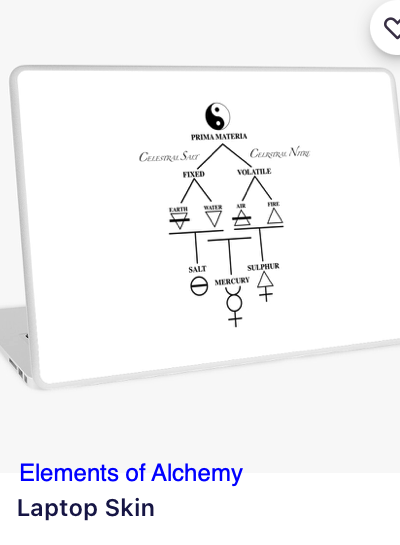
Periodic Table |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Poster | Nucleophiles & Bases |
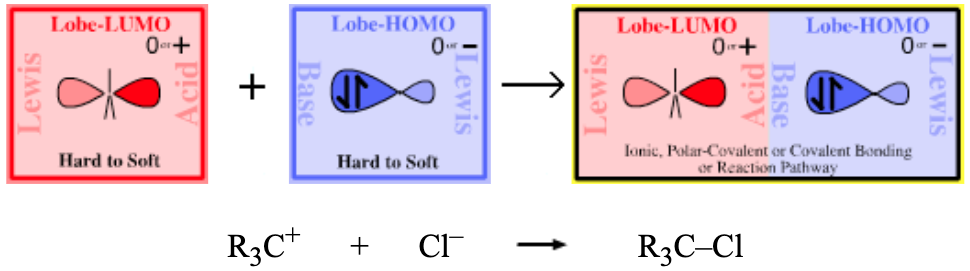
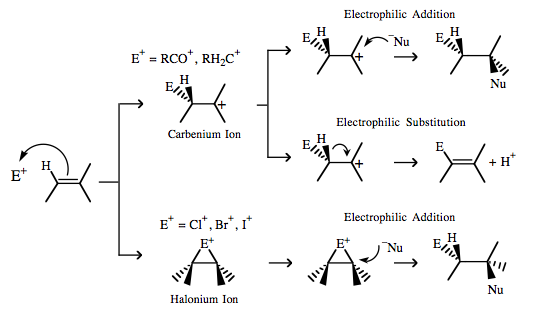
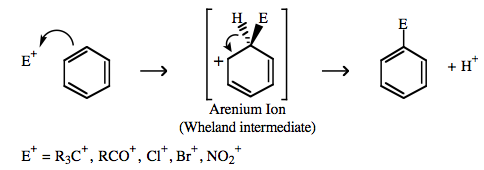
Lewis Acid/Base Interaction Matrix Database
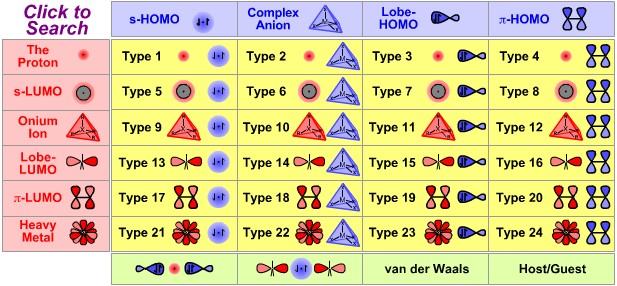 |
| Type 16 Lewis acid/base complex (generic) |
|
|
|
Benzoate ion more here |
|
|
Benzophenone more here |
|
|
Benzyl bromide more here |
|
|
Cyclopropane (generic) more here |
|
|
(+/-) trans 1,2-Dibromocyclohexane more here |
|
|
trans 1,2-Dichloroalkene (generic) more here |
|
|
(+/-) trans 1,2-Dichlorocyclohexane more here |
|
|
Disiamylborane more here |
|
|
gem-Dichloride (generic) more here |
|
|
1,1,2,2- Tetrachloroalkane (generic) more here |
|
|
Triphenylmethyl chloride more here |