Periodic Table |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| What is the Periodic Table Showing? | Periodicity |
The INTERNET Database of Periodic Tables
There are thousands of periodic tables in web space, but this is the only comprehensive database of periodic tables & periodic system formulations. If you know of an interesting periodic table that is missing, please contact the database curator: Mark R. Leach Ph.D. The database holds information on periodic tables, the discovery of the elements, the elucidation of atomic weights and the discovery of atomic structure (and much, much more).
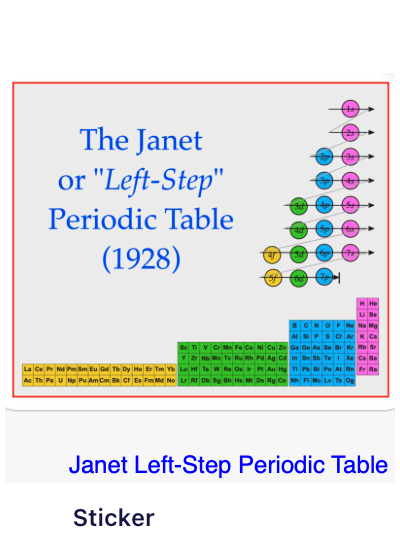
| Year: 1925 | PT id = 1373, Type = structure |
Pauli and The Exclusion Principle
Pauli, W. Über den Zusammenhang des Abschlusses der Elektronengruppen im Atom mit der Komplexstruktur der Spektren. Zeitschrift für Physik, 31, 765–783 (1925).
"Wolfgang Pauli was an Austrian–Swiss theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum mechanics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics 'for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli Principle'. The discovery involved spin theory.
"The Pauli exclusion principle (German: Pauli-Ausschlussprinzip) states that two or more identical particles with half-integer spins (i.e. fermions) cannot simultaneously occupy the same quantum state within a system that obeys the laws of quantum mechanics. This principle was formulated by Austrian physicist Wolfgang Pauli in 1925 for electrons, and later extended to all fermions with his spin–statistics theorem of 1940.
"In the case of electrons in atoms, the exclusion principle can be stated as follows: in a poly-electron atom it is impossible for any two electrons to have the same two values of all four of their quantum numbers, which are: n, the principal quantum number; ℓ, the azimuthal quantum number; mℓ, the magnetic quantum number; and ms, the spin quantum number.
"If two electrons reside in the same orbital, then their values of n, ℓ, and mℓ are equal. In that case, the two values of ms (spin) pair must be different. Since the only two possible values for the spin projection ms are +1/2 and –1/2, it follows that one electron must have ms = +1/2 and one ms = –1/2.
"To preserve the conservation of energy in beta decay, Pauli proposed the existence of a small neutral particle, dubbed the neutrino by Enrico Fermi, in 1930. Neutrinos were first detected in 1956. "
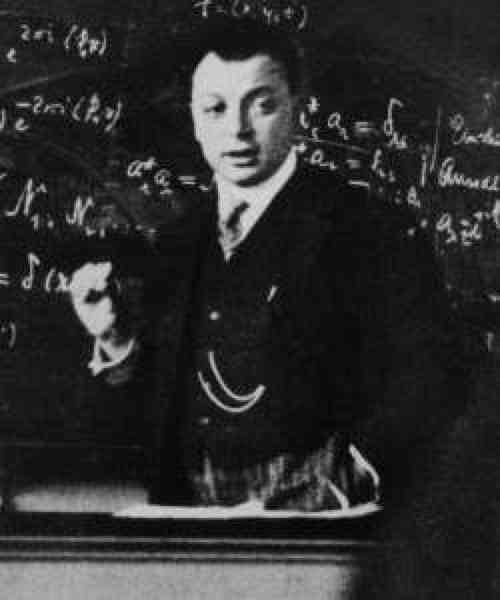
 |
 |
 |
| What is the Periodic Table Showing? | Periodicity |
© Mark R. Leach Ph.D. 1999 –
Queries, Suggestions, Bugs, Errors, Typos...
If you have any:
Queries
Comments
Suggestions
Suggestions for links
Bug, typo or grammatical error reports about this page,please contact Mark R. Leach, the author, using mark@meta-synthesis.com
This free, open access web book is an ongoing project and your input is appreciated.