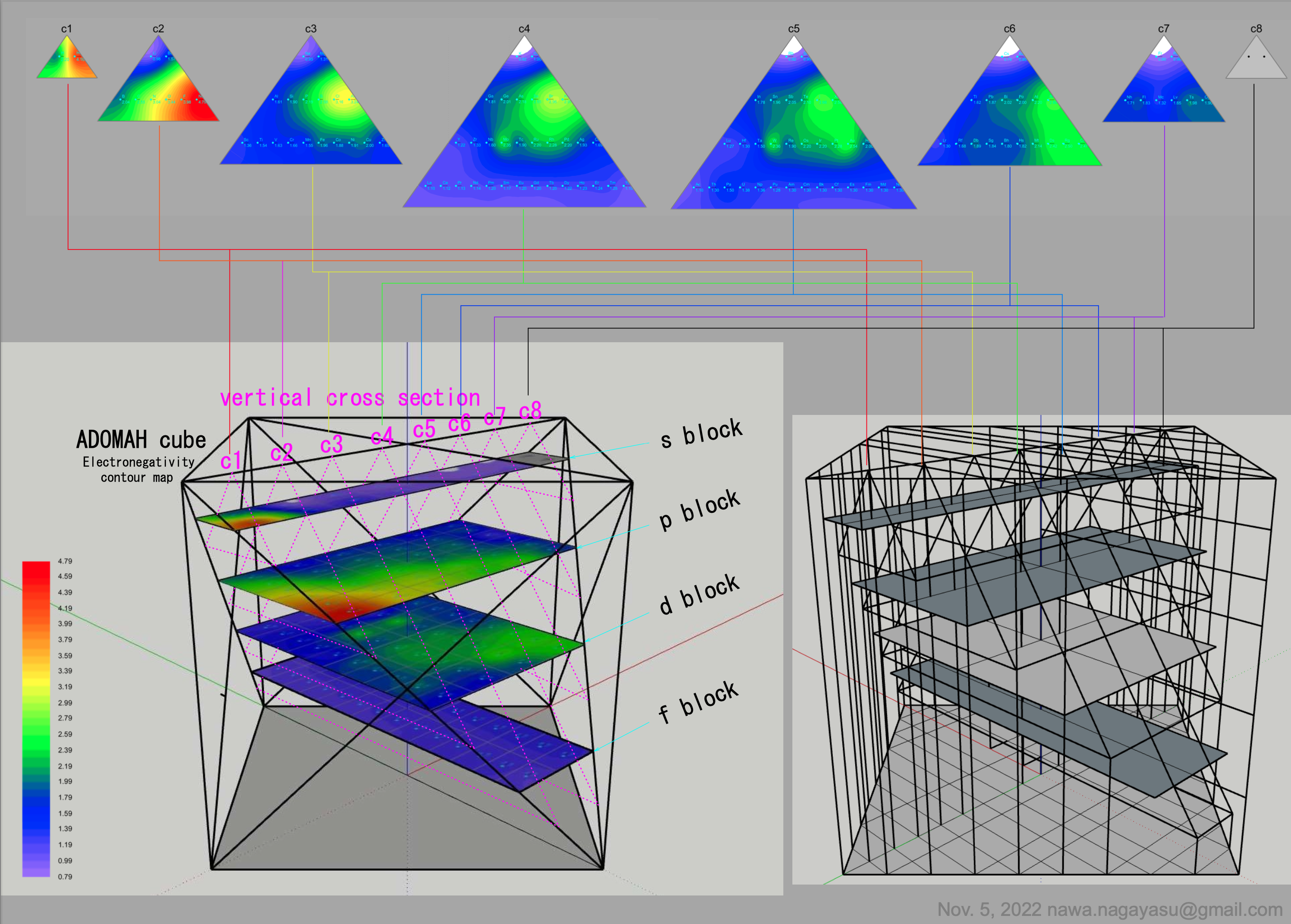
| Year: 2022 | PT id = 1252 |
Vernon's Yin Yang of The Periodic Table
René Vernon writes:
"I was prompted to [develop] this item after reading Eric Scerri's open access article: In Praise of Triads. The nub of Eric’s article is to argue for the LST on the grounds of triad regularity, first-row-anomaly regularity, and consistency with QM.
"It occurs to me that efforts to introduce more regularity to the PT invariably introduce new irregularities elsewhere. For example, as far as triad regularity goes, the left step table (LST) with He over Be introduces its own anomaly in that no element in period 1 (H, He) is part of a triad whereas this is not the case for all periods thereafter. In contrast, all periods of the traditional table have at least one element that is part of a triad.
"As far as QM goes, this tells us that there is a theoretical regularity to the PT. This regularity can be used to inform e.g. the LST, ADOMAH or Julio’s binodes. But such depictions do not reflect the factual relationships we see amongst the chemistry of the elements as well as is the case for the conventional form. A most obvious example is that the LST, while being more consistent with QM, disrupts the bottom-left to top-right trend in metallic to nonmetallic character seen in conventional tables.
(I must caveat that I'm referring to the chemistry of the elements in conditions regularly occurring on Earth. For example, it has been reported that under sufficiently high pressures the elements change their EN and electron configurations. If so, this suggests a need for a different table at high pressure.)
At this point, the chemistry educators enter the picture. They move the s-block to left. Helium is relocated over Ne on the basis of its nobility. (This could change if a few compounds of He were to be synthesized). Somewhat similarly, La was discovered well before Lu, so it ended up under Y, and most folks see no good reason to replace La with Lu. Sure, in the 32-column form, the result is a split d-block but the infrequency with which the 32-column form appears is such that most people are not bothered. The result is the conventional table.
Philosophically, while the n+l based LST might represent the most general form of table, the conventional table appears to currently represent the most pragmatic derivation for chemists and chemistry educators.
Since the PT is classification rather than theory, and there will thus always be hard cases at the boundaries, there will invariably be minor variations in the depiction of the conventional table with respect to e.g. the placement of H, the composition of group 3, or the length of the f block.
And there will always be tables such as MR that focus on particular perspectives of relationships among the the elements.
I’ve tried to sketch what's going in the attached image:"
| Year: 2022 | PT id = 1254 |
99 Elements Sorted by Density & Electronegativity
René Vernon writes:
"A little while I ago I noticed that a scatter plot of EN (revised Pauling) and density values of the elements resulted in a nice distribution, as per the table below.
"According to Hein and Arena (2013) nonmetals have low densities and relatively high EN values; the table bears this out. Nonmetallic elements occupy the top left quadrant, where densities are low and EN values are relatively high. The other three quadrants are occupied by metals. Of course, some authors further divide the elements into metals, metalloids, and nonmetals although Odberg argues that anything not a metal is, on categorisation grounds, a nonmetal.
Note 25 says:
(a) Weighable amounts of the extremely radioactive elements At (element 85), Fr (87), and elements with an atomic number higher than Es (99), have not been prepared.
(b) The density values used for At and Fr are theoretical estimates.
(c) Bjerrum (1936) classified "heavy metals" as those metals with densities above 7 g/cm^3.
(d) Vernon (2013) specified a minimum electronegativity of 1.9 for the metalloids.
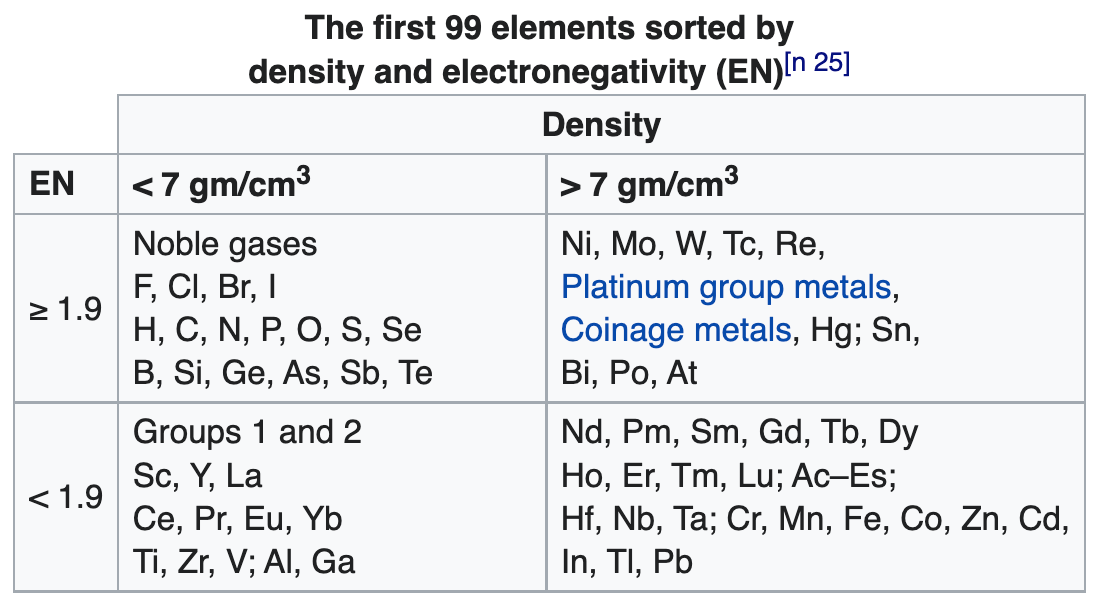
| Year: 2022 | PT id = 1257 |
Tutti Frutti Periodic Table
René Vernon who writes:
"As a potentially powerful teaching and learning instrument: a Tutti Frutti periodic table. I feel younger folk [will] be delighted by it. The overlay of electron configurations and blocks was designed by a colleague of mine."
| Year: 2022 | PT id = 1259 |
Deming's 1923 Periodic Table, Updated by Vernon
René Vernon writes:
"Here is the 21st century version of Deming's 1923 formulation. Lacking elegance perhaps, but that’s messy chemistry for you. 25 columns wide rather than 18 or 32. Split s, p and d blocks. The connecting lines are based on four sources:
"I used [the term] frontier metals to refer to the post-transition metals, since the latter term has never applied well to Al. The frontier adjective comes from a line by Russell and Lee in which they refer to Bi and Po occupying frontier territory on the PT, adjacent to the nonmetals (2006, p. 419).
"As far as metalloids are concerned, Dingle nicely summarized their status: "With ‘no-doubt' metals on the far left of the table, and no-doubt non-metals on the far right…the gap between the two extremes is bridged first by the poor (post-transition) metals, and then by the metalloids— which, perhaps by the same token, might collectively be renamed the 'poor non-metals'." (2017, p. 101)
Ref: Dingle 2017, The Elements: An Encyclopedic Tour of the Periodic Table, Quad Books, Brighton Russell AM & Lee KL 2005, Structure-Property Relations in Nonferrous Metals, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ
| Year: 2022 | PT id = 1275 |
777 Periodic Wedding Cake
René Vernon's version of Courtine’s flat projection (1926) of his periodic tower, the 777 Periodic Wedding Cake:
| Year: 2022 | PT id = 1276 |
Periodic Table of Periodic Tables
René Vernon has collected the PT formulations in this PT database and classifed them as:
Short, Triangular, Medium, Long, Continious, Folding, Spatial & Unclassified
and tabulated them by date. The 'working document' is currently a word file.
 |
 |
 |
| What is the Periodic Table Showing? | Periodicity |
© Mark R. Leach Ph.D. 1999 –
Queries, Suggestions, Bugs, Errors, Typos...
If you have any:
Queries
Comments
Suggestions
Suggestions for links
Bug, typo or grammatical error reports about this page,please contact Mark R. Leach, the author, using mark@meta-synthesis.com
This free, open access web book is an ongoing project and your input is appreciated.